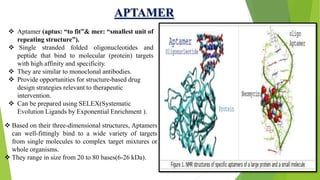
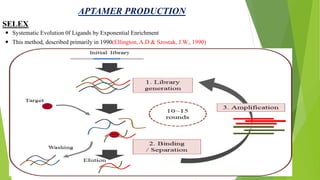
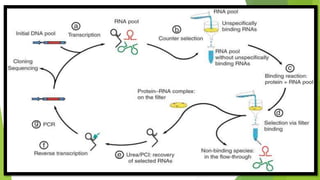
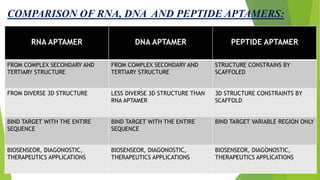
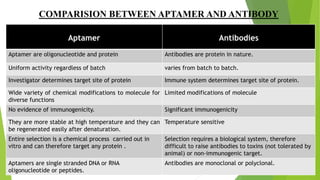
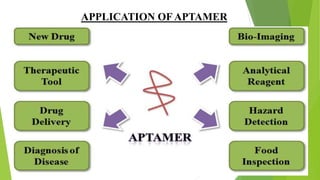
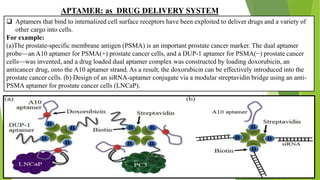
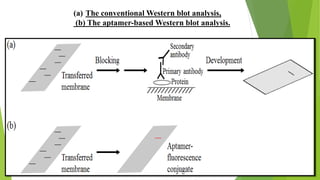
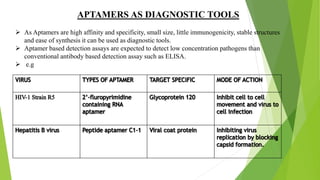
The document discusses aptamers, which are single-stranded folded oligonucleotides or peptides that bind to molecular targets with high affinity and specificity. Aptamers are produced through an in vitro selection process called SELEX that identifies nucleic acid sequences that bind to a target. The document outlines the SELEX process and compares properties of aptamers to antibodies. Potential applications of aptamers discussed include use as therapeutics, drug delivery agents, diagnostic tools, and in bioimaging and Western blot analysis due to their high specificity and low immunogenicity.