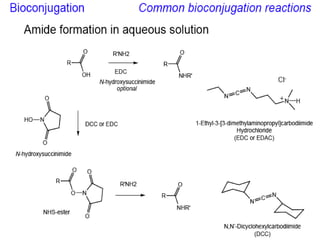
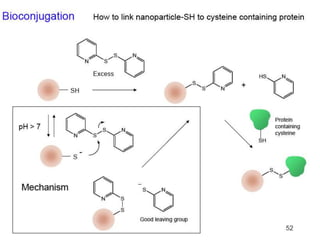
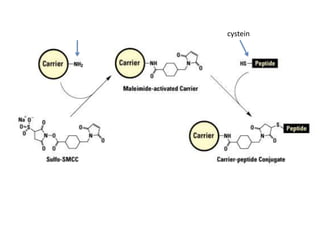
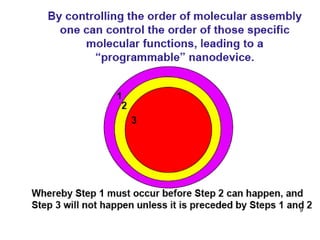
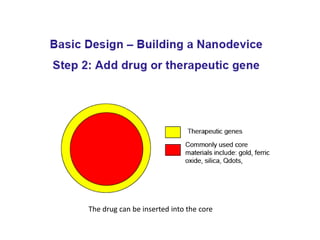
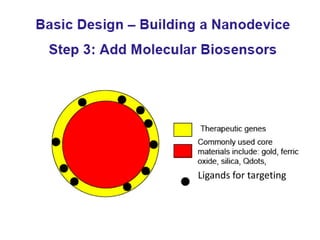
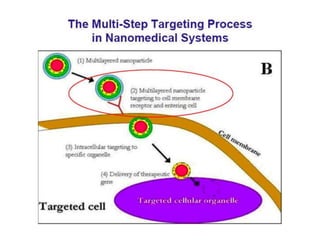
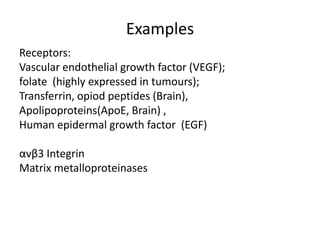
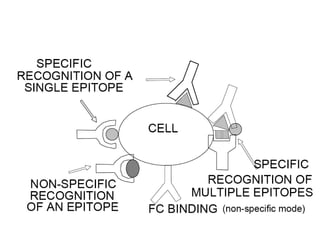
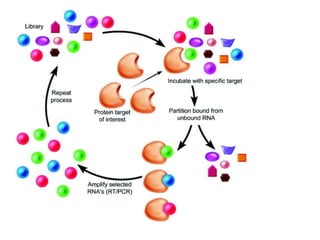
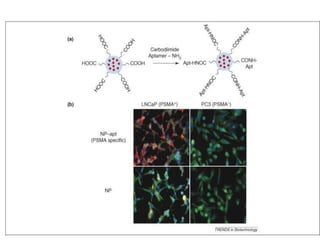
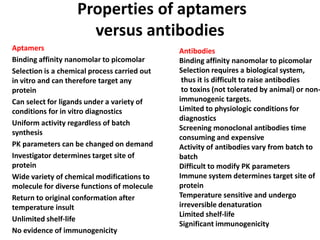
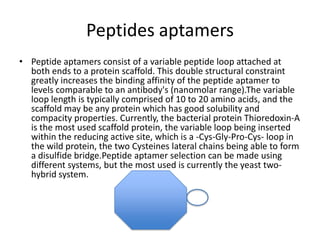
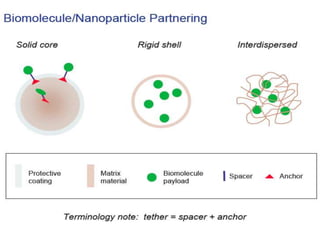
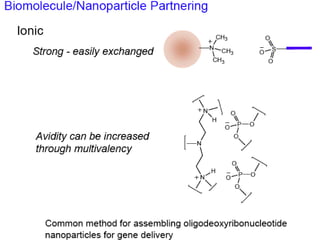
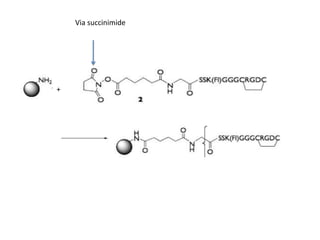
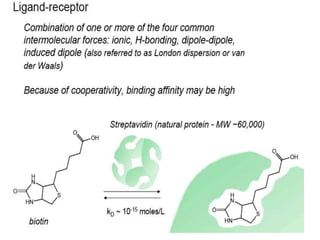
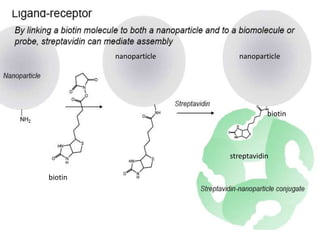
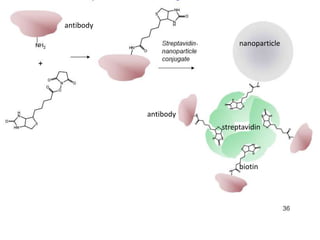
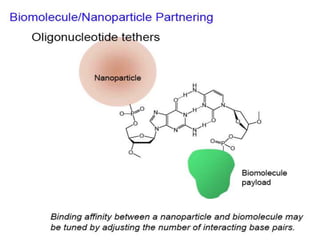
This document discusses surface modification of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. It describes various methods for modifying the nanoparticle surface, including conjugating ligands for cell targeting (e.g. antibodies, peptides, aptamers), encapsulating the nanoparticle core with lipids or polymers, and attaching targeting moieties via linkers like streptavidin-biotin. Common targets for surface ligands include receptors for VEGF, folate, transferrin and others. Aptamers and peptides are also discussed as targeting options.
















![LNA
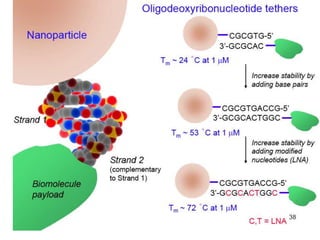
• A locked nucleic acid (LNA), often
referred to as inaccessible RNA, is a
modified RNA nucleotide. The
ribose moiety is modified with an
extra bridge connecting the 2'
oxygen and 4' carbon. LNA
nucleotides can be mixed with DNA
or
RNA
residues
in
the
oligonucleotide whenever desired.
Such oligomers are commercially
available. The locked ribose
conformation
enhances
base
stacking and backbone preorganization. This significantly
increases
the
hybridization
properties (melting temperature)
of oligonucleotides.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3targeting-131126160159-phpapp01/85/targeting-41-320.jpg)