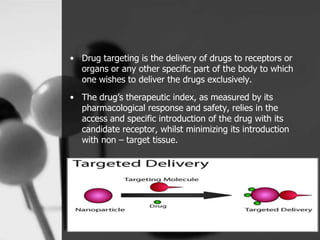
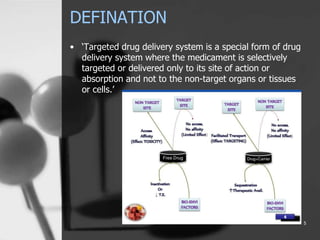
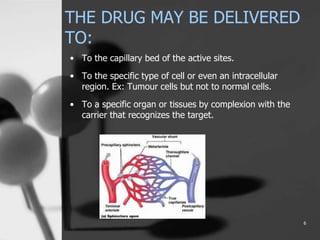
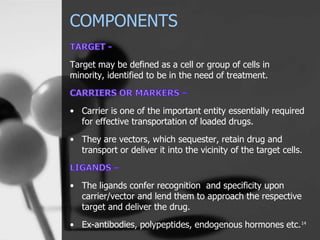
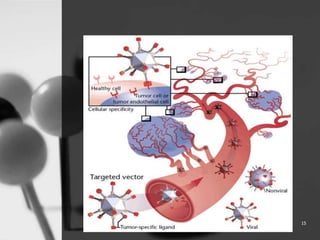
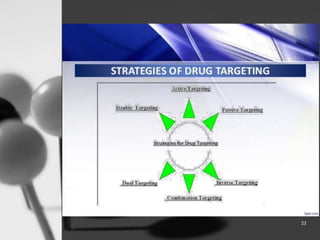
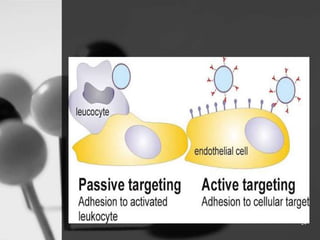
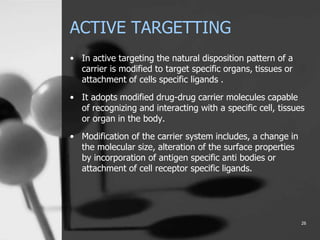
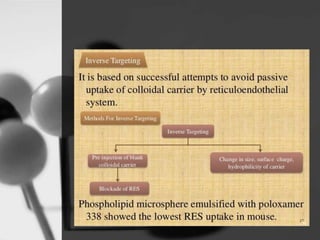
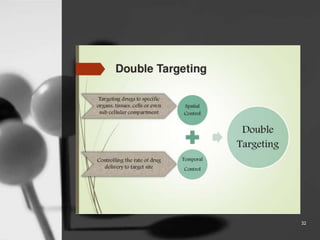
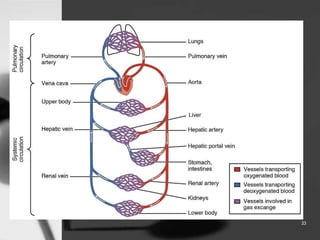
This document provides an overview of targeted drug delivery. It defines targeted drug delivery as concentrating medication in tissues of interest while reducing it in other tissues to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. The objectives of targeted delivery are to selectively and effectively localize drugs to a pre-identified site while increasing therapeutic concentration and restricting drugs to non-specific sites to minimize toxic effects. Targeted delivery can be achieved through passive, active, inverse, dual or double targeting using various carrier systems like nanoparticles, liposomes and polymers.