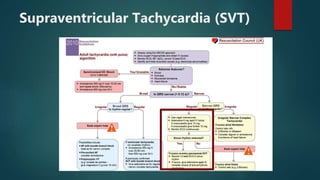
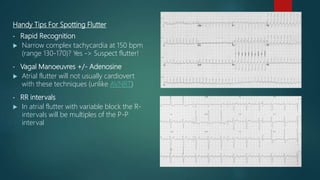
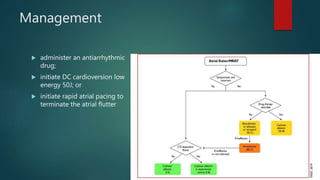
The document discusses the evaluation and management of tachy-arrhythmias, detailing normal heart rhythm parameters and the causes of arrhythmias, as well as a structured ECG analysis approach. It outlines various types of tachycardia, including sinus tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and premature ventricular complexes, along with their management strategies. Key management techniques emphasize patient stability, recognition of adverse features, and appropriate pharmacological and procedural interventions.