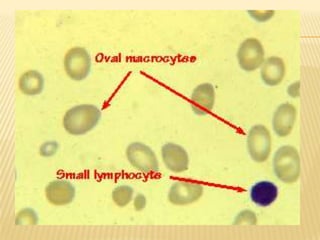
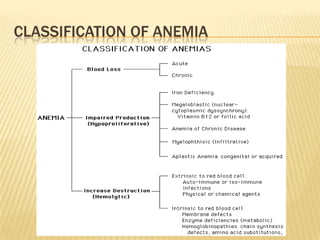
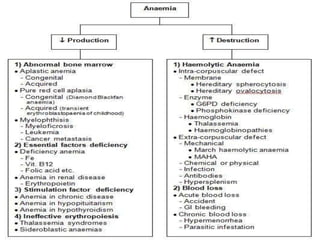
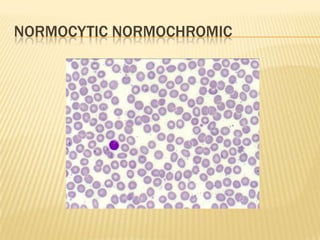
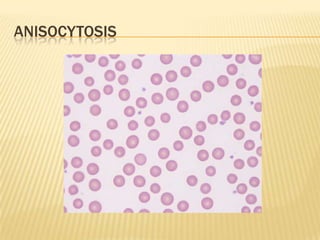
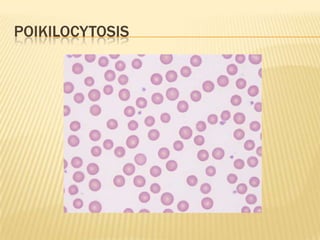
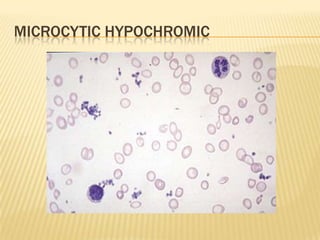
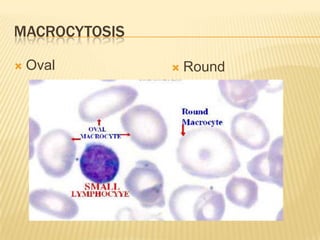
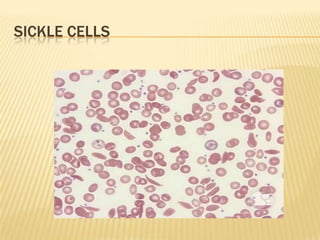
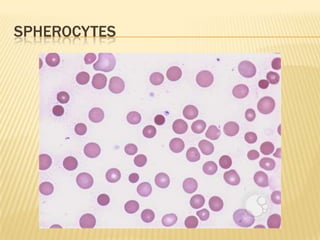
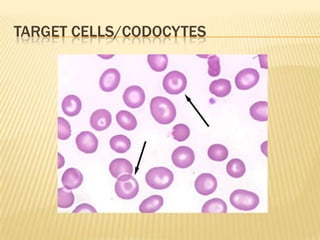
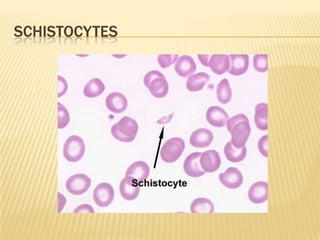
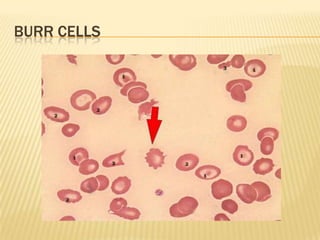
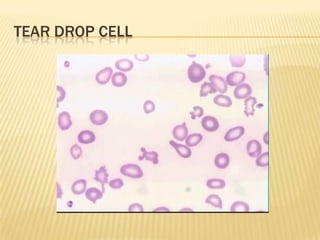
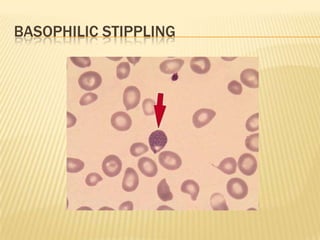
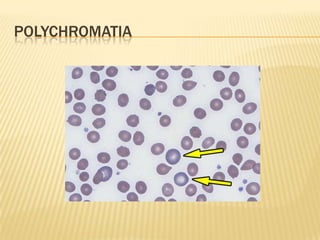
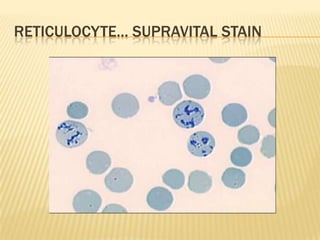
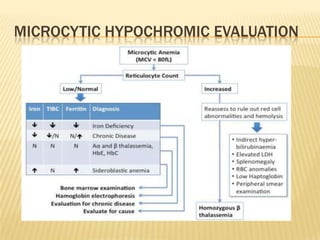
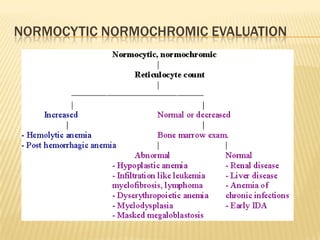
This document provides information on approaches to diagnosing and classifying anemia. It discusses levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells used to define anemia for different age groups and sexes. Methods for measuring hemoglobin and hematocrit are described. A peripheral blood smear examination can identify abnormalities in red blood cell size, shape, and contents to classify anemia types. Red cell indices like MCV, MCH and MCHC further characterize anemia as microcytic, macrocytic, or normocytic. Causes and evaluations are discussed for the major anemia types: iron deficiency, megaloblastic, and normocytic anemia.