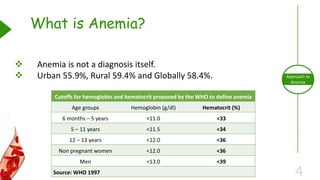
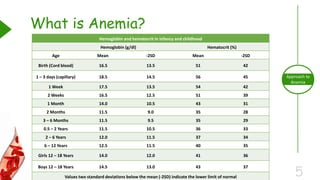
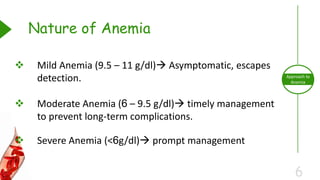
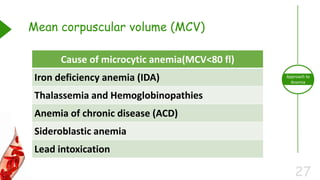
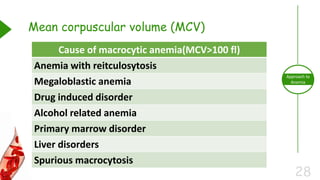
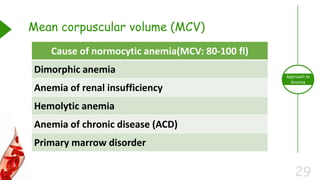
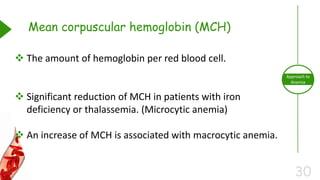
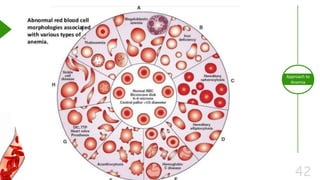
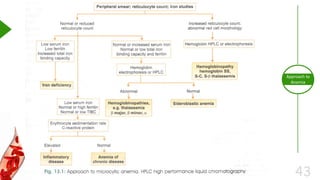
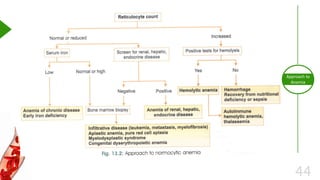
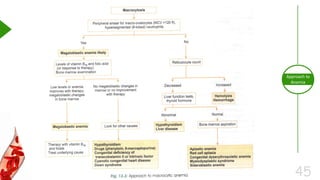
This document outlines the approach to anemia, defining it as a reduction in circulating red blood cells affecting 1.6 billion people globally. It covers the classification, causes, diagnostic approaches, and clinical features of anemia, emphasizing the importance of thorough history-taking and laboratory investigations. The conclusion reiterates that anemia is not a diagnosis itself and underscores the necessity for a comprehensive evaluation to determine its causes.