This document summarizes an academic presentation on applications of geophysical survey methods, including:
- Gravity surveys can be used to explore for hydrocarbons, study regional geology, locate mineral deposits, and monitor volcanoes. They help determine density variations underground.
- Magnetic surveys detect variations in the Earth's magnetic field to map archaeological artifacts, locate buried infrastructure like pipes and tanks, explore for ores and fossil fuels, and study tectonics and geology.
- Electrical resistivity surveys measure subsurface resistivity variations to detect archaeological features, map groundwater, and identify contaminant plumes or unstable ground conditions.
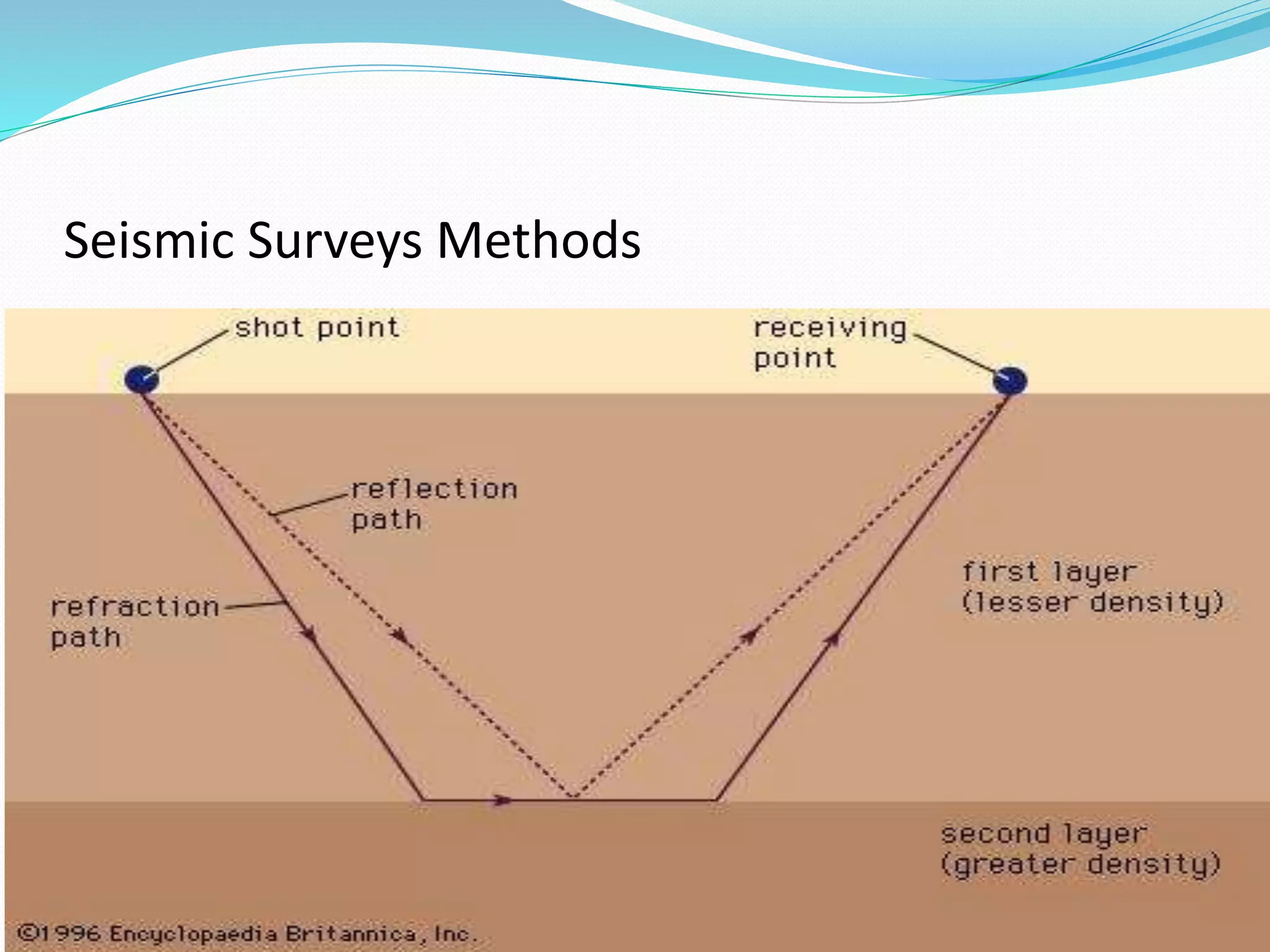
- Seismic surveys use acoustic impulses to image underground rock layers for applications like