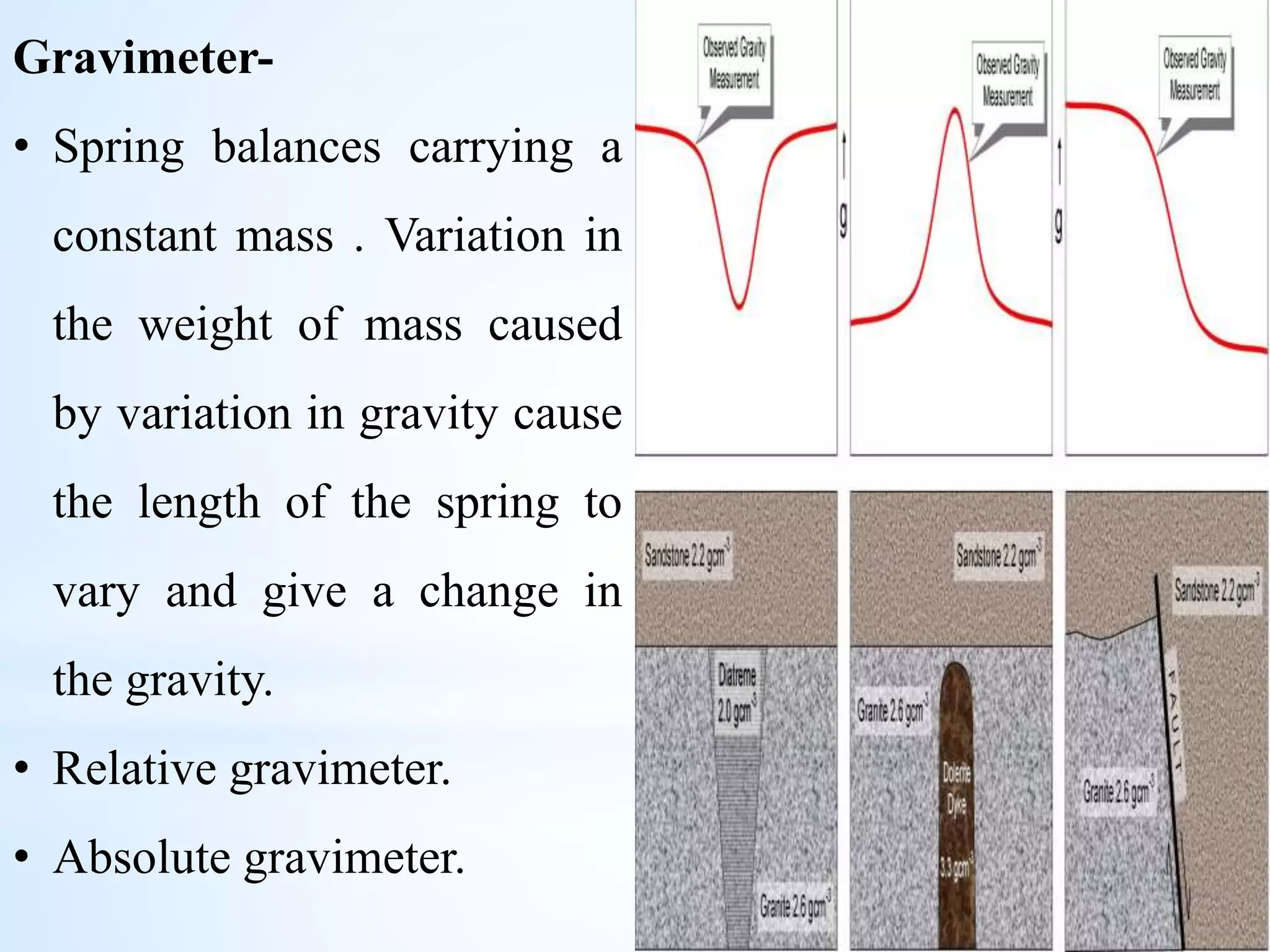
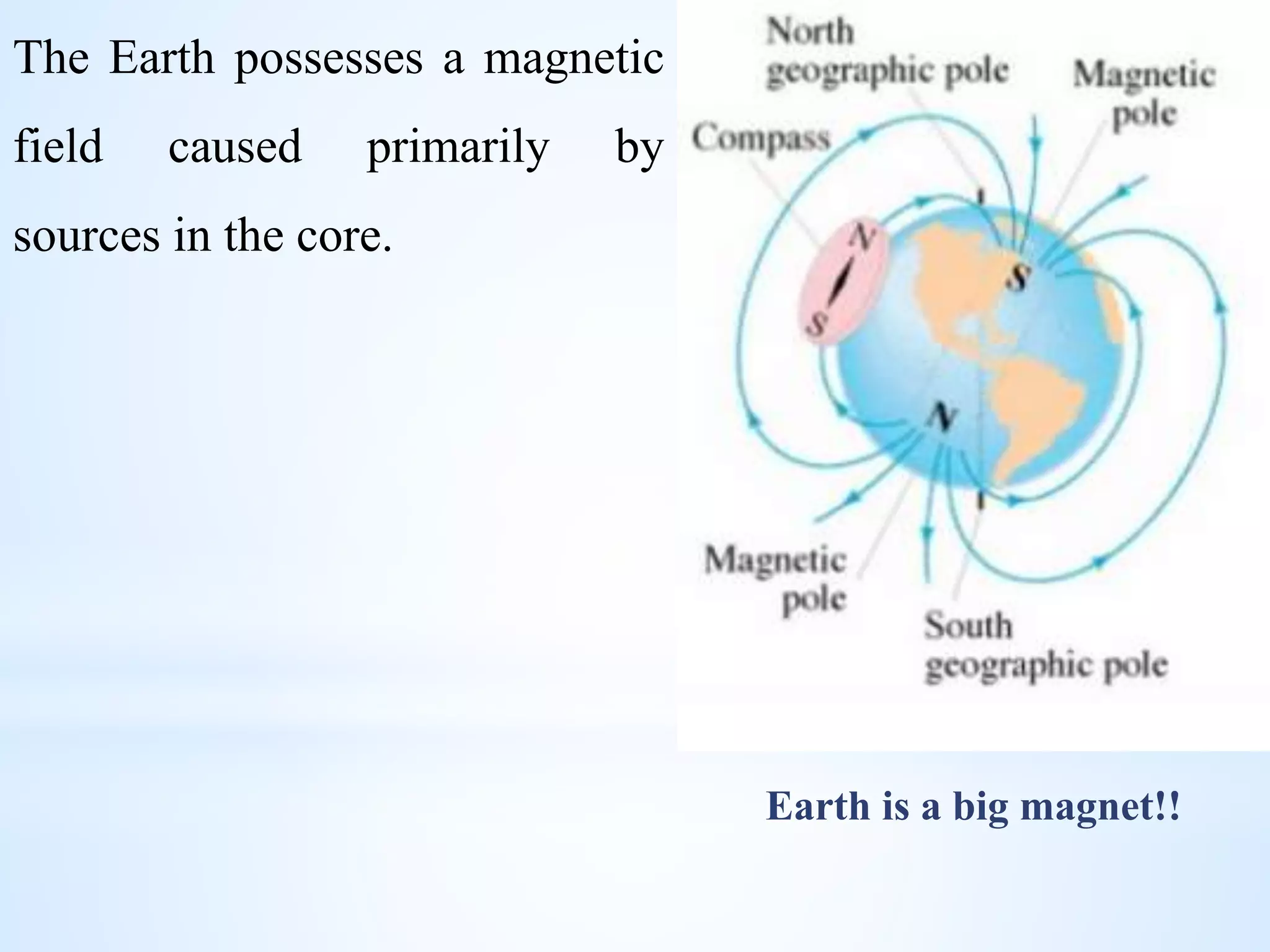
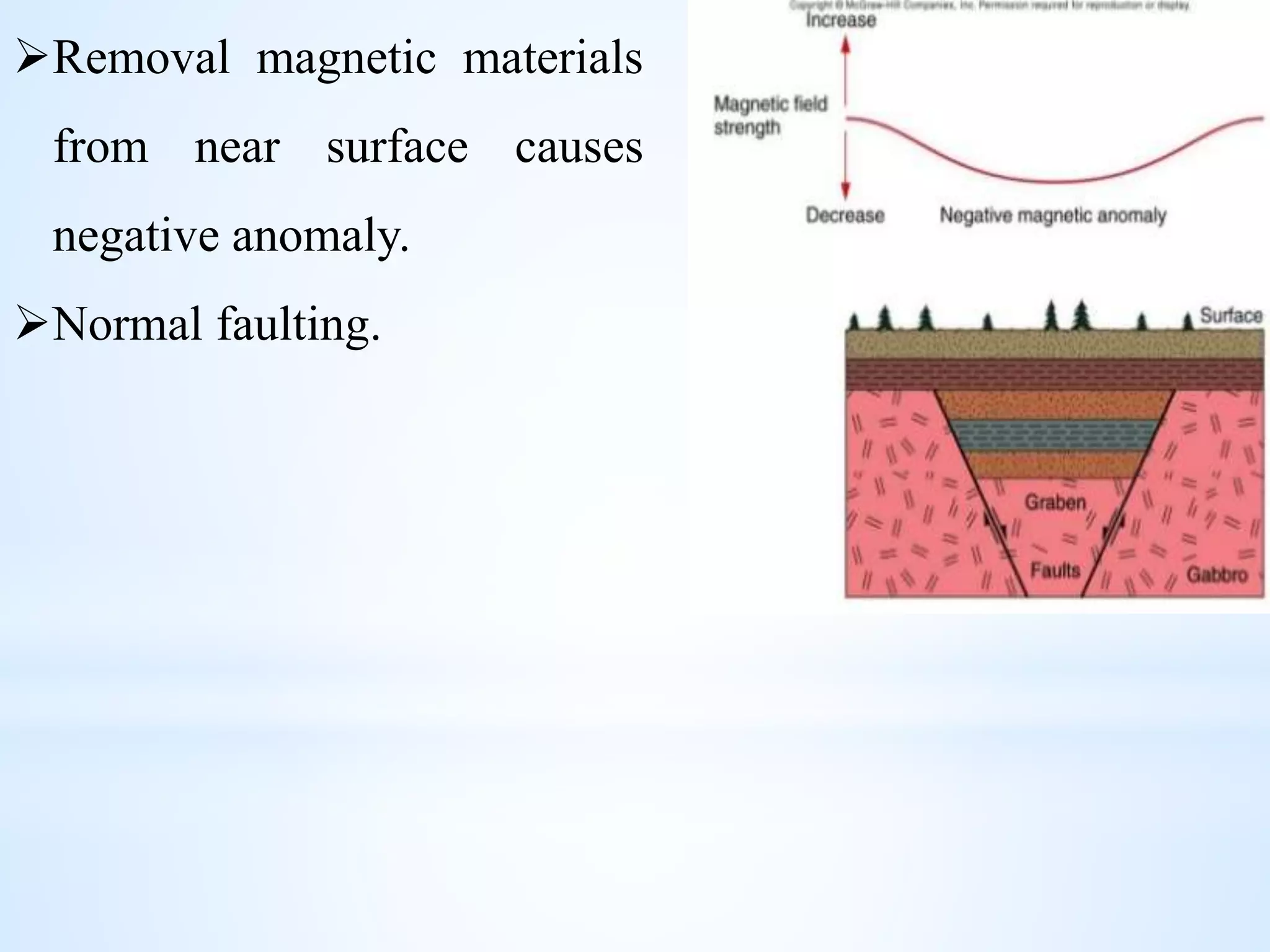
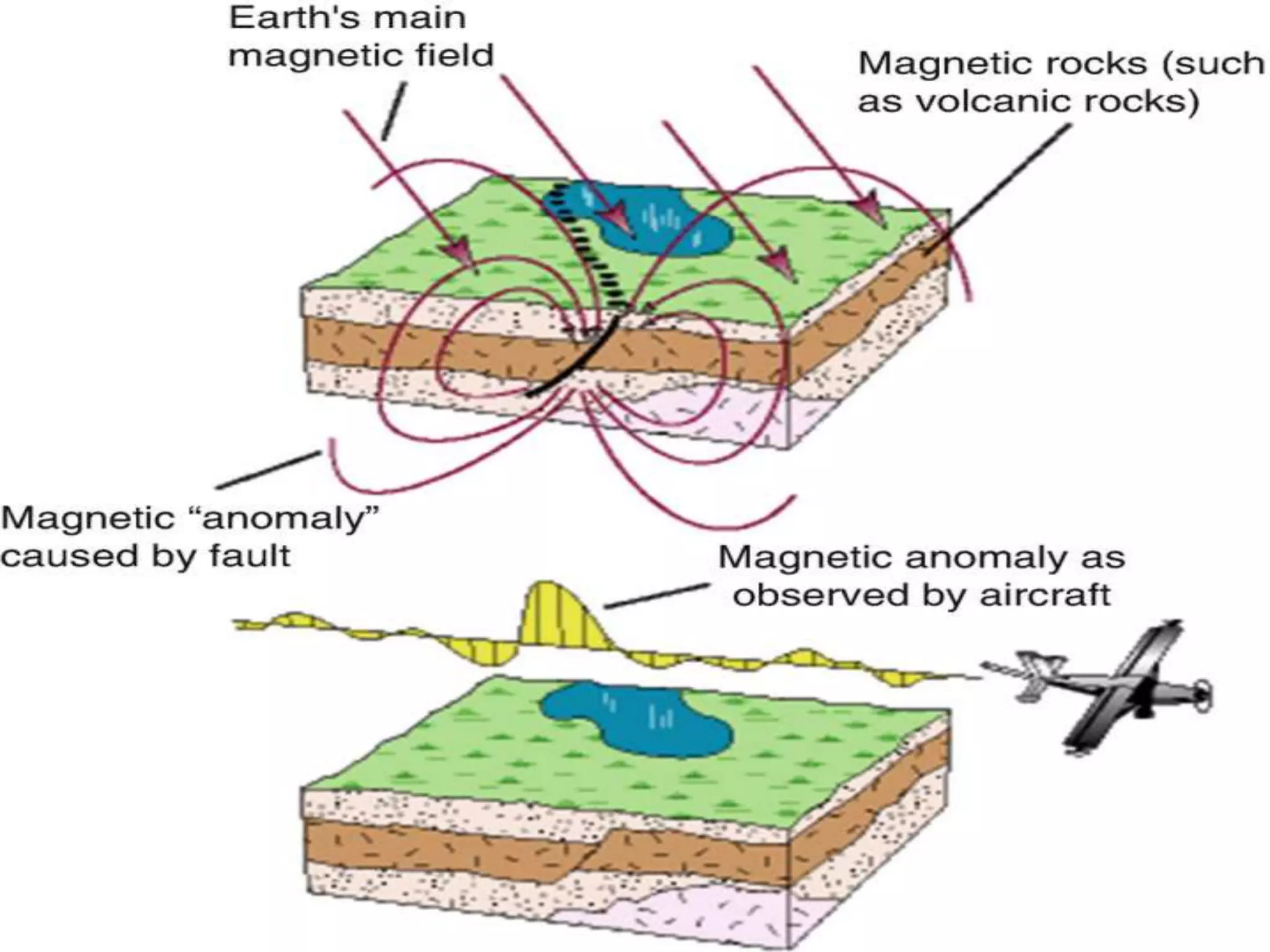
Gravity and magnetic surveying are non-destructive geophysical techniques. Gravity surveying measures variations in the gravitational field to infer subsurface density variations, while magnetic surveying measures variations in the magnetic field to detect magnetic materials below the surface. Both methods work by measuring spatial anomalies - deviations from a predefined reference level for the gravitational or magnetic field. These anomalies are interpreted to determine properties of subsurface rock layers and structures.