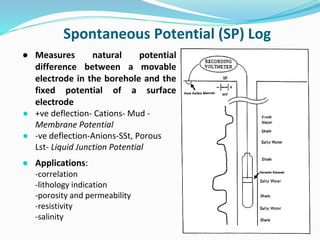
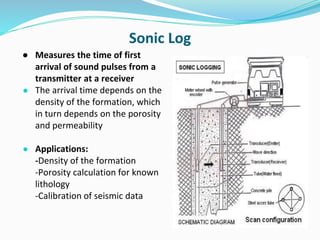
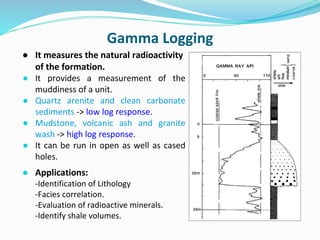
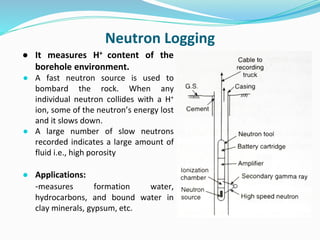
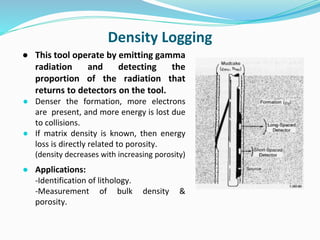
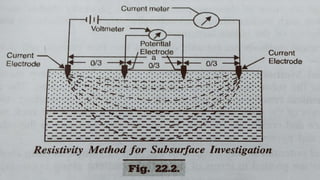
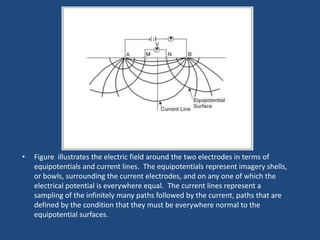
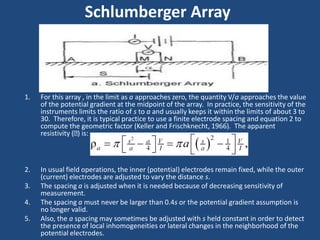
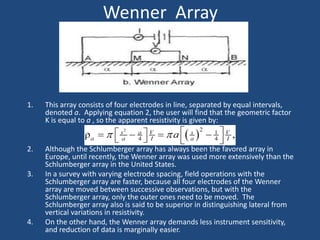
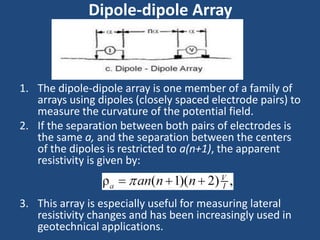
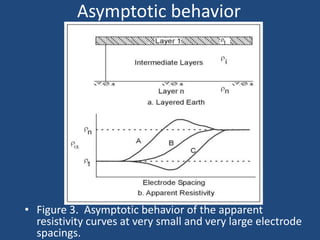
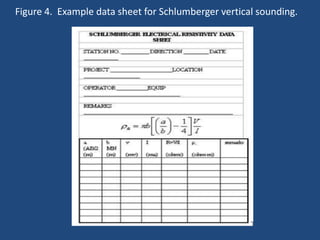
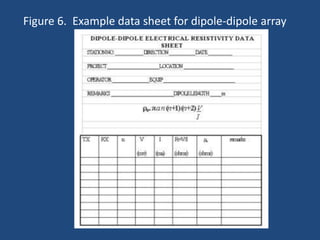
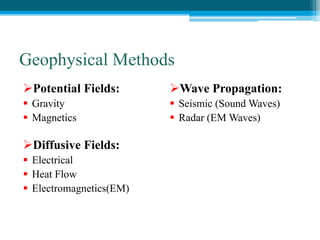
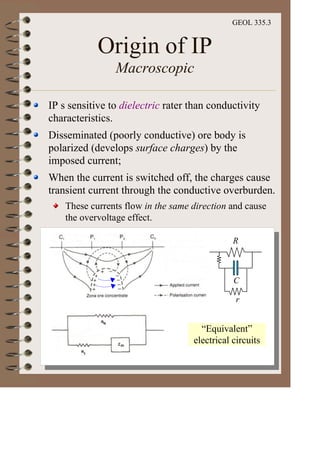
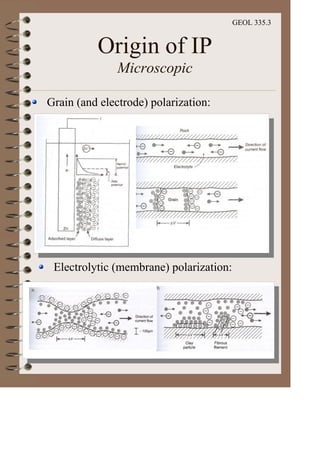
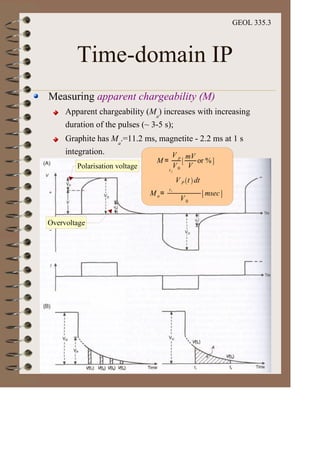
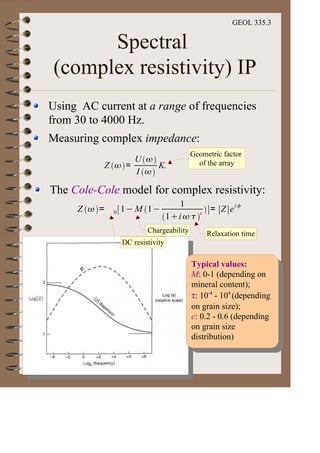
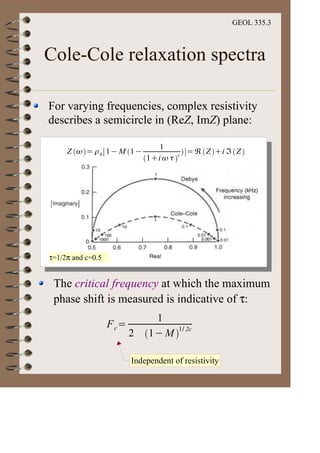
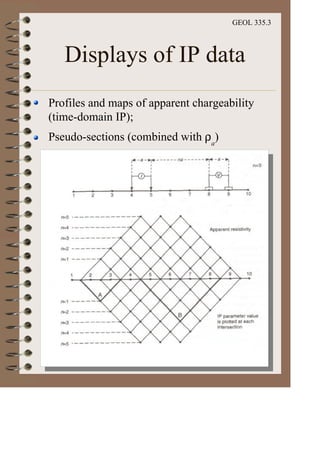
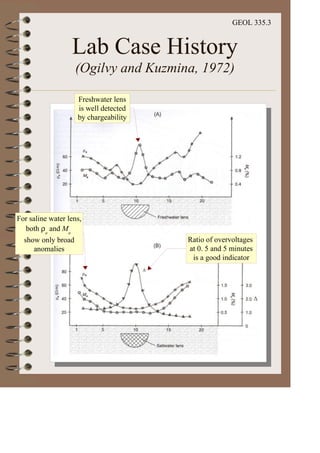
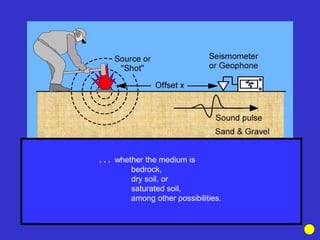
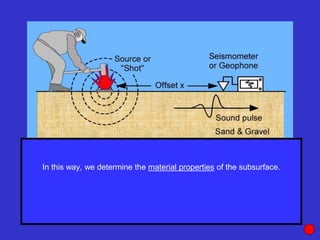
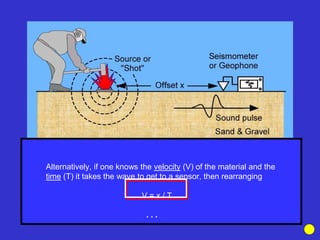
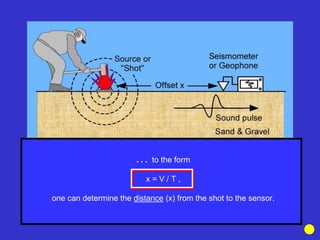
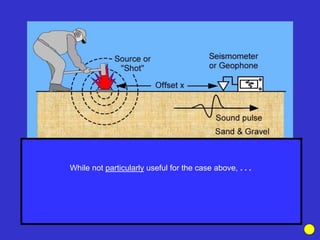
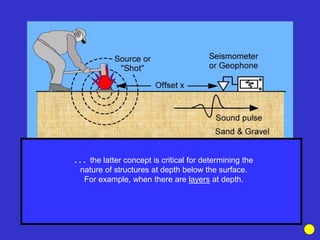
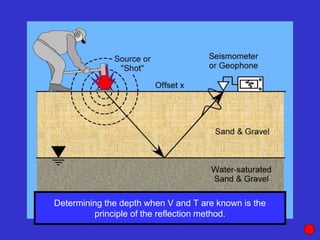
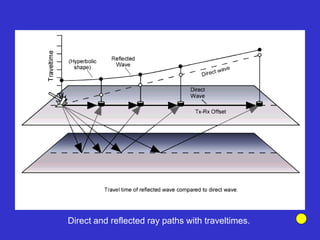
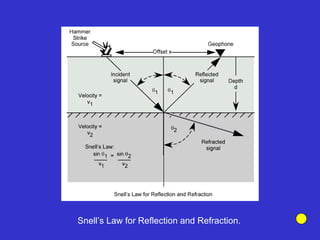
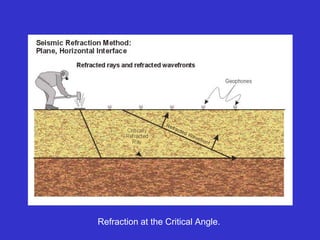
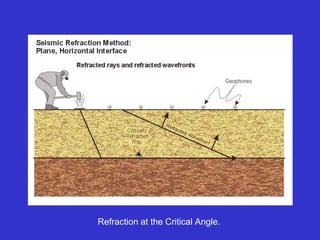
The document discusses the electrical resistivity method for geophysical investigations. It begins by defining electrical resistivity and describing how it is measured. Resistivity depends on factors like moisture content and can be used to distinguish different earth materials. Common electrical methods involve introducing a current and measuring potential gradients to determine resistivity. This allows interpreting subsurface stratigraphy and structures. Applications include mapping geology, locating aquifers, and engineering investigations. In summary, the electrical resistivity method measures resistivity distributions in the ground to interpret subsurface compositions and locate features like water-bearing zones.











































































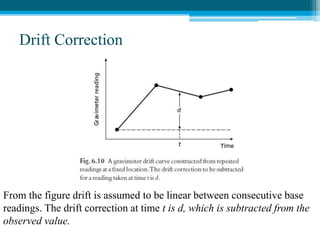

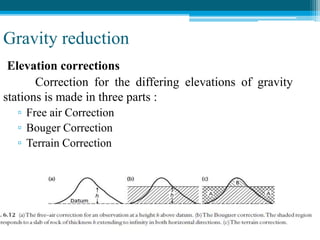




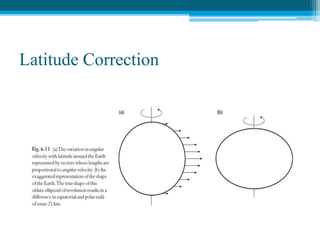









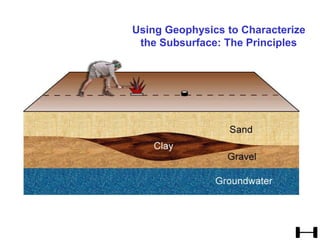

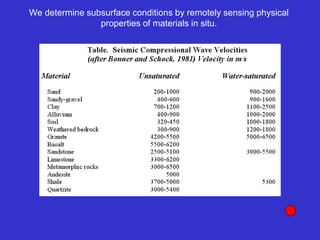
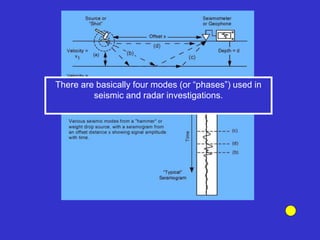
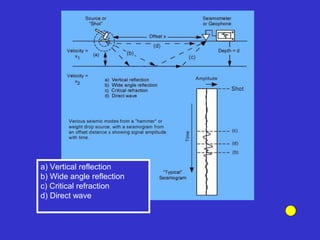
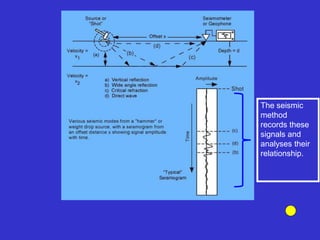
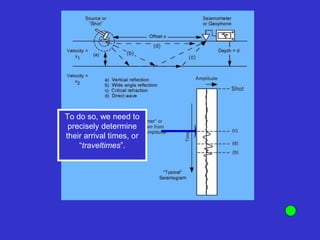
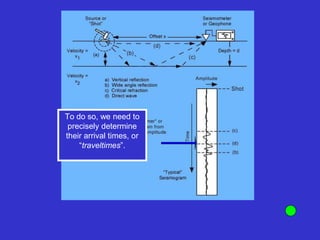
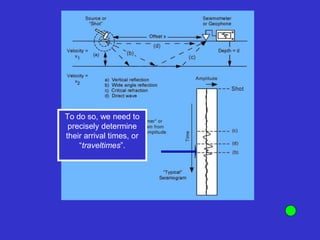
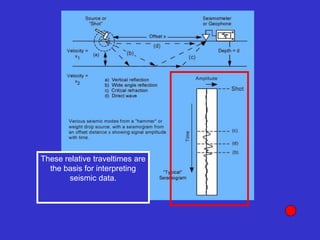
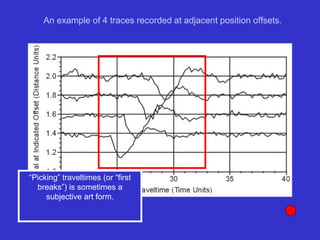
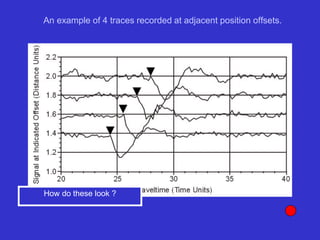
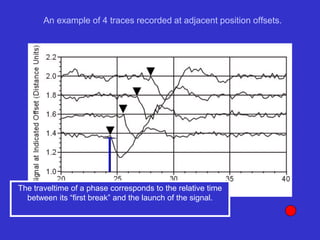











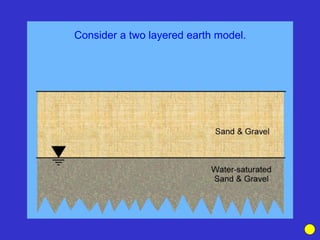
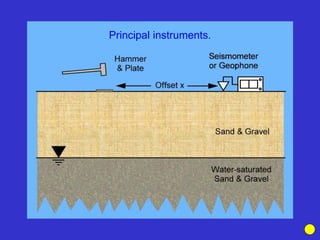
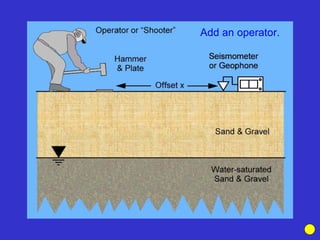
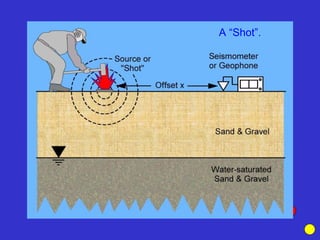
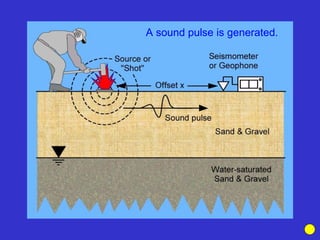
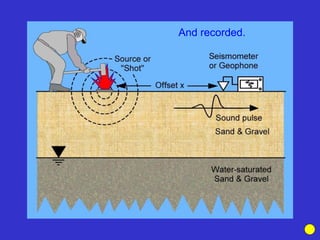
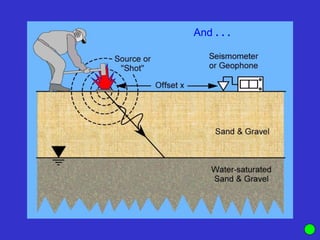
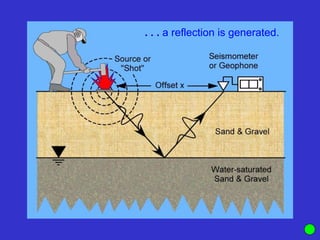
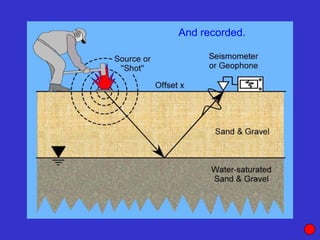
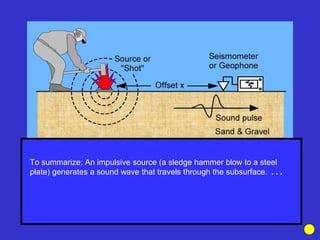
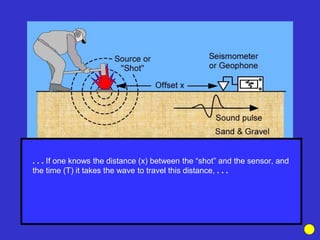
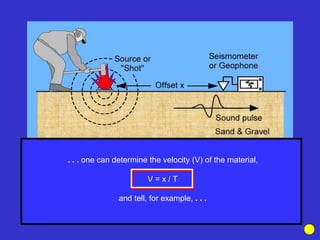

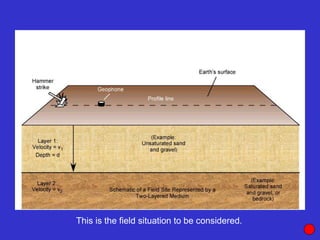






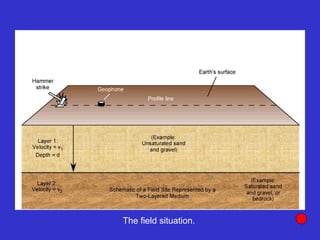
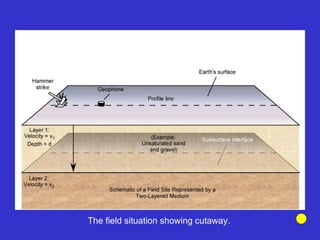
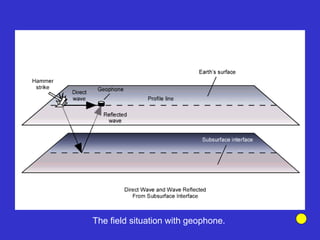














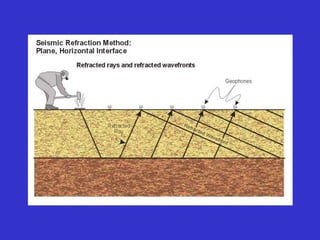
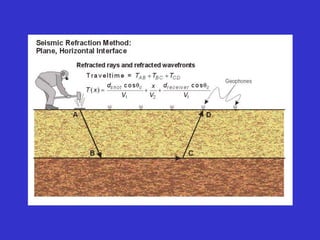
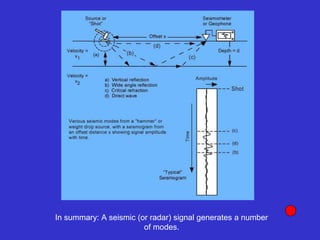

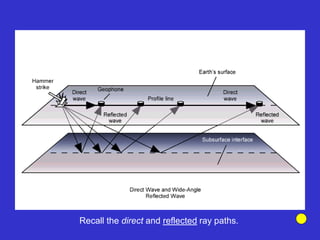
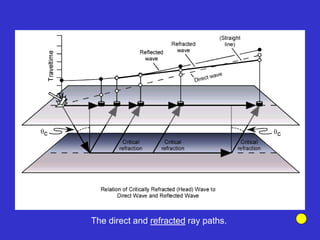
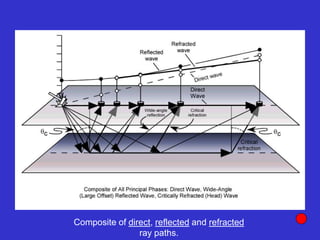
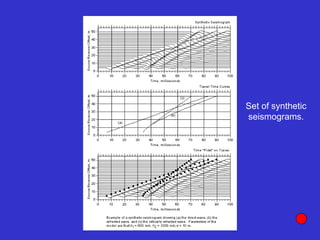

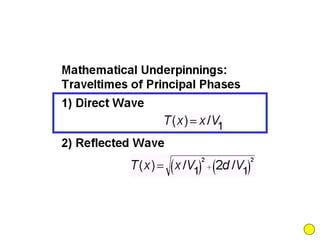
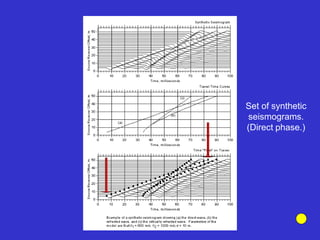
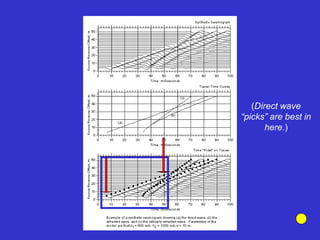
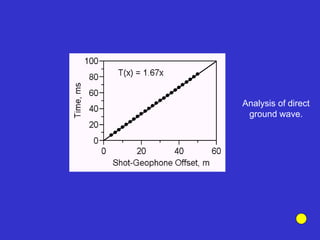
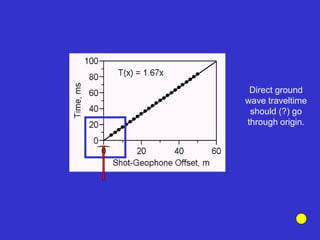













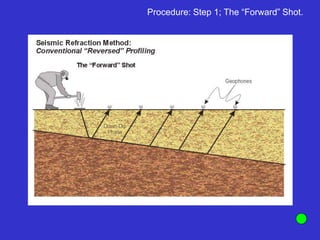
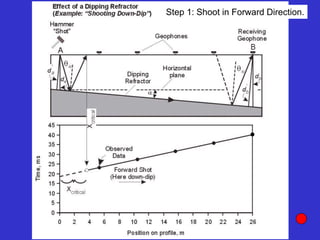
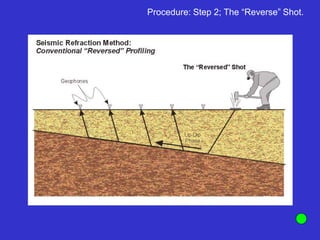
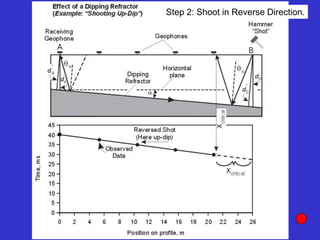
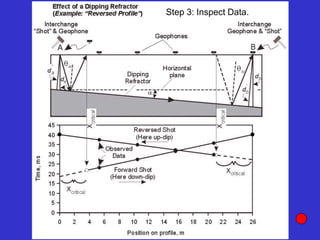
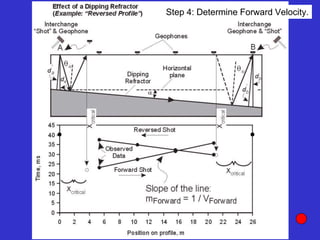
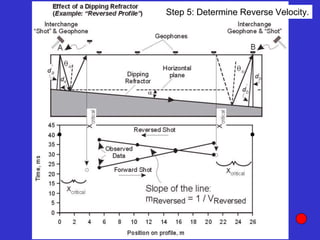
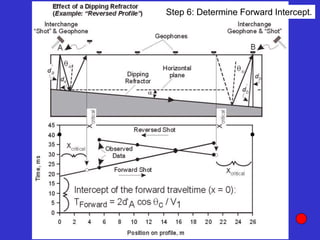
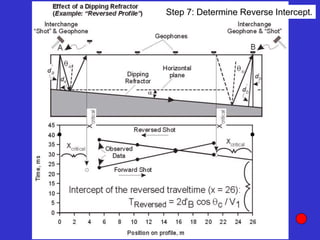
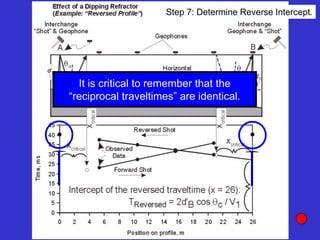


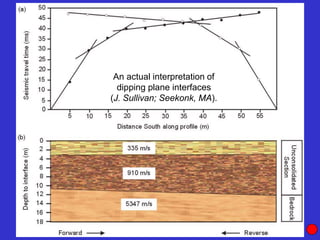
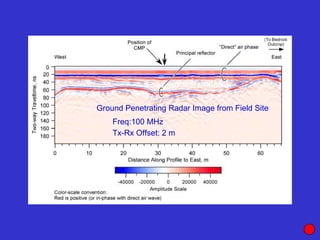
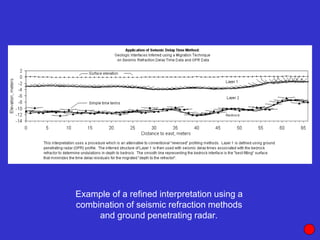
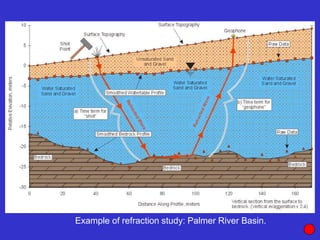
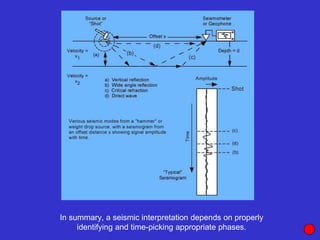
![Subsurface structure above bedrock at field site.
Composite interpretation using seismic
refraction, DC resistivity, EM, GPR and gravity.
[Seismic interpretation from Jeff
Sullivan (personal communication.).]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/explorationgeophysicsiiisemester-230219165334-f02cfa0d/85/Exploration-Geophysics-III-semester-pdf-248-320.jpg)