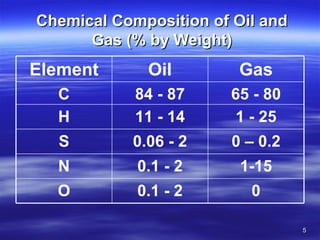
Petroleum, or hydrocarbons, are a mixture of liquids, solids, and gases that occur naturally beneath the earth's surface and are composed primarily of hydrogen and carbon. Petroleum exists in several forms, including crude oil, natural gas, and semi-solid forms like asphalt and tar. Crude oil is a liquid hydrocarbon that contains dissolved gases and other impurities, floats on water, and is soluble in various organic compounds. Natural gas is composed mainly of lighter hydrocarbon gases like methane. Semi-solid forms include heavy hydrocarbons and bitumens. Petroleum exploration involves studying the geology and structures beneath the earth's surface to locate potential hydrocarbon deposits.