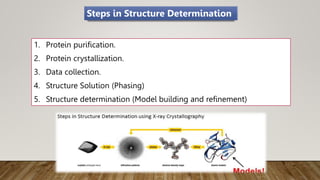
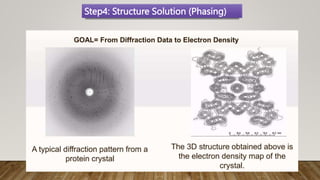
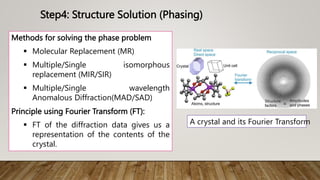
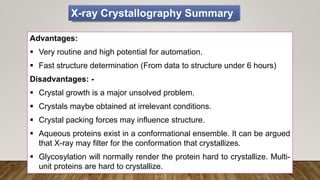
X-ray crystallography is a technique used to determine the three-dimensional structures of proteins at high resolution. It involves growing protein crystals, collecting X-ray diffraction data from the crystals, solving the phase problem to obtain electron density maps, and building atomic models into the density. X-ray crystallography provides insights into protein function by revealing how proteins interact with other molecules at the atomic level. While it is a powerful technique, protein crystallization remains a major challenge, and crystal structures may not always reflect the conformations proteins adopt in solution.