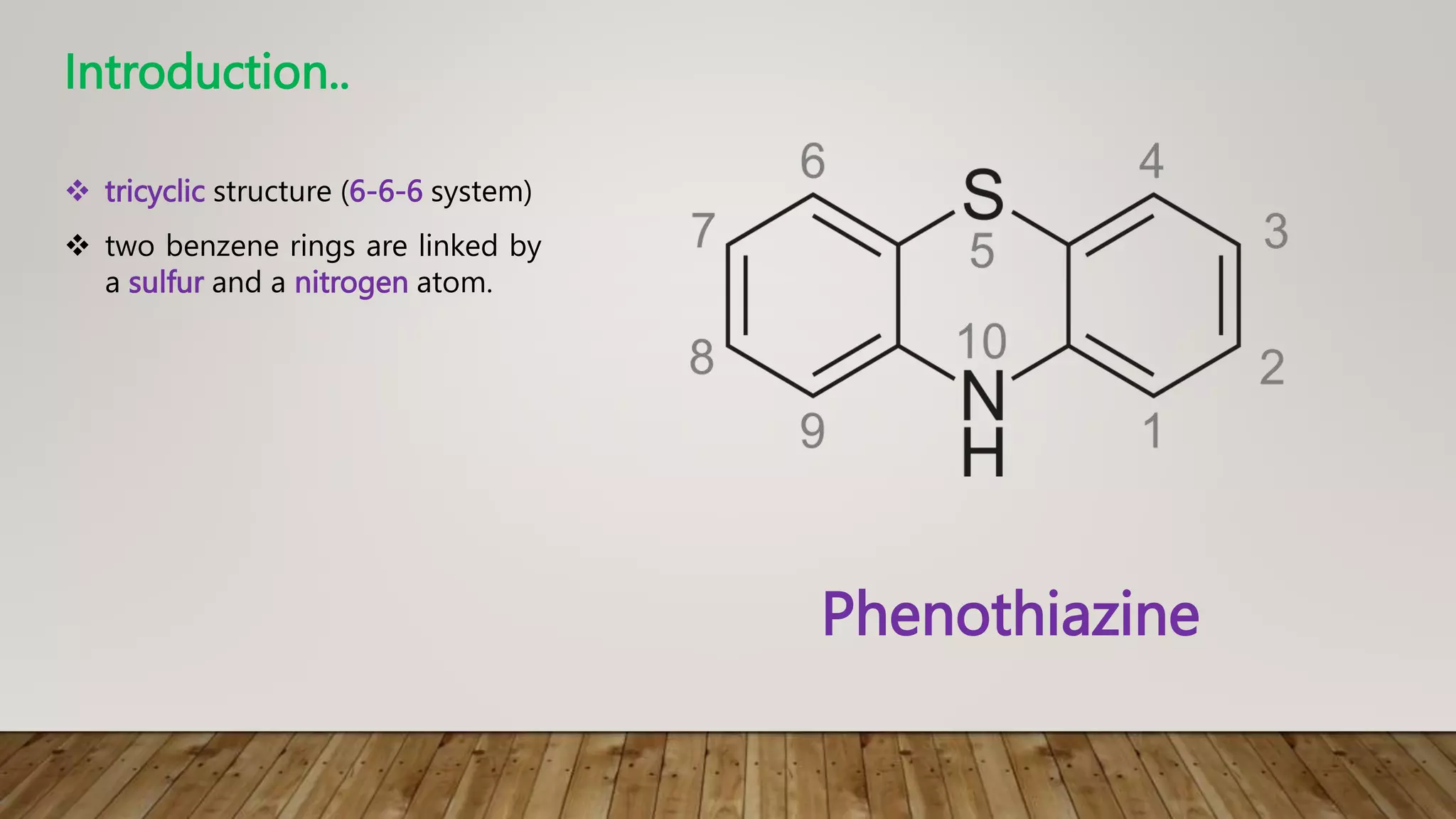
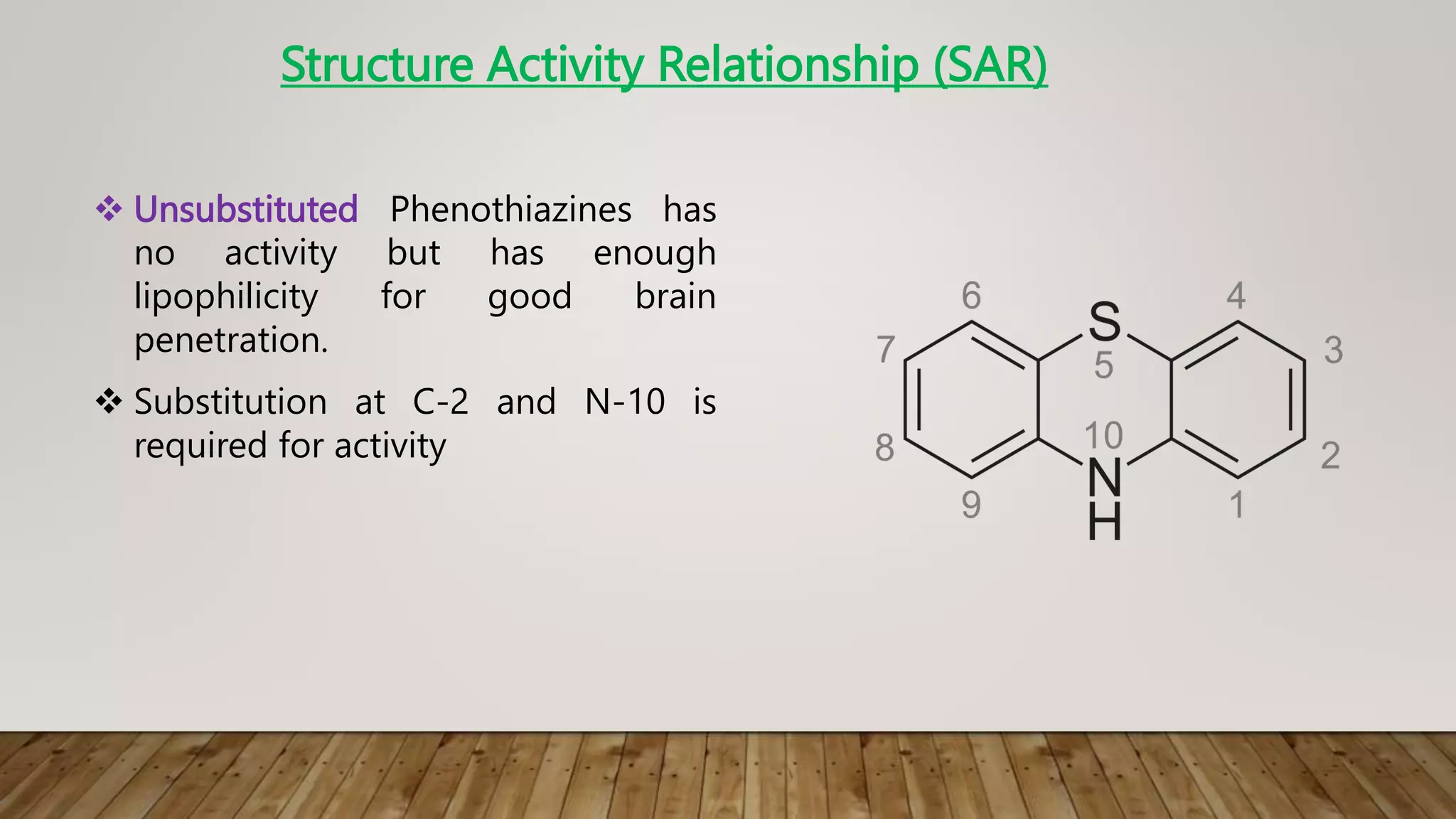
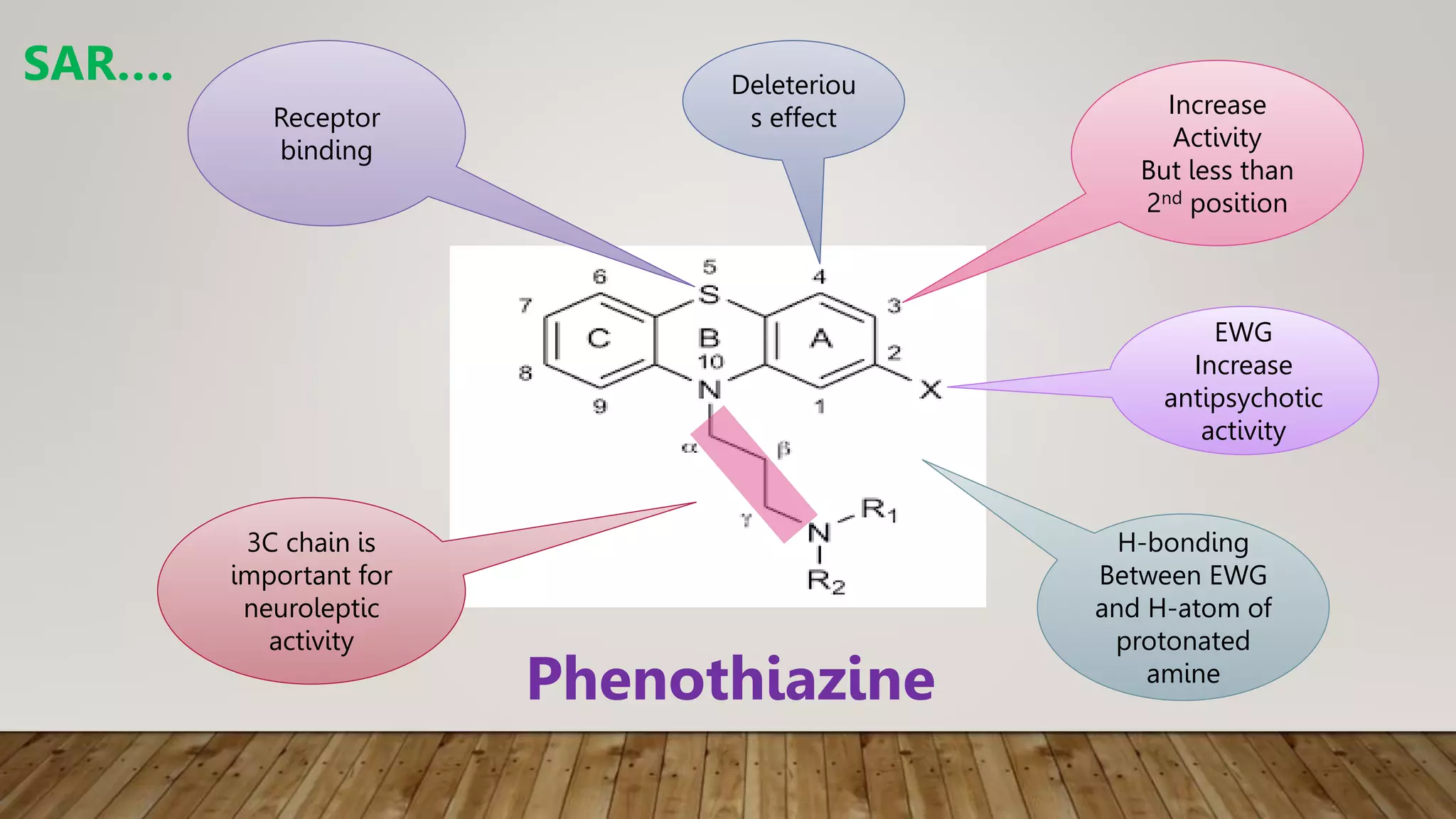
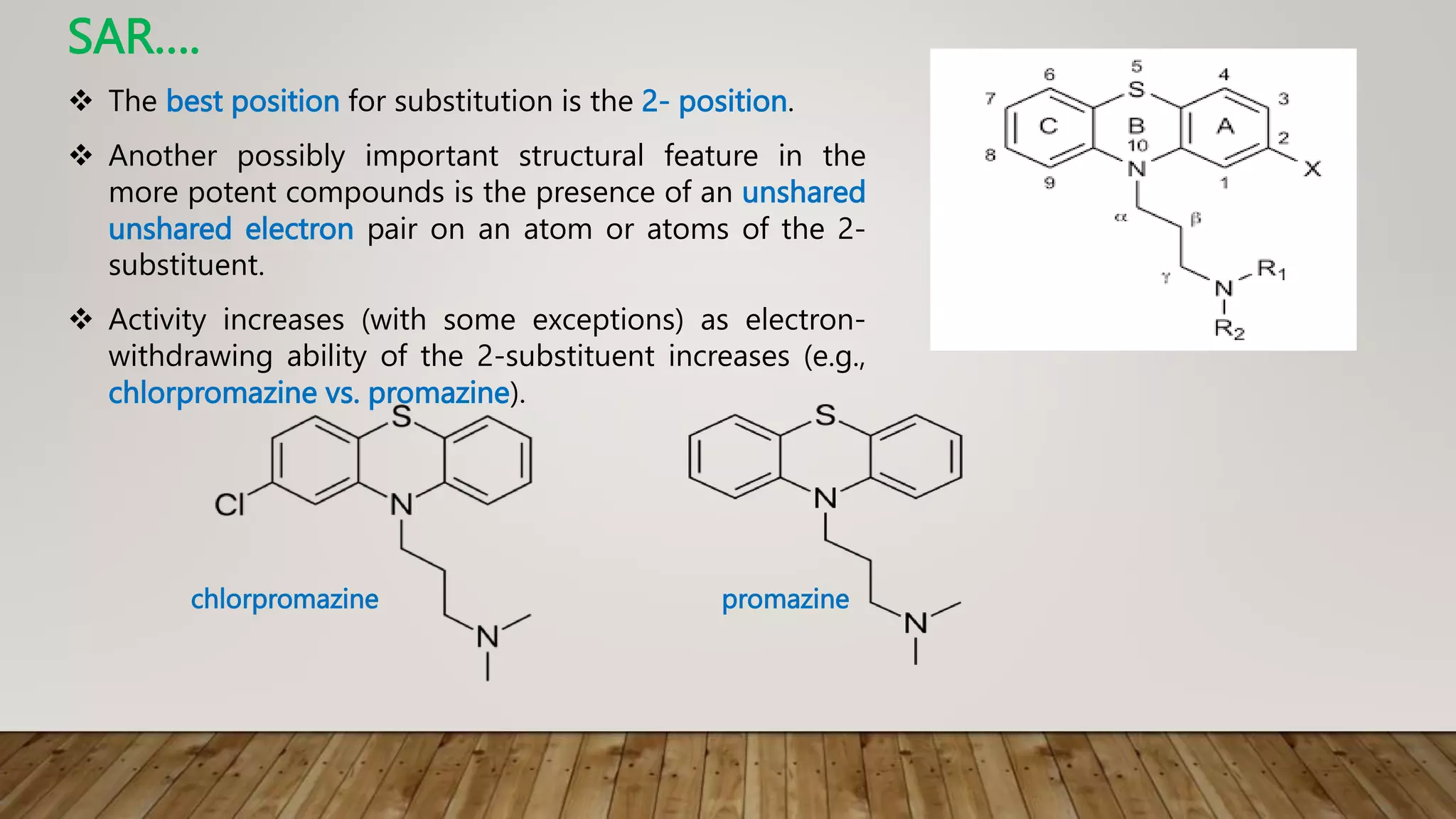
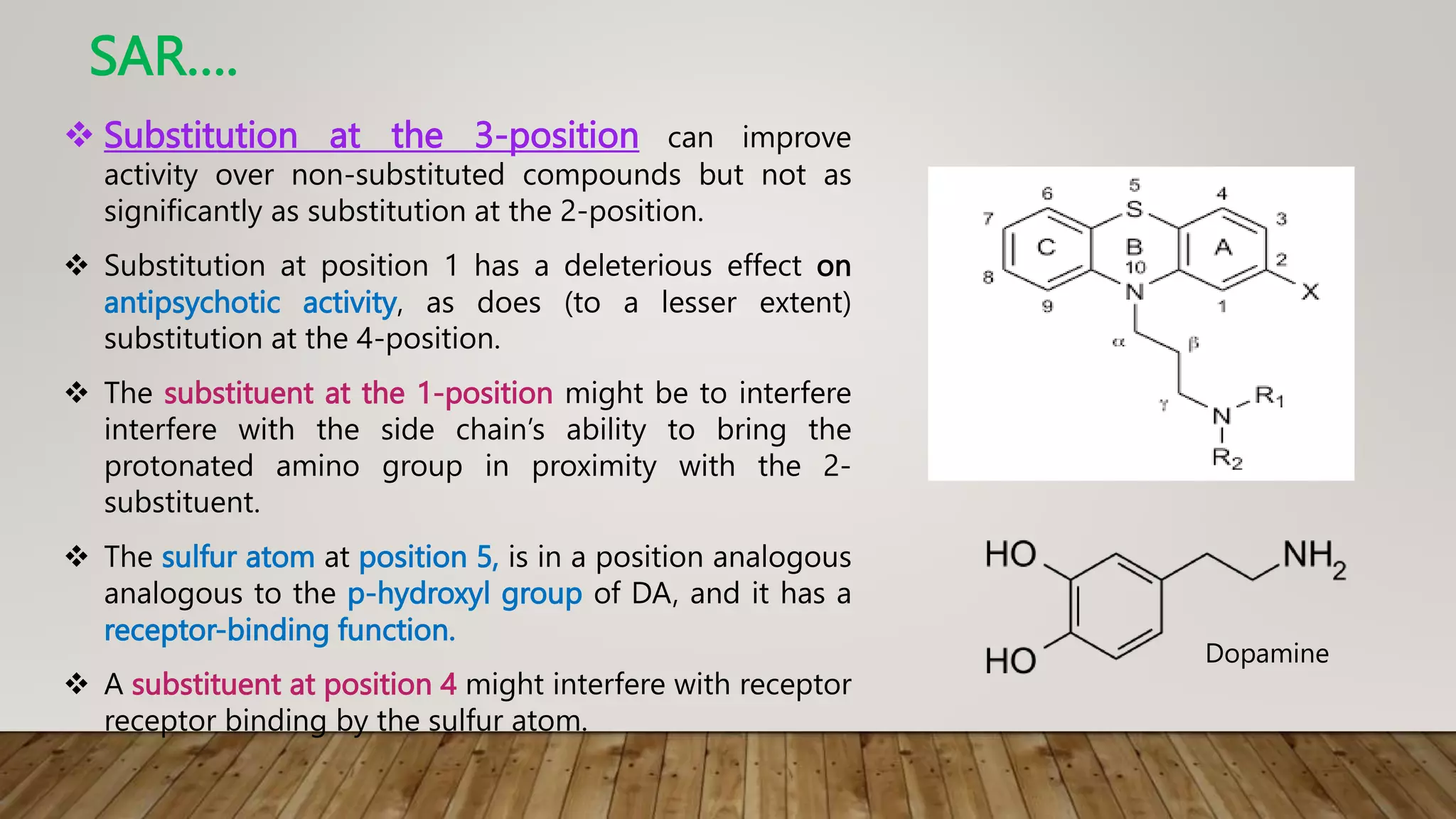
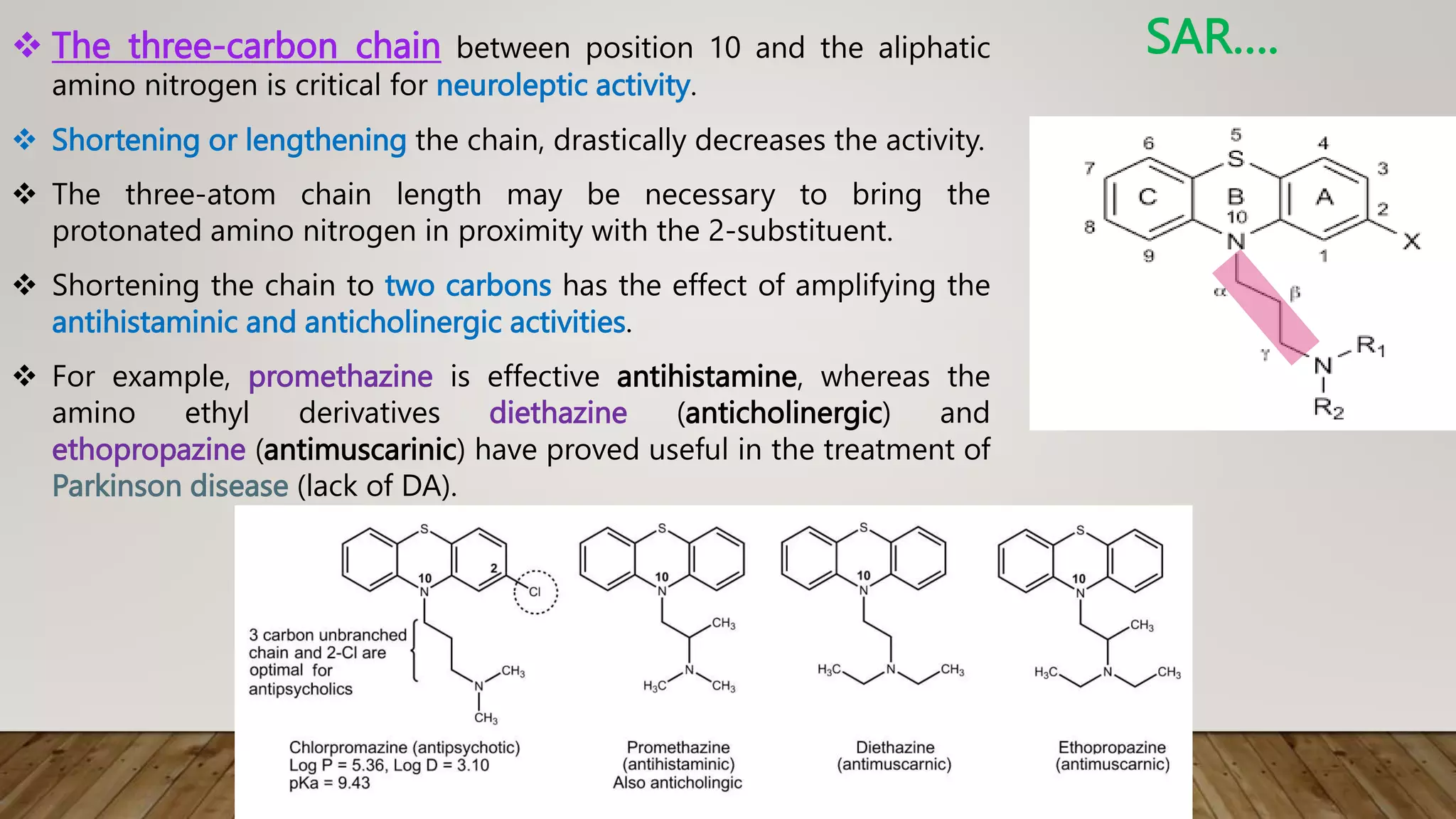
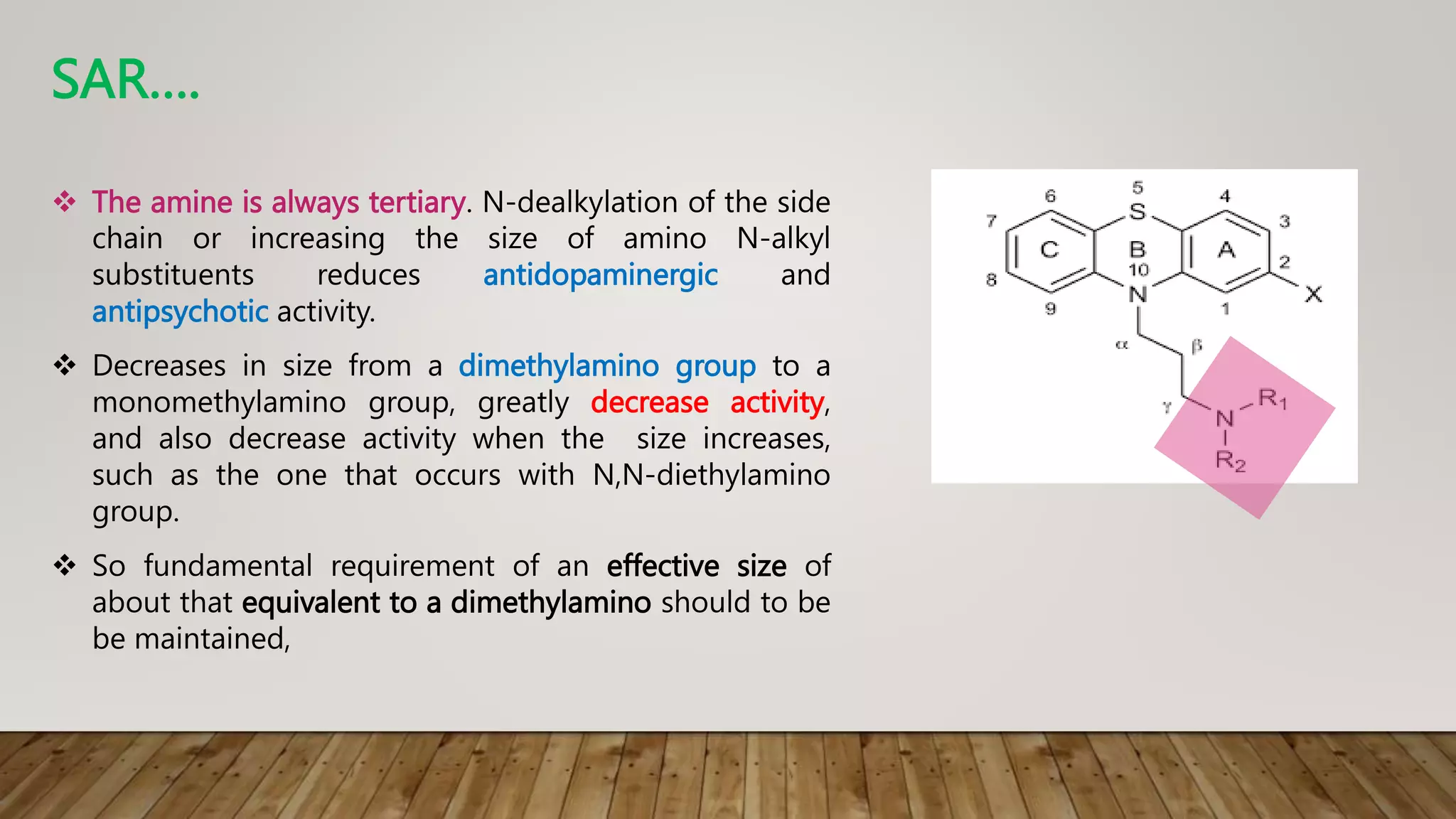
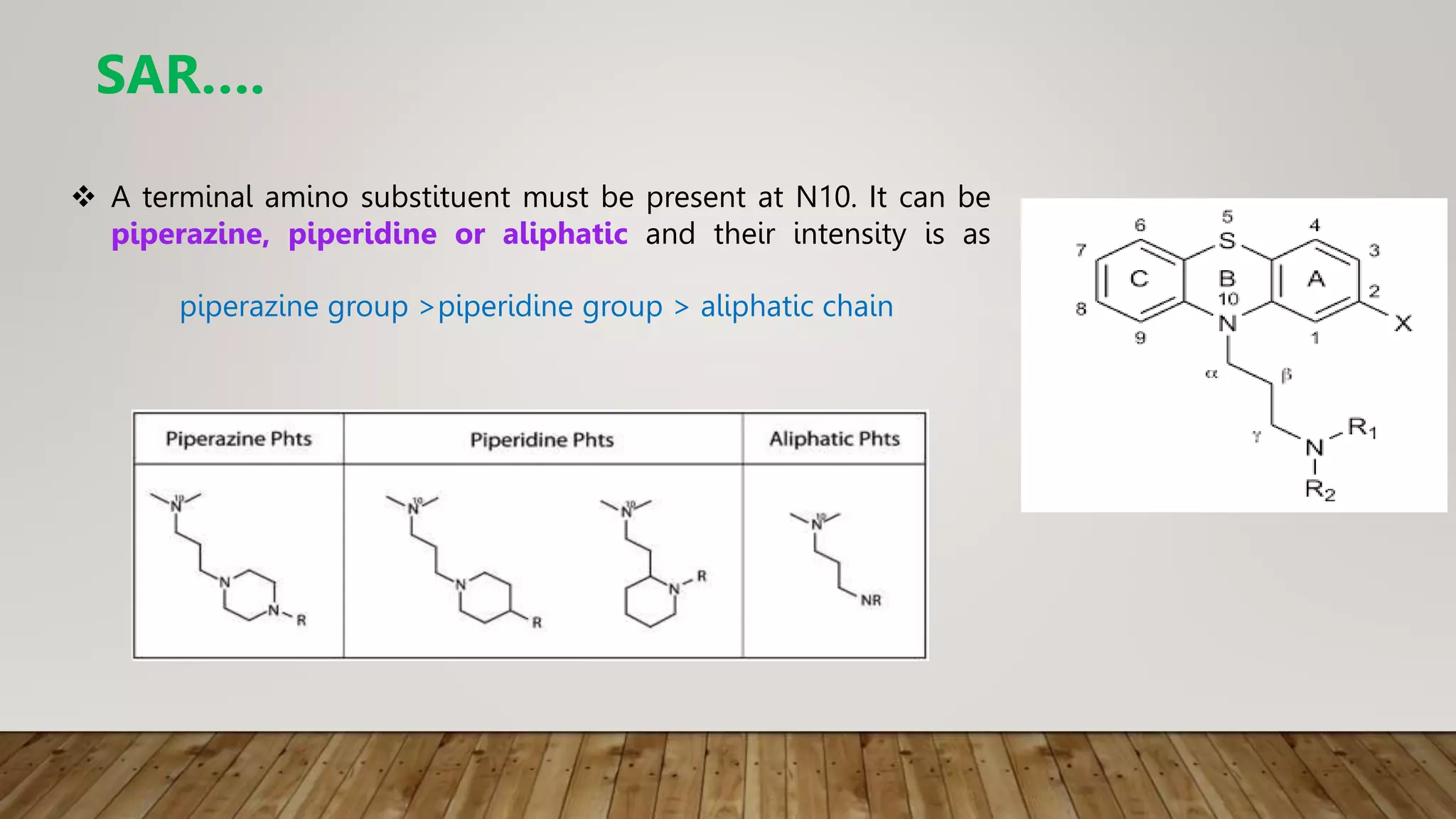
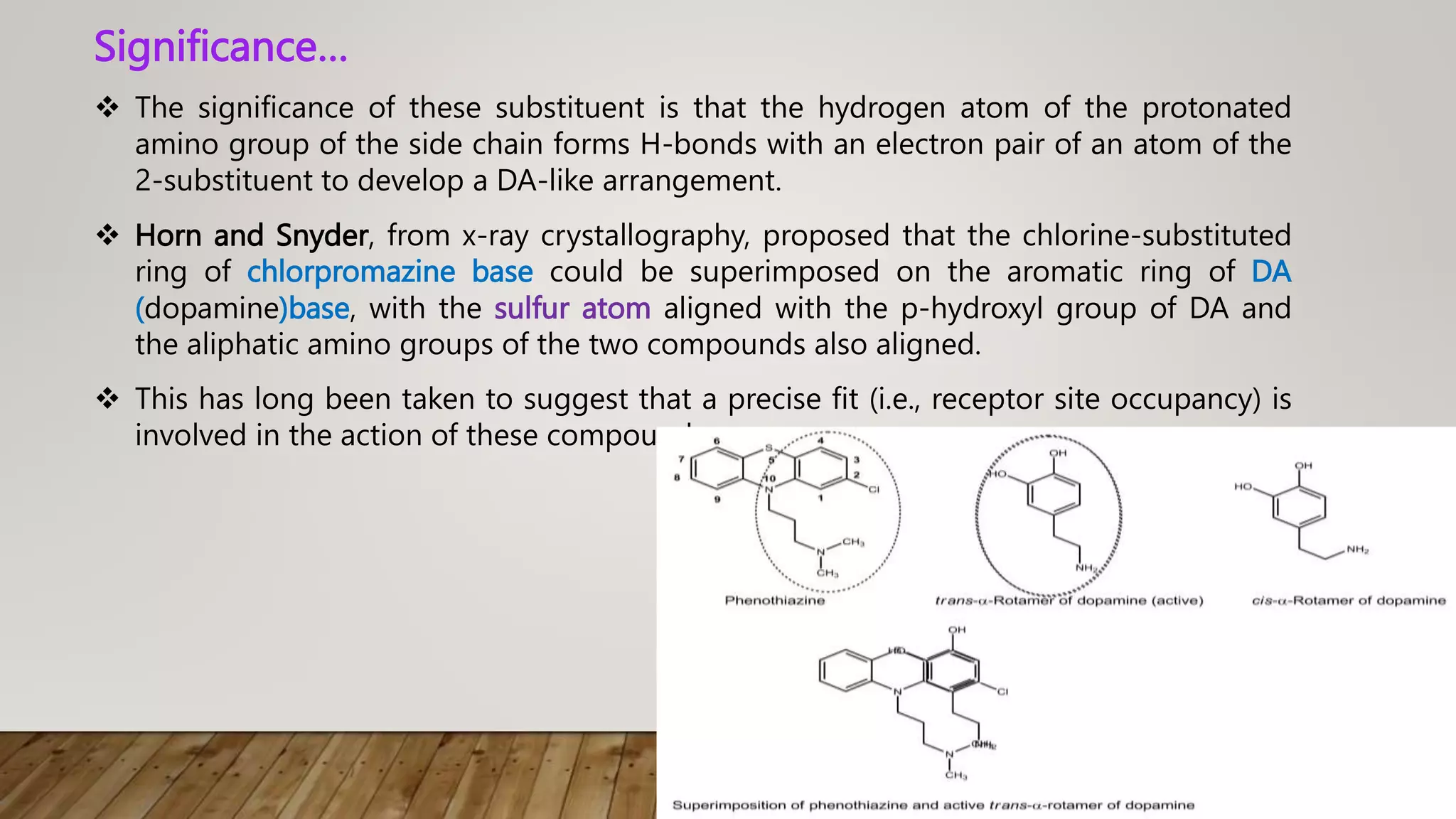
This document summarizes the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of phenothiazine drugs. It states that the best position for substitution is at the 2-position, as electron-withdrawing groups at this position increase antipsychotic activity. A three-carbon chain between positions 10 and the amino nitrogen is important for neuroleptic activity. The amino group must be tertiary and a terminal amino substituent is required at position N10. The significance is that the protonated amino group forms hydrogen bonds with the 2-substituent in a dopamine-like arrangement, allowing competitive antagonism of dopamine receptors to treat psychoses.