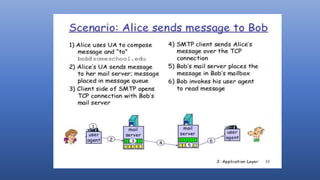
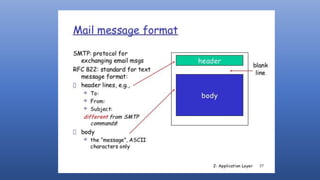
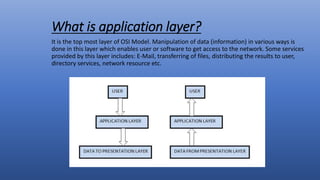
The application layer is the topmost layer of the OSI model. It provides services to software applications and users including email, file transfer, web access, and directory services. Domain Name Service (DNS) translates human-friendly domain names to IP addresses, allowing applications and users to access resources by name. Electronic mail systems use SMTP for message transfer between mail servers and access protocols like POP and IMAP for users to retrieve messages from their mailboxes on servers. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) underlies the World Wide Web, with clients making requests from and servers responding with web pages and other objects. While the application layer enables useful services, special client software or proxy servers may be required, and intensive processing is needed for applications







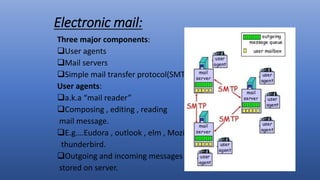

![Mail access protocols
• SMTP : delivery /storage to receiver servers
• Mail access protocol : Retrieval from server.
POP : post office protocol[RFC:1939]
• Authorization(agent to server)and downloaded.
IMAP : Internet Mail Access Protocol[RFC:1730]
• More feature(more complex)
• Manipulation of stored message on server
HTTP:Gmail,Hotmail,Yahoo!,mail etc.…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationlayerinnetworksystem-171002172719/85/Application-layer-in-network-system-12-320.jpg)