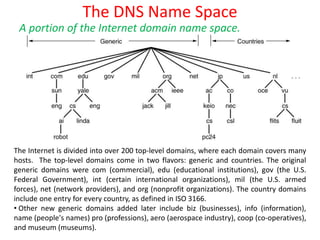
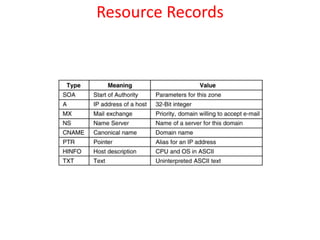
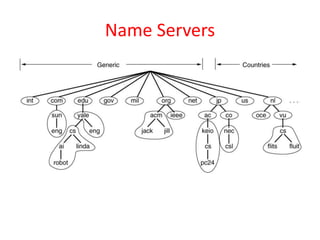
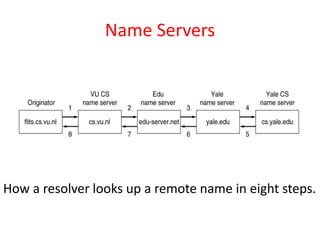
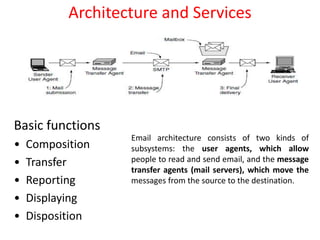
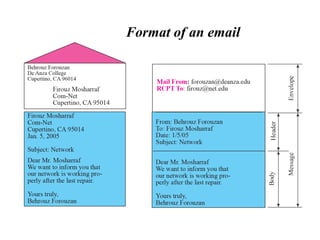
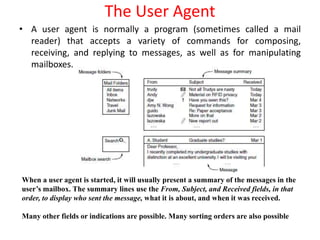
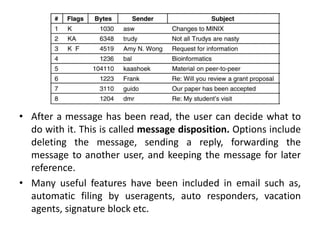
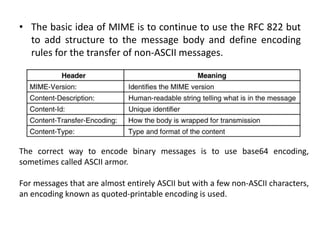
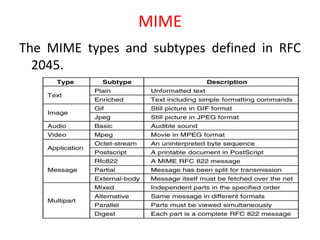
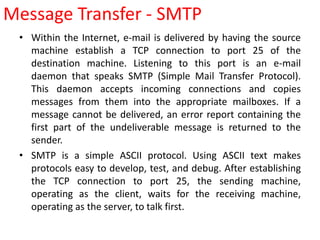
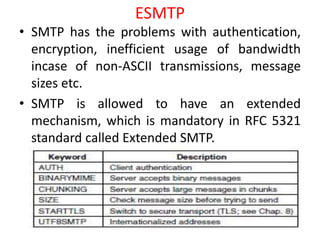
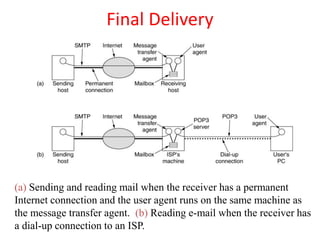
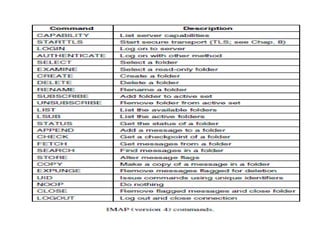
DNS maps domain names to IP addresses by using a distributed database and servers. It translates human-friendly domain names like www.example.com to numerical IP addresses like 192.0.2.1 that computers use to locate each other on the network. The DNS database contains resource records that associate domain names with IP addresses and other information. Name servers query the DNS database to resolve domain names and return IP addresses to applications and users.