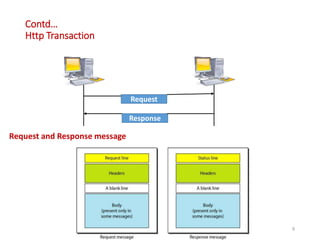
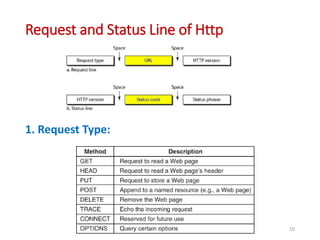
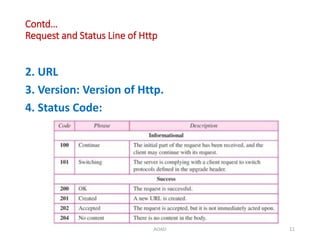
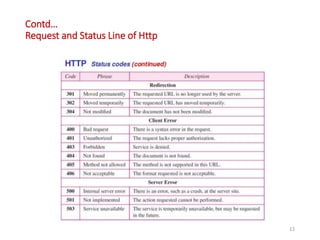
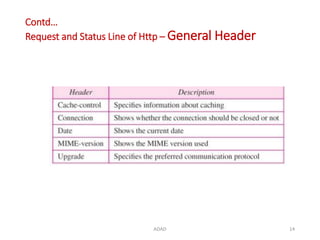
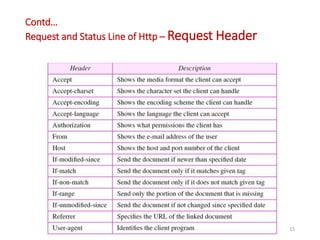
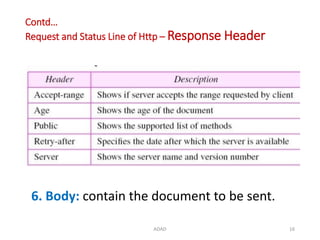
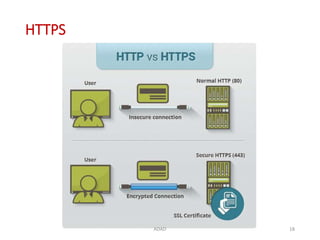
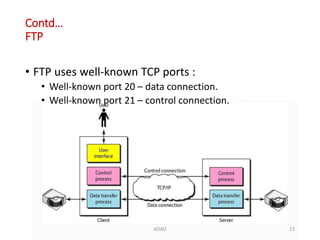
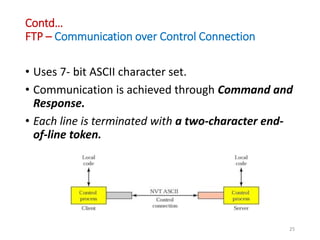
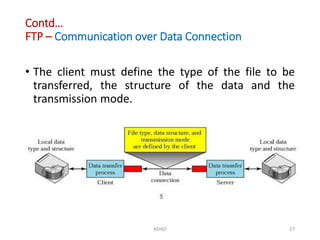
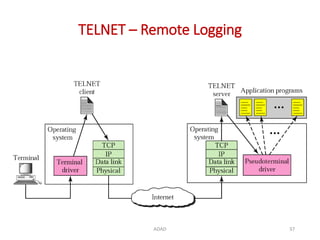
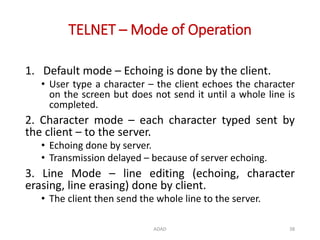
The document discusses various protocols in the application layer of computer networks, including DHCP, HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, TFTP, SFTP, and Telnet. It details their functions, how they operate, their significance in data transfer and security, and the roles of standard ports in communication. Each protocol is explained with a focus on their operational mechanics and use cases in network environments.