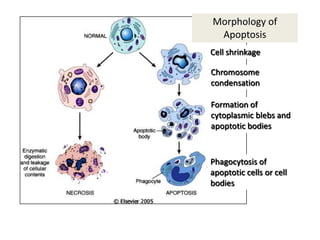
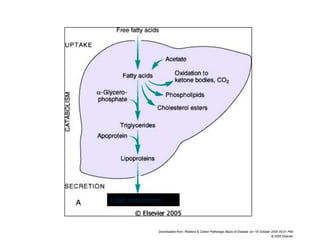
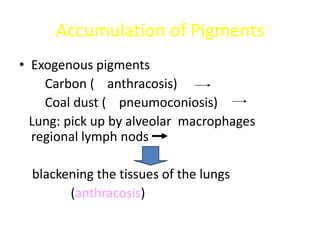
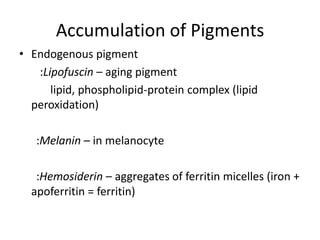
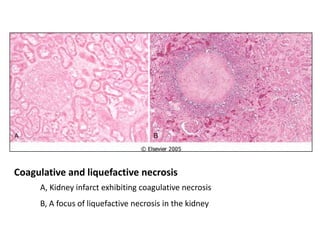
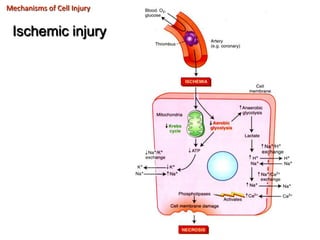
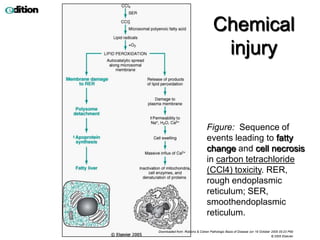
This document summarizes different types of cell death including apoptosis and necrosis. It describes the morphology and causes of apoptosis and discusses examples of apoptosis occurring in physiological and pathological situations. It also discusses various mechanisms of intracellular accumulations including lipids, proteins, glycogen, and pigments. Finally, it outlines the morphology and patterns of cell injury and necrosis.