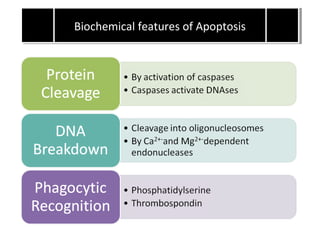
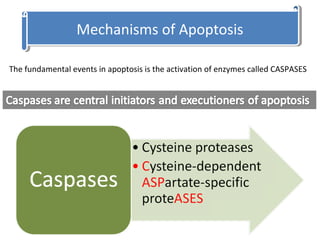
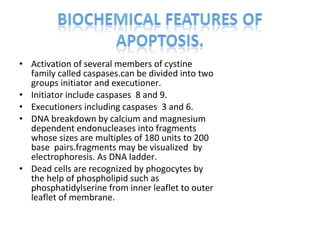
Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death that eliminates unwanted cells through activation of intracellular gene products. It occurs physiologically during embryogenesis and in adult tissues, and pathologically to remove cells damaged beyond repair. The key events of apoptosis include activation of caspase enzymes, DNA fragmentation, and recognition of dead cells by phagocytes. Apoptosis occurs via intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, both activating executioner caspases that break down nuclear and cellular components, leading to removal of dead cells without inflammation.