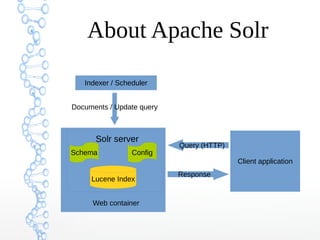
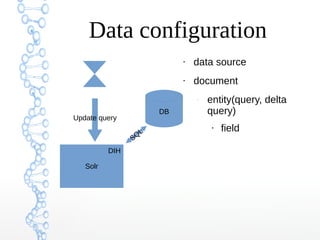
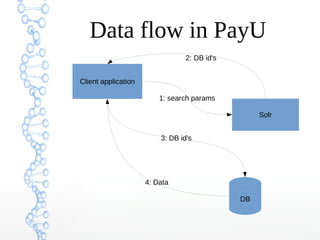
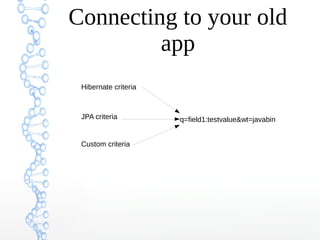
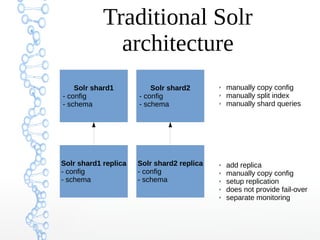
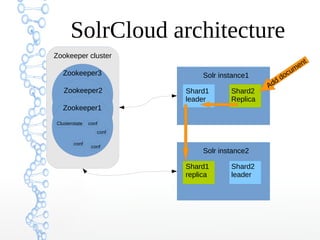
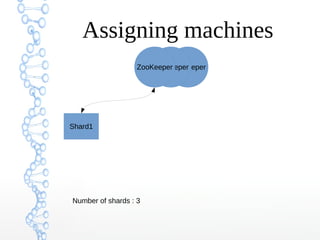
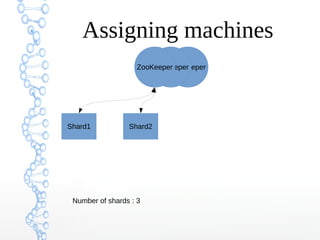
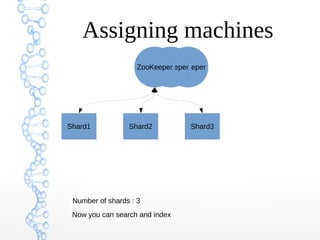
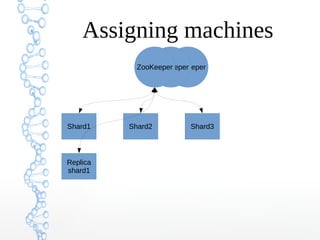
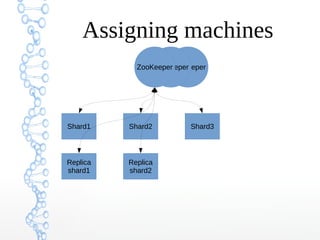
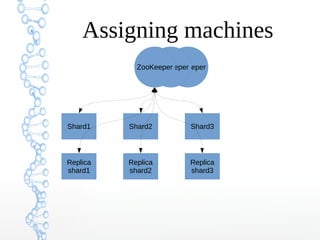
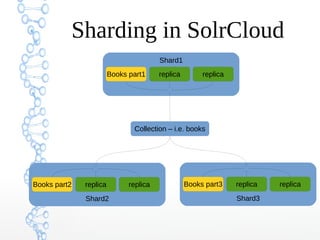
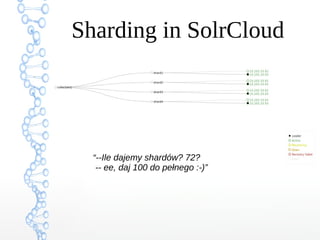
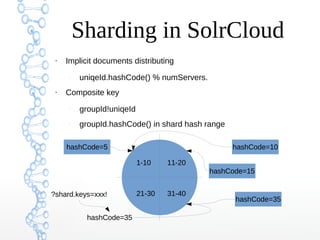
This document provides an overview of searching in the cloud using Apache Solr. It discusses how Solr allows for full-text search across distributed servers and datasets. Key features of SolrCloud include centralized configuration in Zookeeper, automatic failover, near-real-time indexing, leader election, and optimistic locking for durable writes across shards. The document also covers Solr schemas, indexing data from various sources, caching, and using SolrJ and SolrCloud.
















![SolrJ POJO
public class Item {
@Field
String id;
@Field("cat")
String[] categories;
@Field
List<String> features;
}
//...
Item item = new Item();
item.id = "one";
item.categories = new String[] { "aaa", "bbb", "ccc" };
server.addBean(item);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solrcloudver1-130923043259-phpapp01/85/Apache-SolrCloud-32-320.jpg)