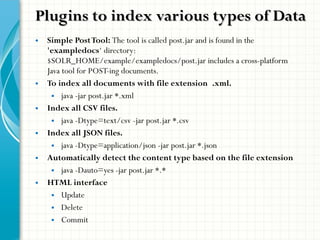
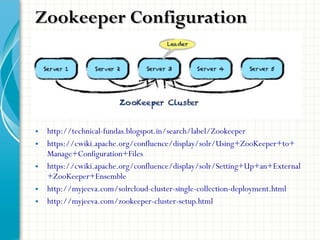
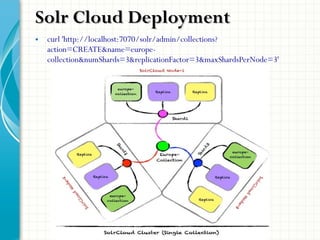
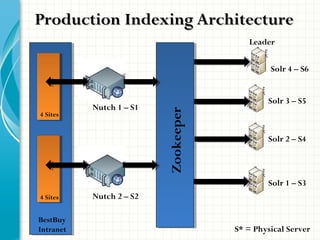
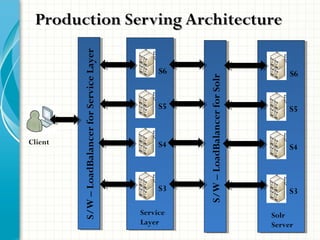
The document serves as a comprehensive introduction to Apache Solr, detailing its installation, configuration, key features, and functionalities. It covers support for various data types, indexing methods, search query capabilities, and integration with client APIs. Additionally, it discusses advanced topics such as SolrCloud deployment, SSL configuration, and production architecture.












![ Full text search
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?q=India
Search only within a field
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?q=category:newsAND “Modi in
Australia”
Control which fields are displayed in result
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?q=video&fl=id,category
Provide ranges to fields
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?q=price:[0TO400]&fl=id,name,price
Faceting information
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?
q=news&fl=id,description&facet=true&facet.field=category
More like this (MLT)
• http://localhost:8983/solr/select?
q=India&mlt=true&mlt.fl=headline&mlt.mindf=1&mlt.mintf=1&fl=id,sco
re&rows=100
• More information on how this works and the options available can be found at
Search QueriesSearch Queries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solrtrainingpersonal-170502172213/85/Introduction-to-Solr-15-320.jpg)