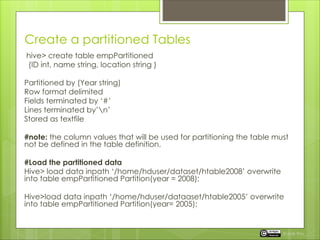
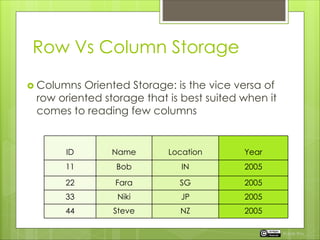
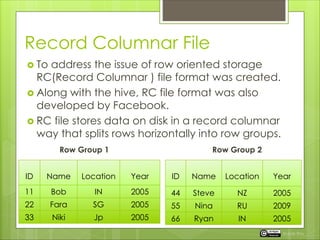
The document discusses the importance of table partitioning in Hive to enhance query efficiency by splitting data based on specific conditions, such as year. It provides examples of creating and loading partitioned tables, executing HQL commands, and explores different storage formats like text, sequence files, and RC files. Additionally, it contrasts row-oriented and columnar storage, highlighting the benefits of record columnar file format developed by Facebook.