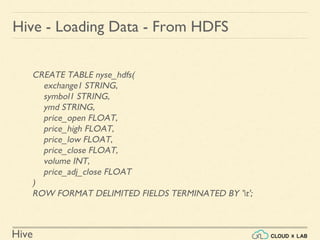
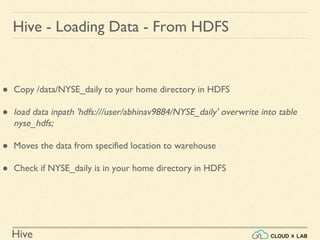
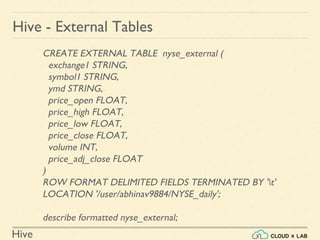
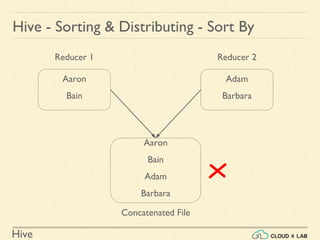
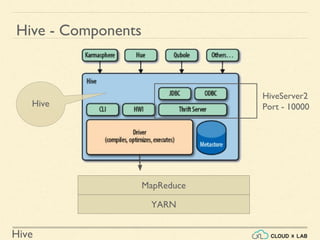
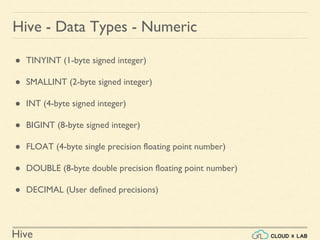
The document provides an introduction to Hive, a data warehouse infrastructure tool that processes structured data in Hadoop with SQL-like queries, addressing developer challenges in writing MapReduce logic. It discusses Hive components, limitations, data types, and various commands for data management, including creating and managing tables and partitions. Additionally, it covers the connection to visualization tools like Tableau and includes practical examples, commands, and insights on optimizing data processing using Hive.






![Hive
Hive - Data Types - Complex
arrays: ARRAY<data_type>
maps: MAP<primitive_type, data_type>
structs: STRUCT<col_name : data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...>
union: UNIONTYPE<data_type, data_type, ...> ( Hive version > 0.7.0 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h9-180514111837/85/Introduction-to-Apache-Hive-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-10-320.jpg)

![Hive
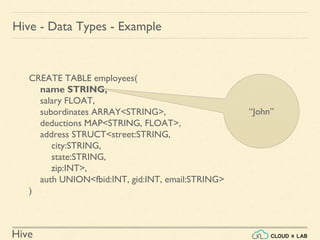
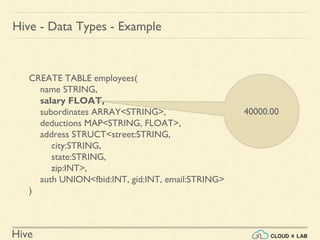
Hive - Data Types - Example
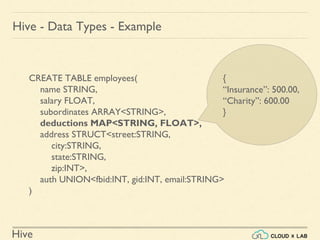
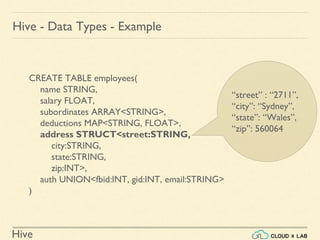
CREATE TABLE employees(
name STRING,
salary FLOAT,
subordinates ARRAY<STRING>,
deductions MAP<STRING, FLOAT>,
address STRUCT<street:STRING,
city:STRING,
state:STRING,
zip:INT>,
auth UNION<fbid:INT, gid:INT, email:STRING>
)
[“Michael”, “Rumi”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h9-180514111837/85/Introduction-to-Apache-Hive-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-14-320.jpg)