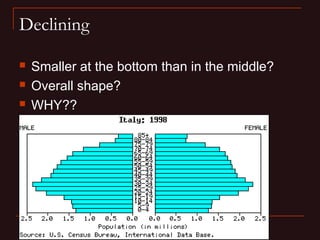
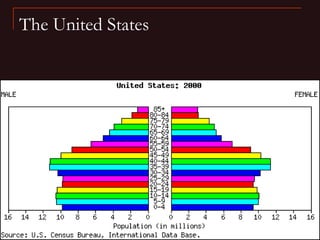
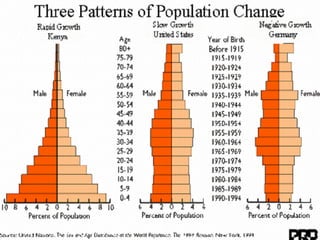
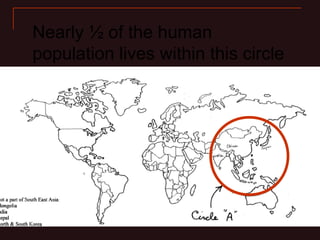
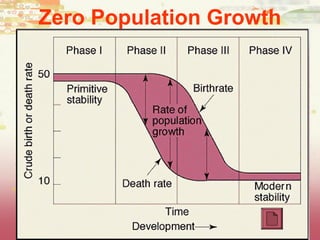
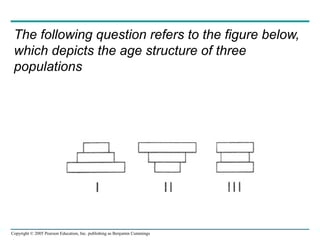
This document provides learning objectives and content about populations and population growth. It discusses key concepts such as:
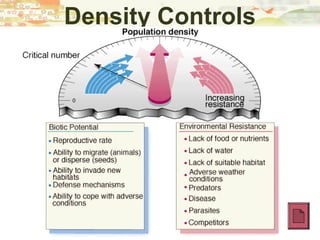
- Biomes and limiting factors that influence population distribution and density. Examples of density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors are given.
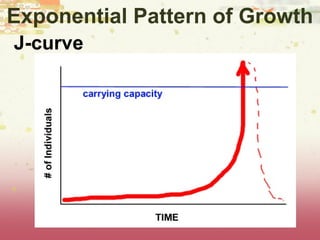
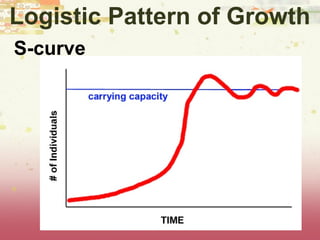
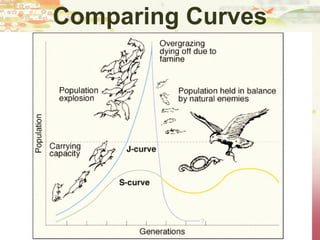
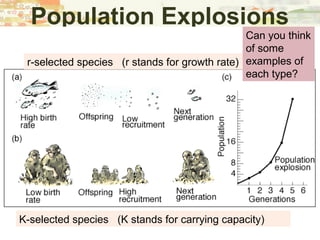
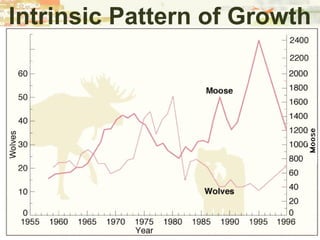
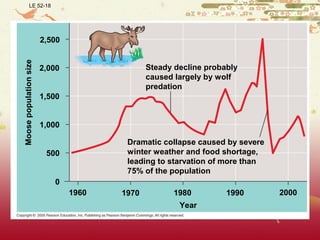
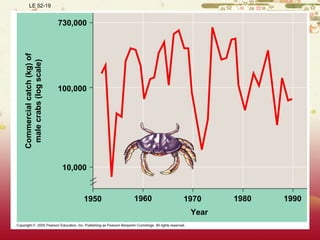
- Patterns of population growth including exponential, logistic, and intrinsic growth curves. Population explosions in r-selected and K-selected species are compared.
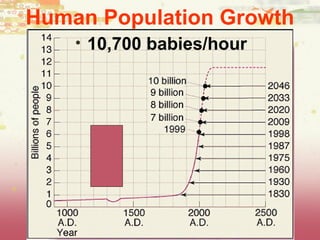
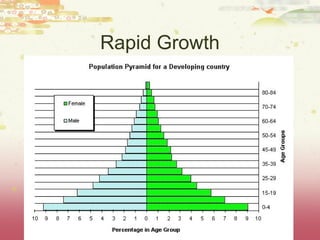
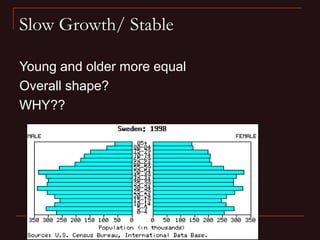
- Factors influencing human population growth rates and methods of controlling rapid growth such as family planning programs and economic development.
- The concept of carrying capacity and its relevance to predicting ultimate human population size.