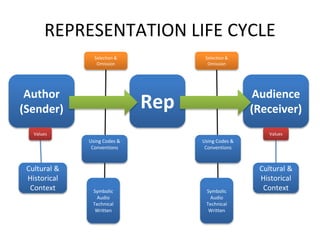
This document provides an overview of representation and how meaning is constructed through the process of representation. It discusses how representations are constructed by authors and interpreted by audiences based on codes, conventions, and sociocultural contexts. Representations can depict individuals, groups, ideas, and more. Meaning is created not just by what is depicted but also what is omitted. Audiences interpret representations based on their own knowledge and experience.