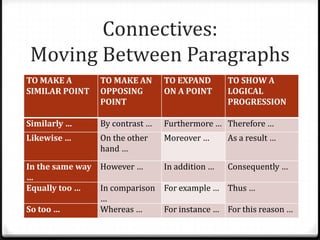
The document provides guidance on how to analyze persuasive texts, including how to identify the main contention, arguments, and persuasive techniques used by the author. It recommends asking questions about what is being said, how it is said, and why it is persuasive. The response should include an introduction stating the text, author, contention, and tone. Body paragraphs should follow the TEEL structure and discuss how techniques shape the reader's view. Connectives should link paragraphs, and the conclusion should summarize the contention and persuasive strategies.





![SENTENCE STARTERS: INTRO
0 The writer asserts that …
Contending that … , the writer then …
The author quickly establishes the main contention that …
0 In a … tone, the writer declares that …
0 The point of view presented by [name of writer] is …
0 Adopting a controversial position, the writer argues that …
0 The writer argues that … which influences the reader to …
0 The use of … positions the reader to share the writer’s
viewpoint that …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/languageanalysisessaywriting-121010220248-phpapp01/85/Language-Analysis-Essay-Writing-6-320.jpg)