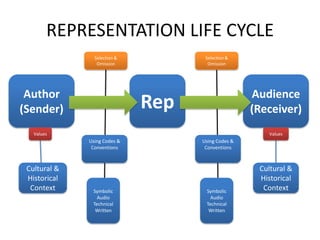
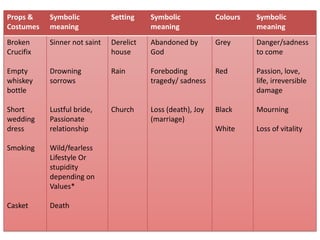
Realism in media representations is complex with different meanings and interpretations. Whether a representation is considered realistic often depends on the values, experiences, and perspectives of both the creator and the audience. The same representation could appear realistic to some and not to others. Realism is contextual and subjective.