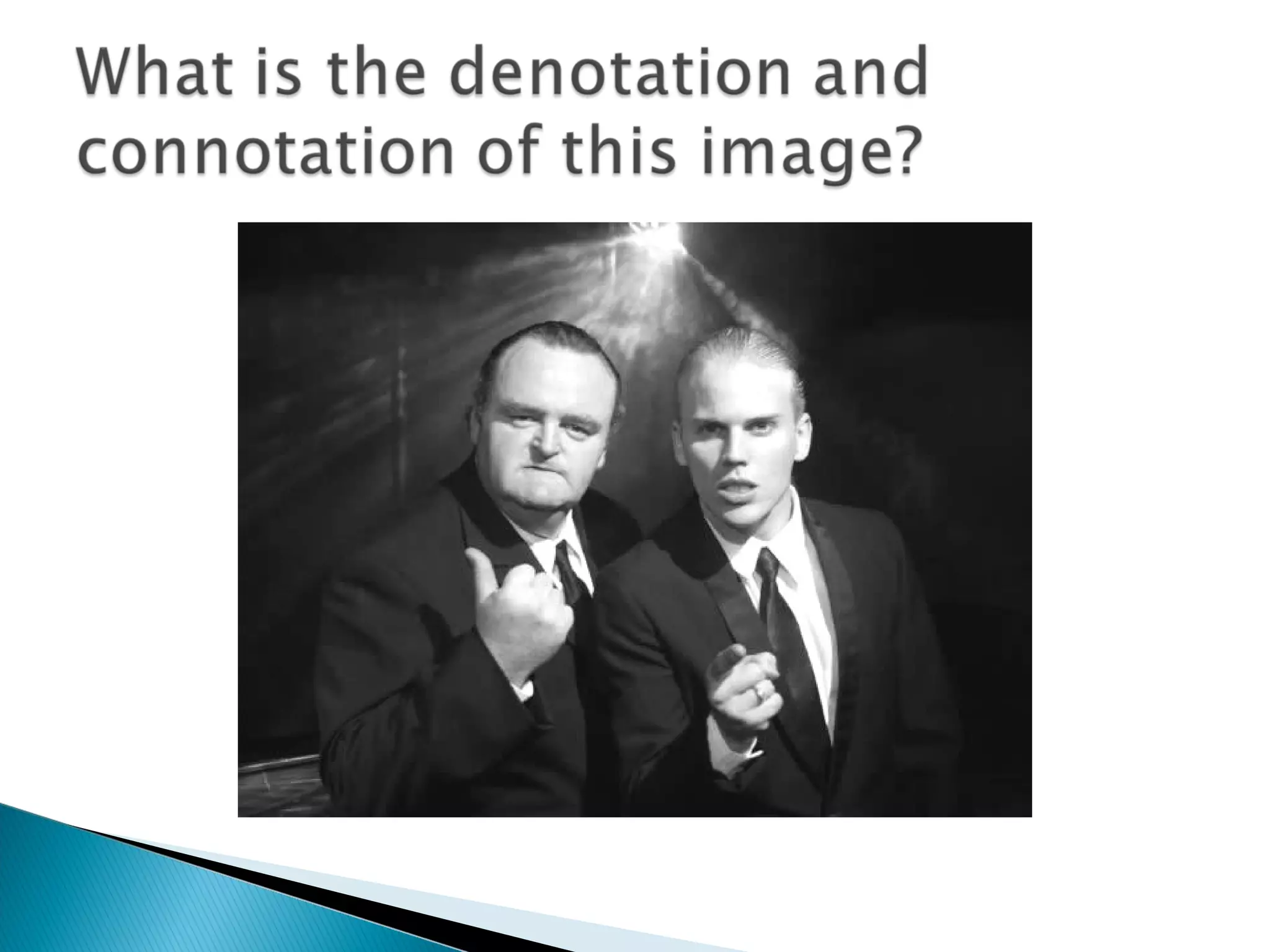
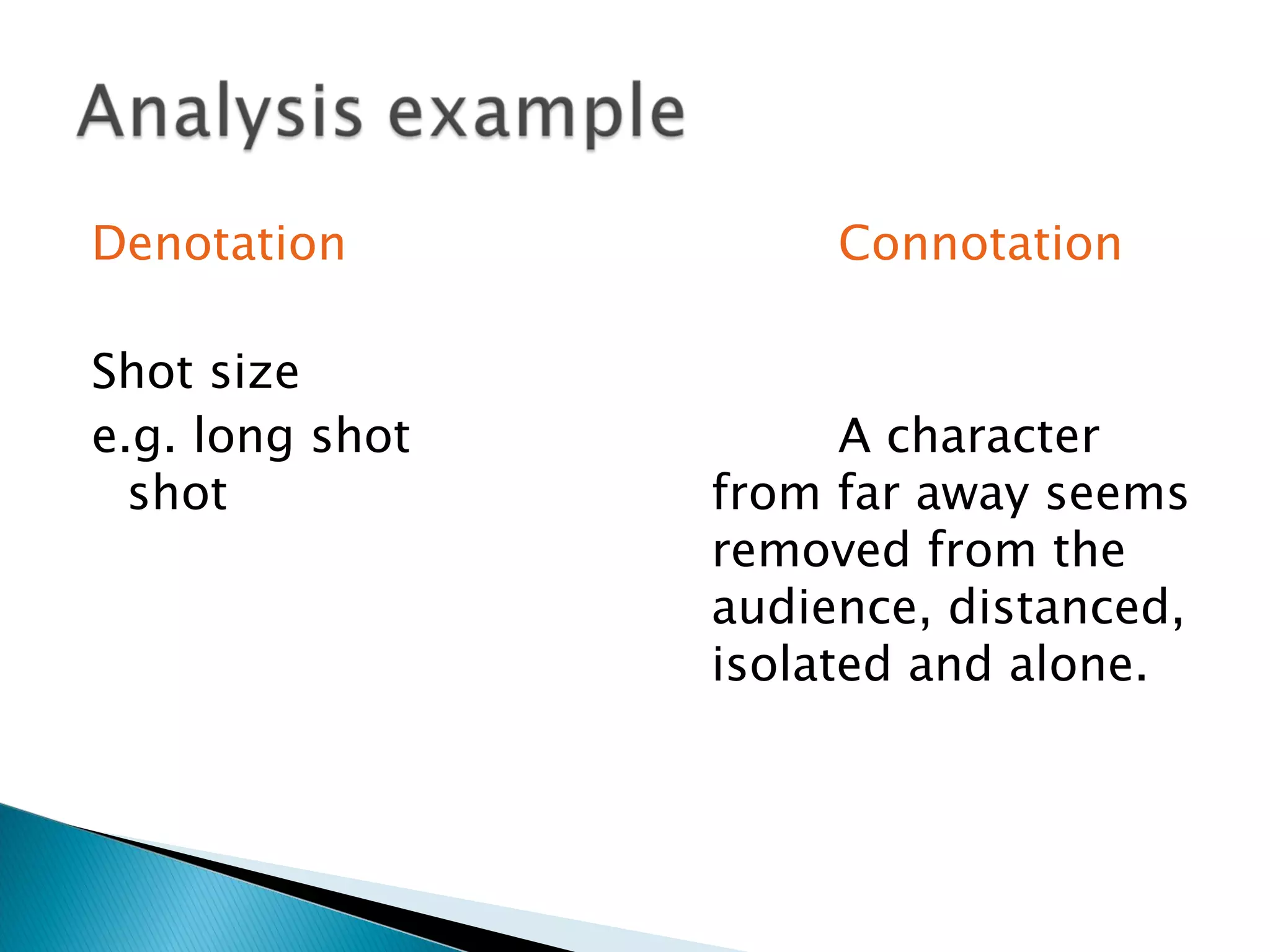
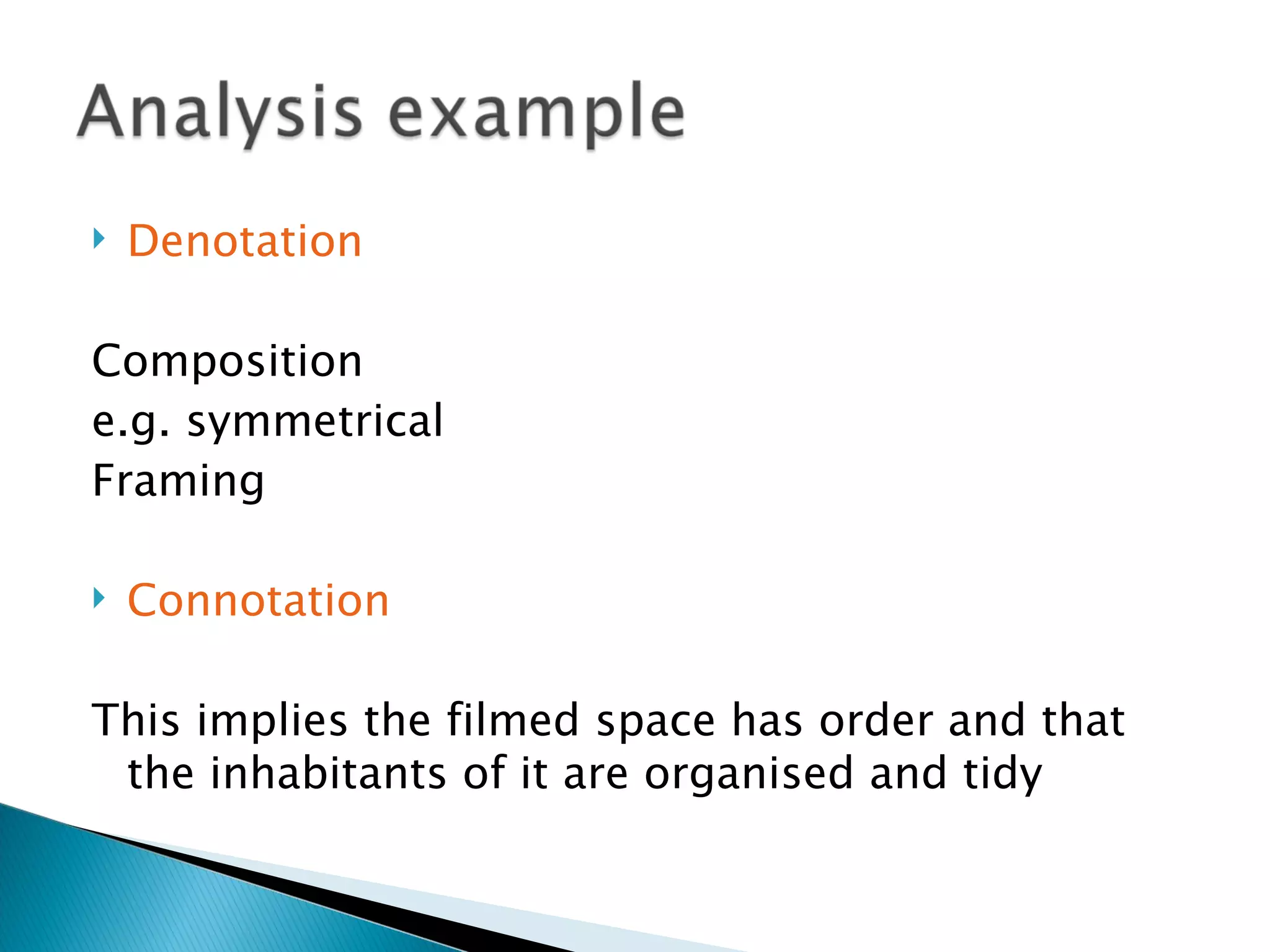
The document discusses media language and how meaning is constructed in media texts. It explains that media language refers to how texts are constructed to create meaning for audiences. All media is constructed with particular audiences and messages in mind. Deconstructing media involves identifying the different elements and contextual factors that give a text meaning. Semiotics explores how meaning is constructed through signs and codes, and how audiences interpret denotation and connotation.