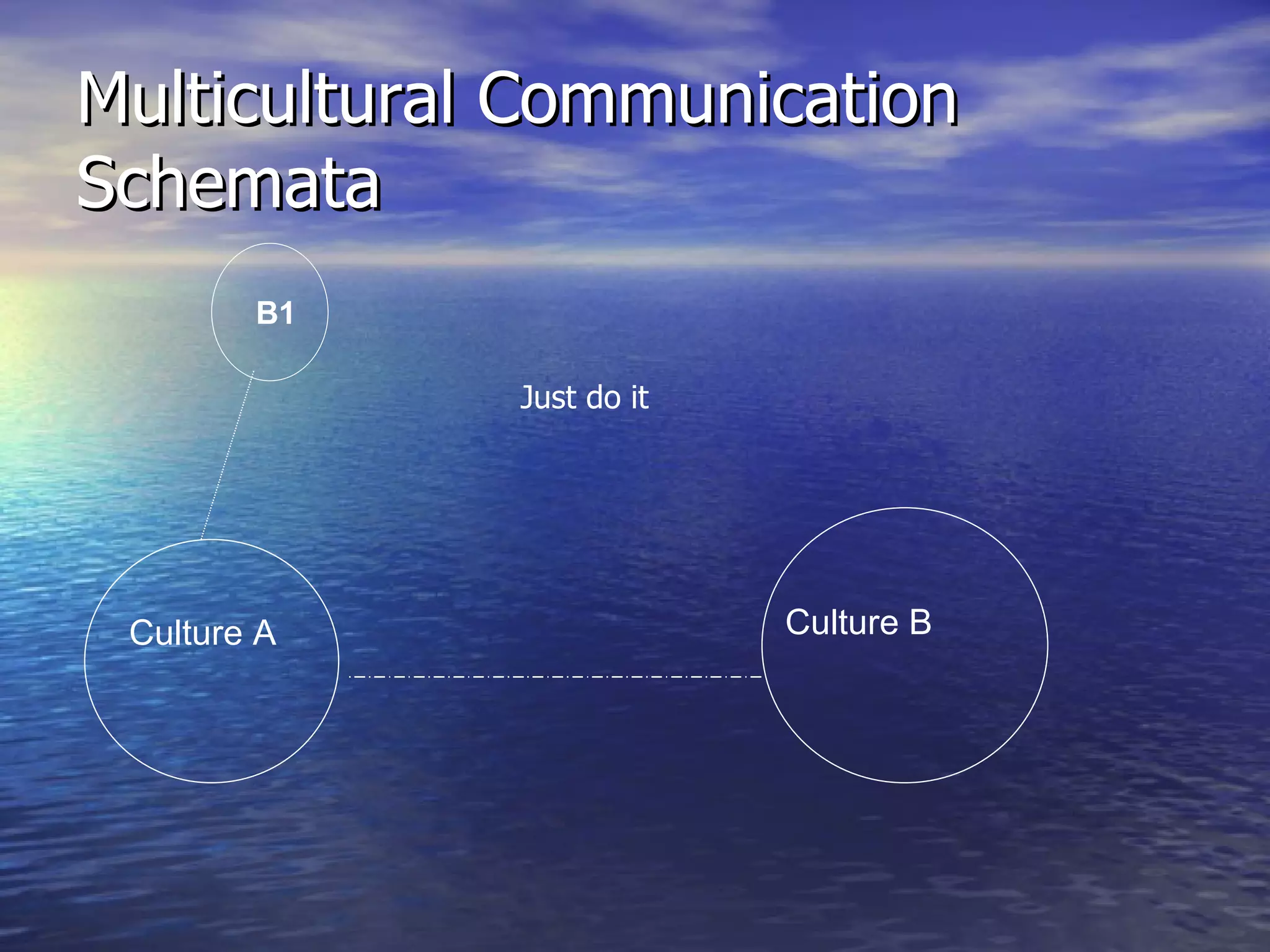
1. Culture plays an important role in how people communicate and behave.
2. When communicating across cultures, there can be misunderstandings due to differences in cultural norms, values, and ways of assigning meaning.
3. To communicate effectively across cultures, it is important to be aware of one's own cultural biases and mental representations, as well as cultural differences in communication styles like high versus low context.