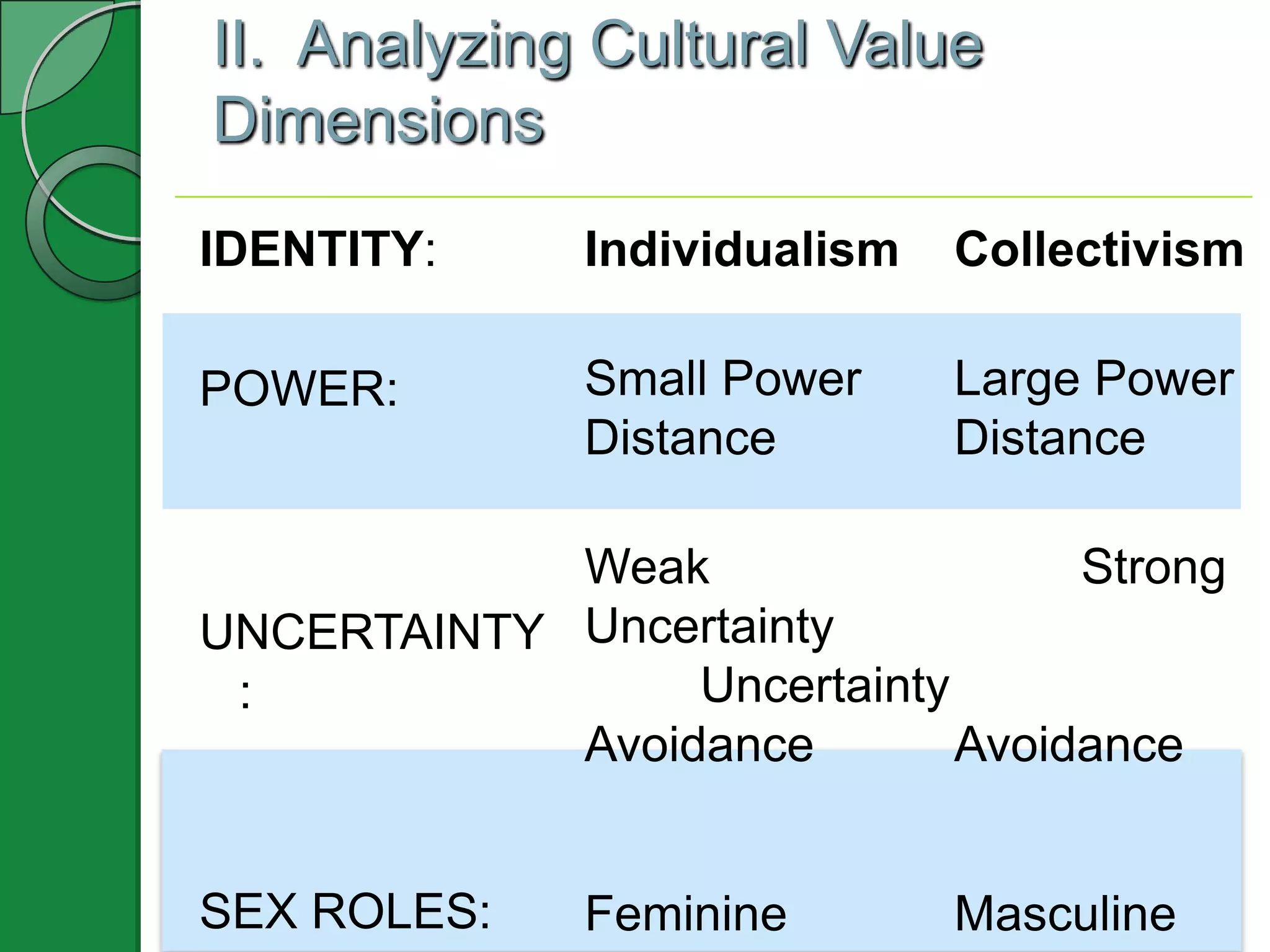
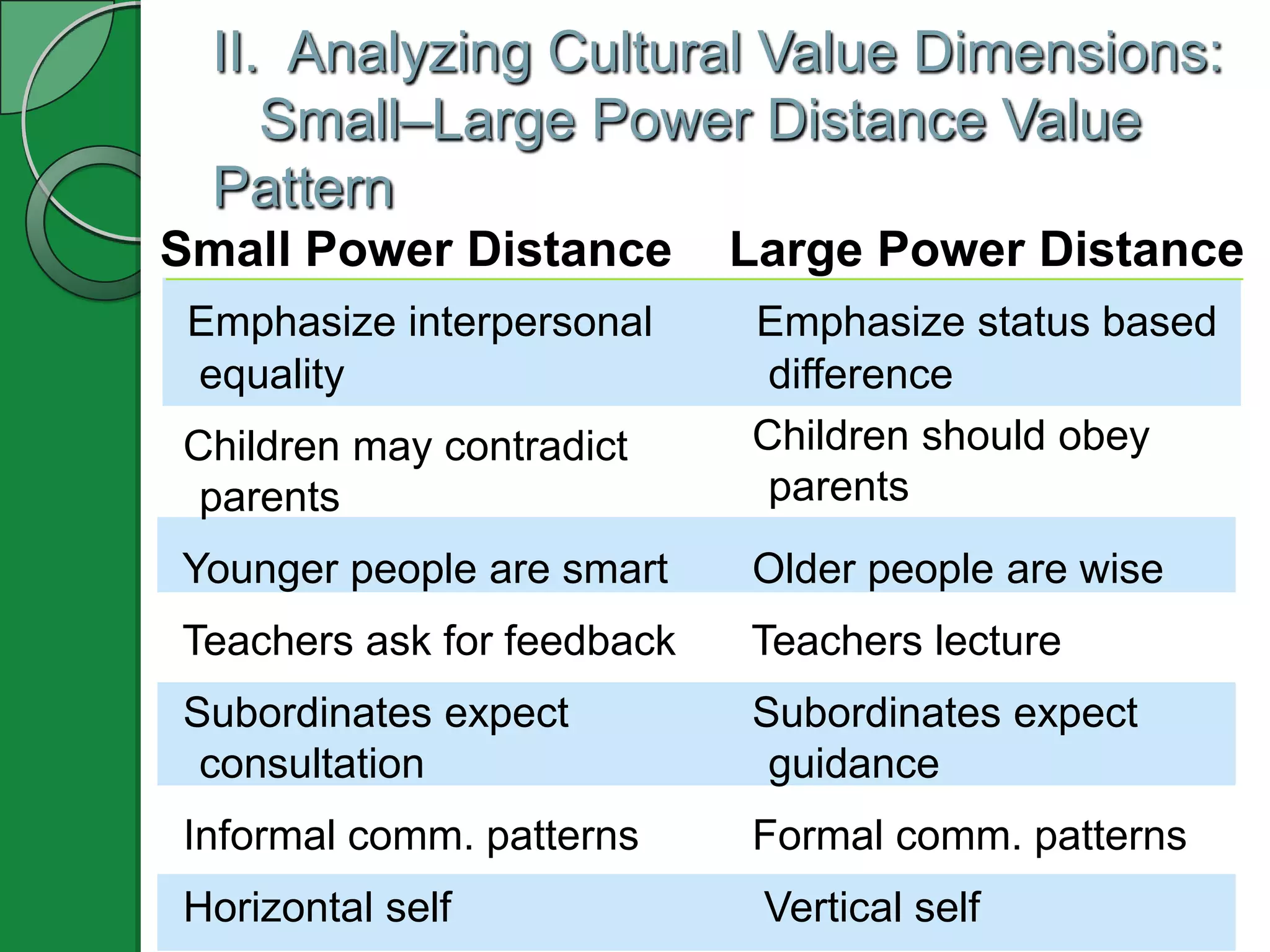
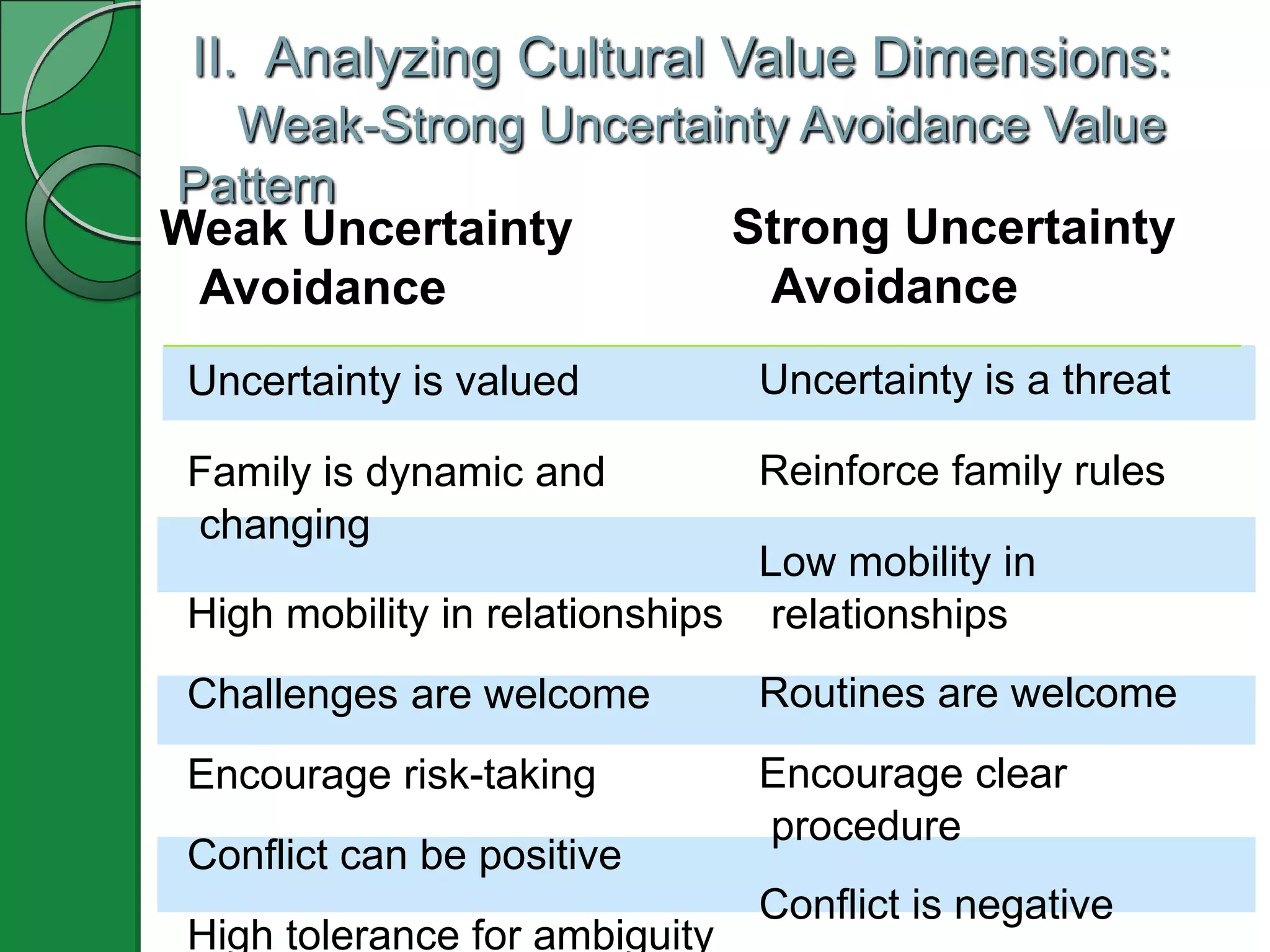
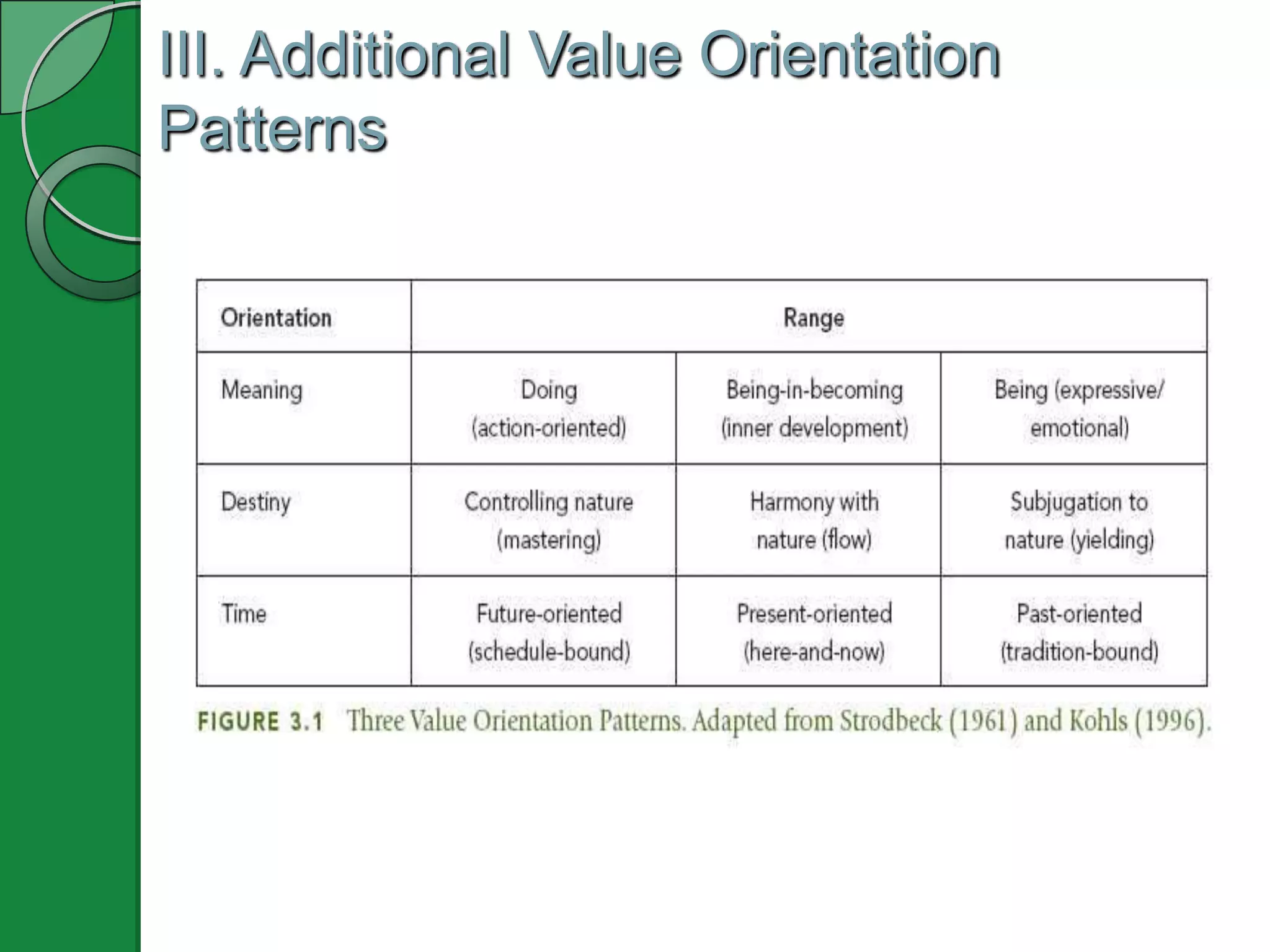
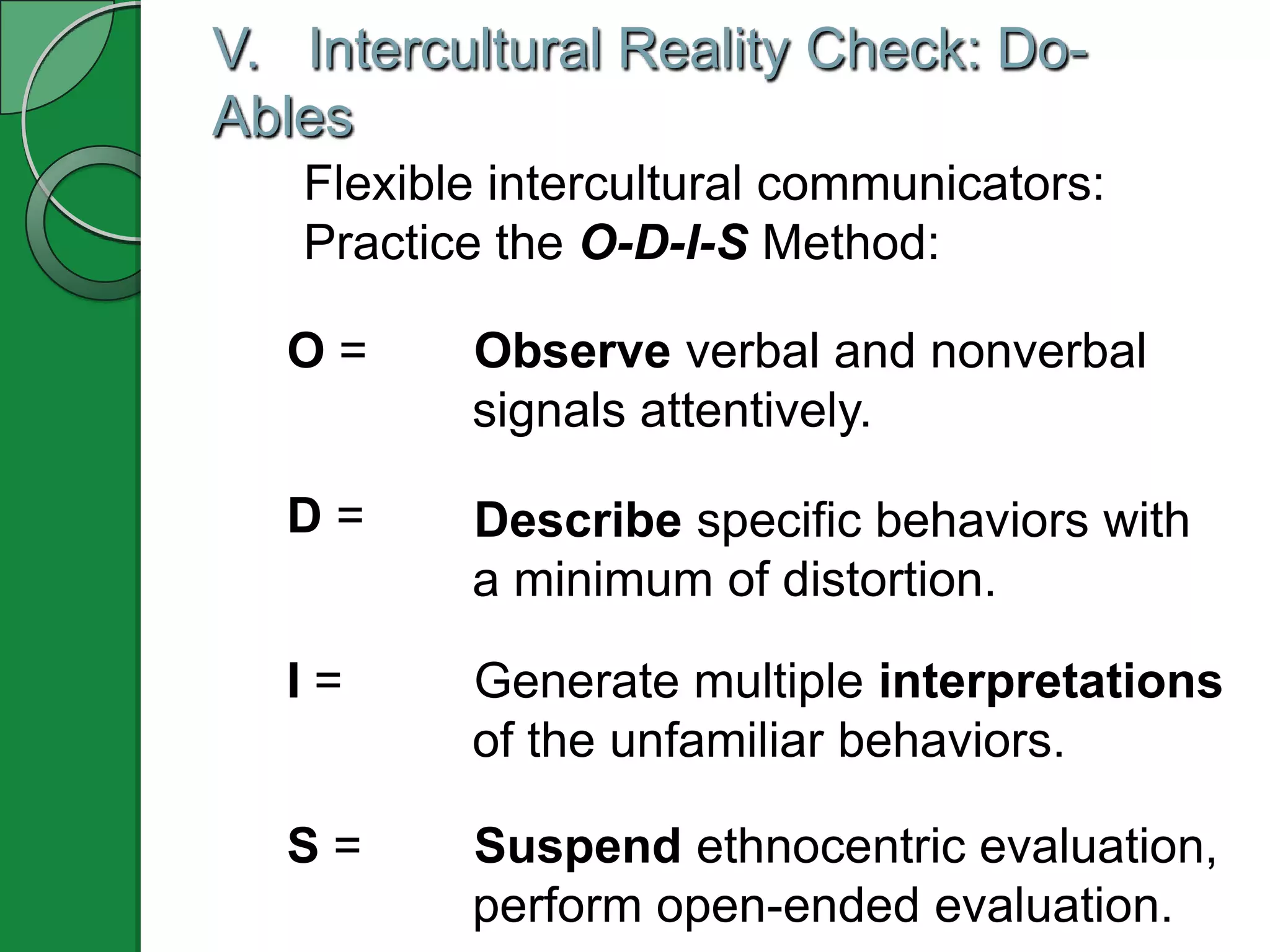
This document appears to be a PowerPoint presentation about cultural values and intercultural communication. The presentation covers the following topics in 3-5 slides each: functions of cultural values, analyzing cultural value dimensions like individualism vs collectivism and masculinity vs femininity, additional value orientations, individual socialization development, and an intercultural reality check method called O-D-I-S. It includes examples, media clips, a self-assessment inventory, and an values exploration exercise to apply the concepts.