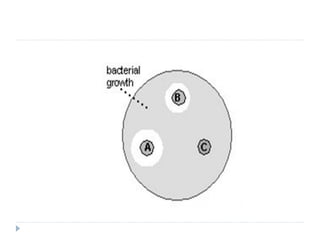
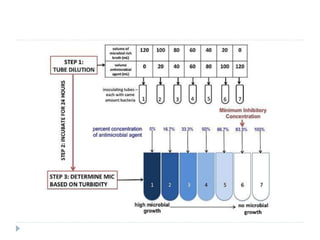
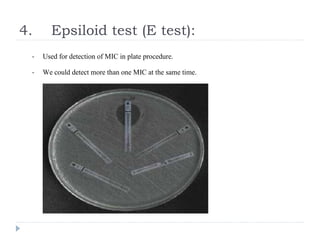
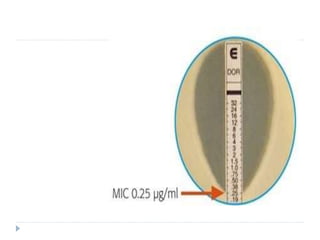
The document discusses various methods for antibiotic sensitivity testing, including Kirby Bauer disk diffusion, comparative methods, dilution methods, and Epsiloid tests. The Kirby Bauer method involves placing antibiotic disks on an inoculated agar plate and measuring inhibition zones. The comparative method compares inhibition zones to a control, classifying sensitivity as sensitive, intermediate, or resistant. Dilution methods detect the minimum inhibitory concentration by making serial dilutions of antibiotics and observing bacterial growth. Epsiloid tests also detect minimum inhibitory concentrations using plastic strips containing exponential gradients of antibiotics.