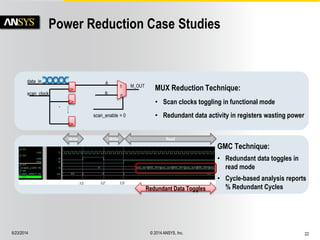
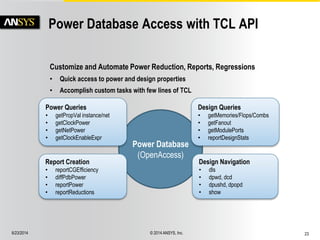
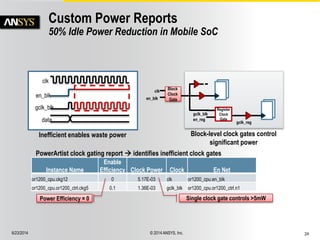
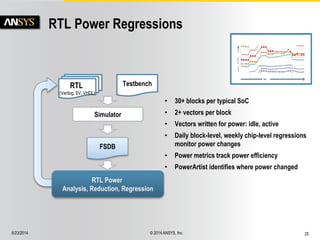
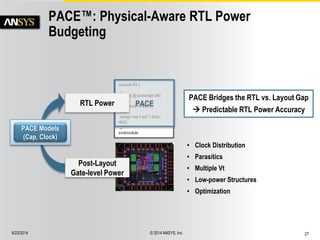
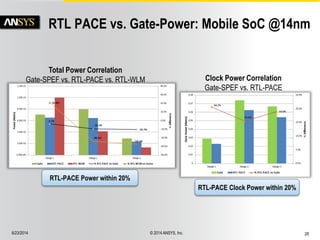
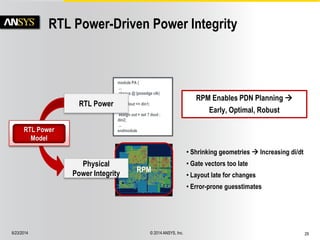
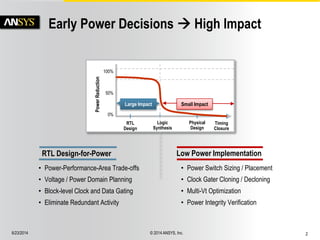
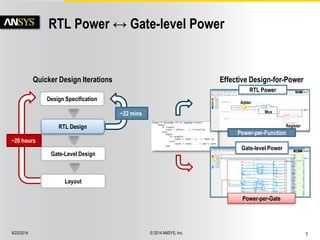
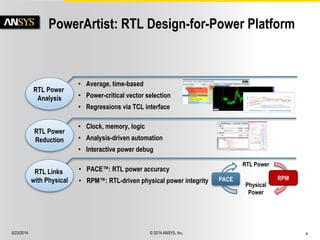
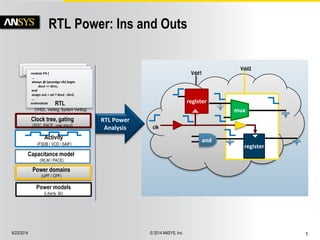
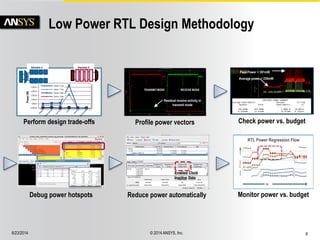
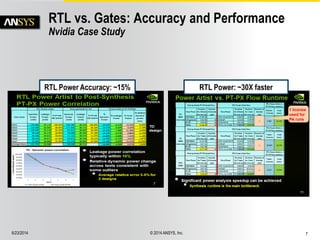
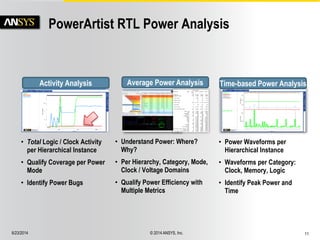
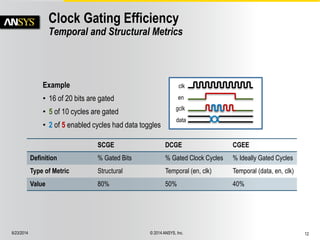
The document discusses the PowerArtist RTL design-for-power platform, which aids in low power implementation through various techniques such as clock gating, power optimization, and analysis-driven automation. It highlights case studies demonstrating significant power savings and improved design efficiency through RTL power regression and integration with physical design. The document emphasizes the importance of early power decisions and offers methodologies for identifying and reducing power consumption effectively.





![6/23/2014 © 2014 ANSYS, Inc. 15
PowerArtist RTL Power Reduction
Original RTL Low-Power RTL
openPDB powerartist.pdb
set RPT [open $output_file "w"]
set ungated_registers [getRegisters -cg none]
foreach I $ungated_registers {
set dyn_power [getPropVal $i Dynamic_Power "inst"]
set bit_width [getInstWidth $reg]
set file [getPropVal $iFile_Name "inst"]
set line_num [getPropVal $i Line_Number "inst"]
}
1. Interactive Power
Debug
2. Automated Power
Reduction
3. Customizable Power
Reports
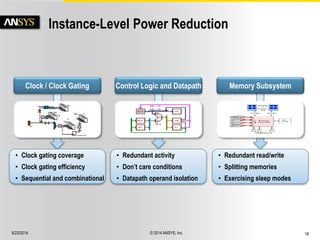
• Block-level Power “Bugs”
• Large Power Savings
• Instance-level Power Reduction
• 15 Analysis-driven Techniques
• TCL Queries to OADB
• Automation Beyond
PowerArtist Reports](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansyspowerartistrtldfpoverview-141016123716-conversion-gate01/85/PowerArtist-RTL-Design-for-Power-Platform-14-320.jpg)
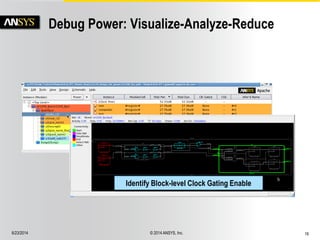
![6/23/2014 © 2014 ANSYS, Inc. 17
Block-Level Power Reduction
Clock Active, Data Inactive
Clock Inactive, Data Active
Block-level
Clock Gating
Block-level
Data Gating
Block-level Activity Analysis:
Clock and Data Ports
1.1 Clock Pins
-------------------------------------------------------
Redundant Total Pin Mode Instance
Cycles Cycles Name Name Name
-------------------------------------------------------
200 201 CLKA read top.core1.t1.dpmem.m1
-------------------------------------------------------
1.2 Input and Redundant Pins
-------------------------------------------------------
Redundant Total Pin Mode Instance
Toggles Toggles Name Name Name
-------------------------------------------------------
1 1 AB[8] read top.core1.t1.dpmem.m1
-------------------------------------------------------
Wasted Activity
per Mode
Clock Activity per
Hierarchy
Constant high activity
Missed clock gating?
Redundant activity
in read mode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansyspowerartistrtldfpoverview-141016123716-conversion-gate01/85/PowerArtist-RTL-Design-for-Power-Platform-16-320.jpg)