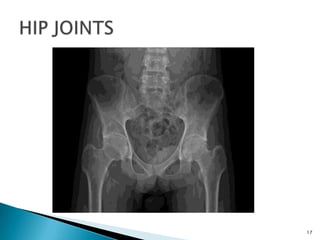
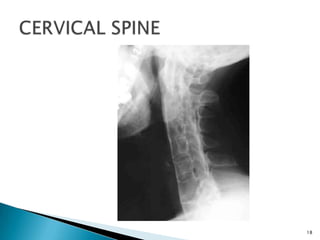
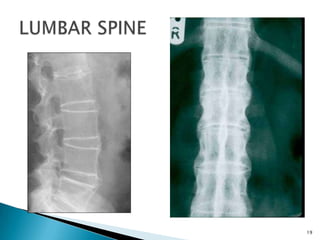
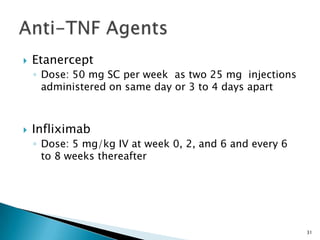
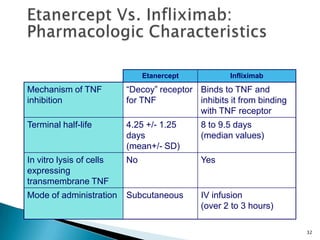
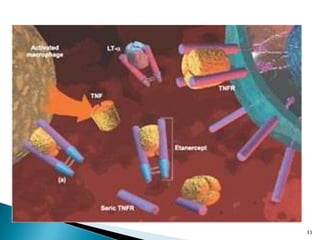
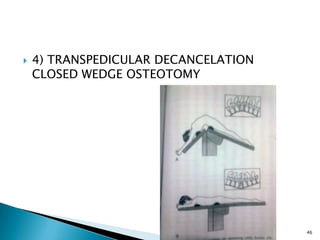
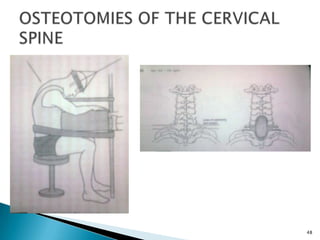
The document discusses the investigation and treatment modalities for ankylosing spondylitis. It states that each patient should receive an individualized evaluation and treatment plan to provide the best outcome. Treatment involves a team approach including orthopedists, rheumatologists, physiotherapists and others. Drug therapy aims to relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, and produce immunosuppression. Physical therapy focuses on maintaining joint movement and strengthening muscles. Surgery may be considered for severe deformities or other complications.