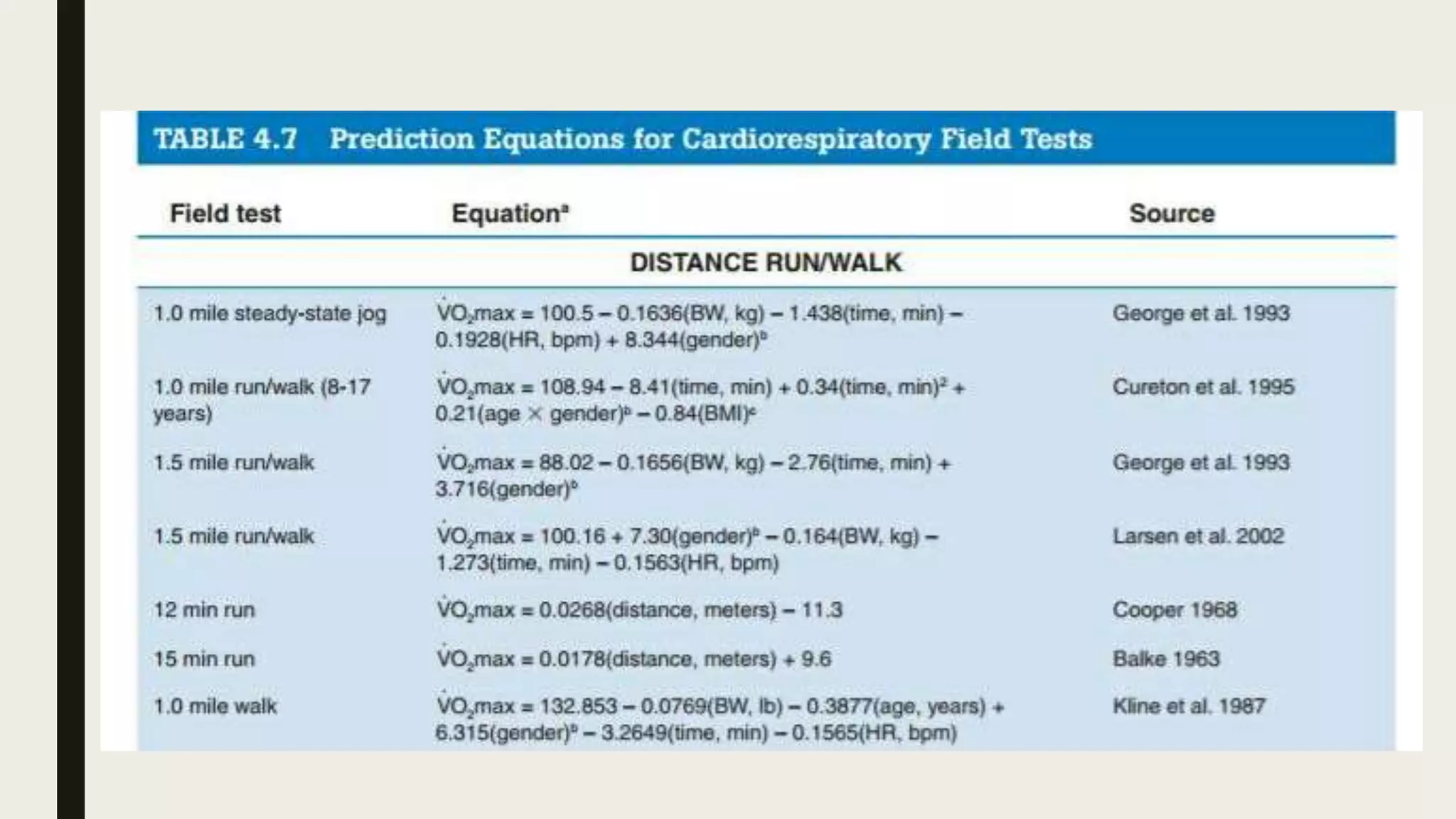
This document discusses various field tests that can be used to assess cardiorespiratory fitness without expensive equipment. It describes distance run tests like the 1-mile or 12-minute run that evaluate aerobic capacity. Walking tests and step tests are also covered that involve measuring heart rate before and after the activity. The document provides details on administering selected tests and measuring pulse rates accurately.