The document provides information on embedded operating systems and compares two examples - Android OS and Symbian OS. It discusses key aspects of each OS like architecture, components, features, strengths, and weaknesses. Some key points:
- Embedded operating systems are designed for compactness, efficiency, and reliability for embedded systems. Examples given are Android and Symbian.
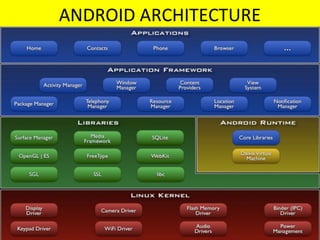
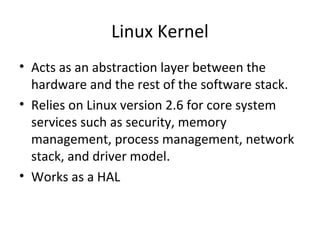
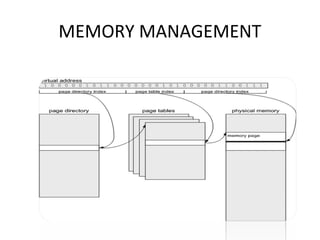
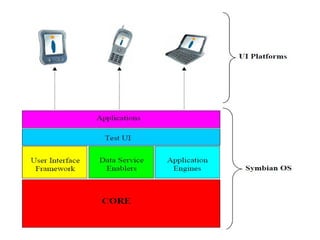
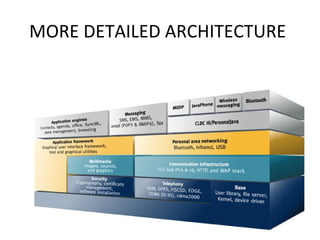
- Android uses a layered architecture including applications, framework, Android runtime, and Linux kernel. Symbian uses a microkernel architecture with emphasis on compatibility and large UI code.
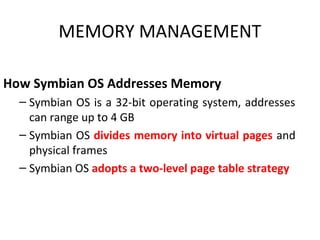
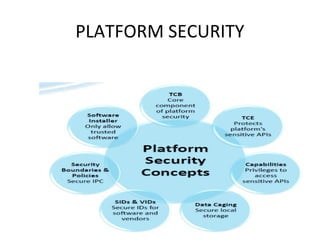
- Both discuss components like memory management, security features, and advantages/disadvantages compared to each other. Android supports more applications while Symbian needs feature updates.