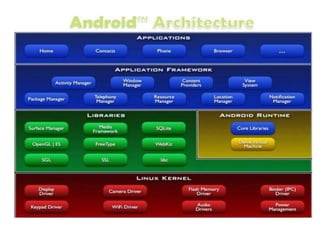
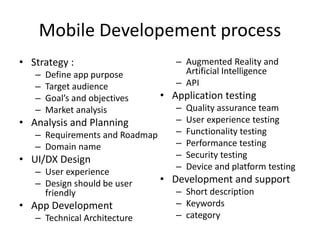
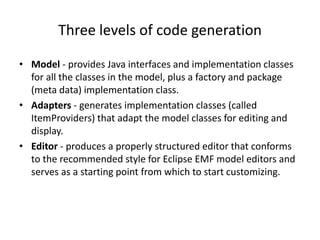
This document provides an overview of the Android framework, including its core components and architecture. It discusses the Linux kernel, libraries, Android runtime, application framework, and applications that make up the Android software stack. It also describes the Android SDK, Eclipse IDE, and mobile development process used for building Android applications.