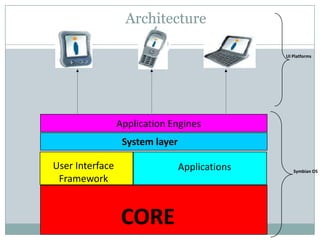
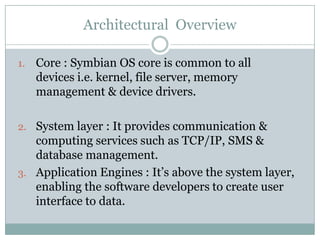
The document provides an overview of Symbian OS, including its origins as an operating system designed for mobile phones. It discusses the need for Symbian OS, its evolution through different versions, its architectural layers including the core, system layer, application engines and user interface, and software development tools and programming languages like C++ and Java. The advantages of Symbian OS are its open platform nature, power management features, and multitasking abilities. Disadvantages include that it is not available for PCs.