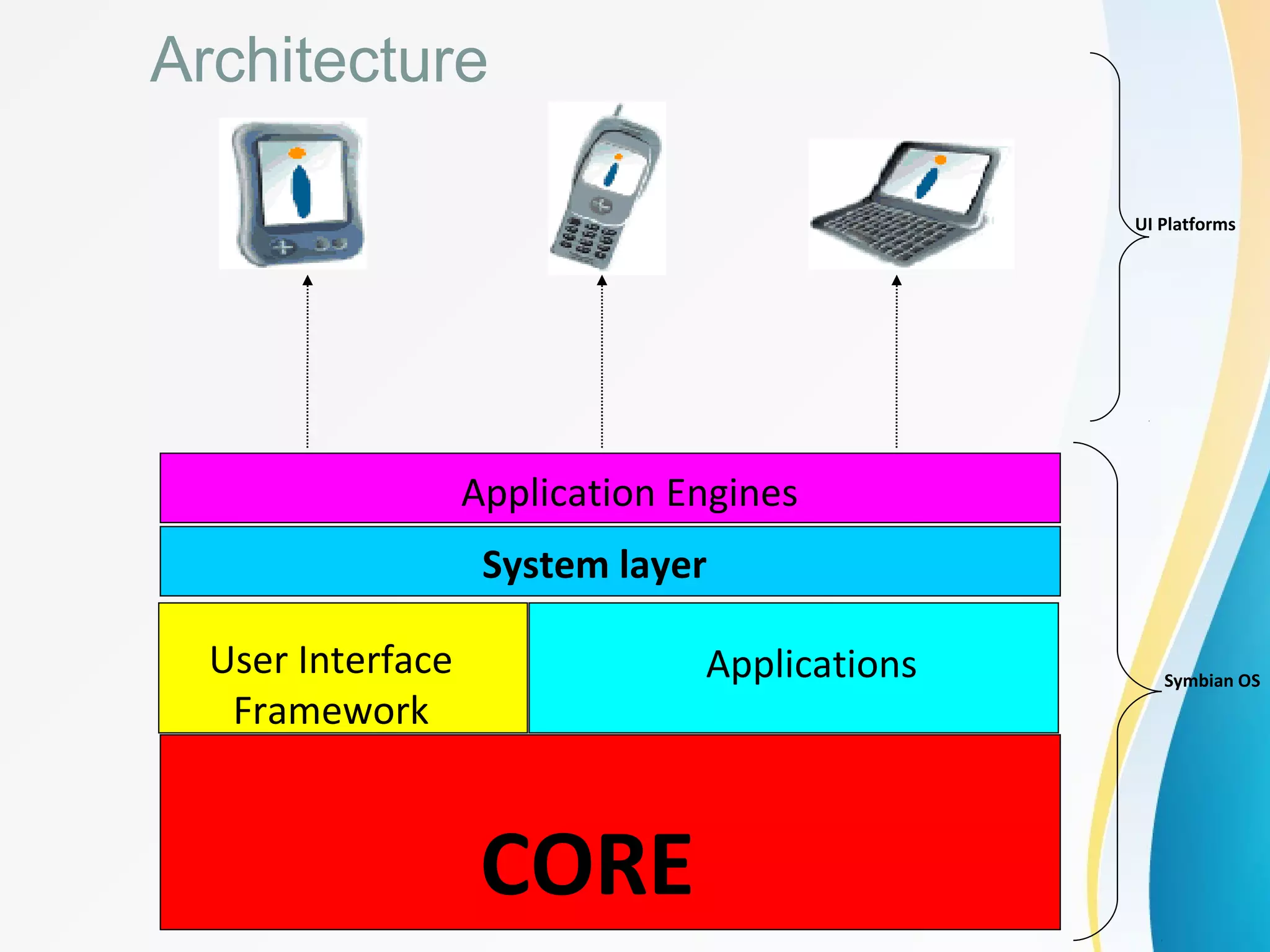
Symbian is a mobile operating system designed for smartphones. It was developed by Symbian Ltd. and addressed the needs of the mass market by being small, mobile, and always available on devices while also providing an open platform. The architecture of Symbian includes layers for the core OS, system services, application engines, and user interface. It is written in C++ and supports development through IDE tools and languages like Java. Advantages include its open nature and power management features, while disadvantages are lack of PC availability and some security vulnerabilities.