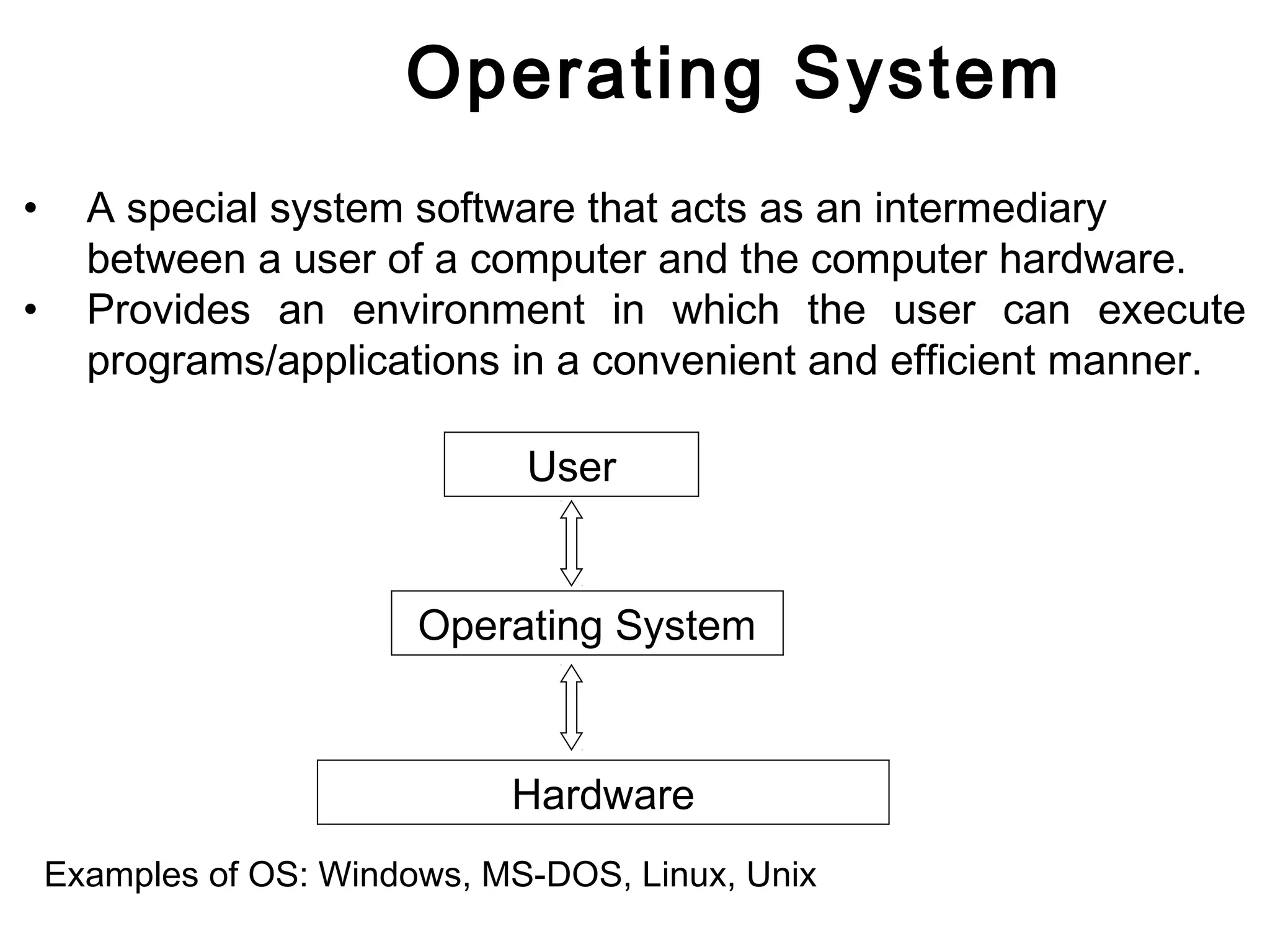
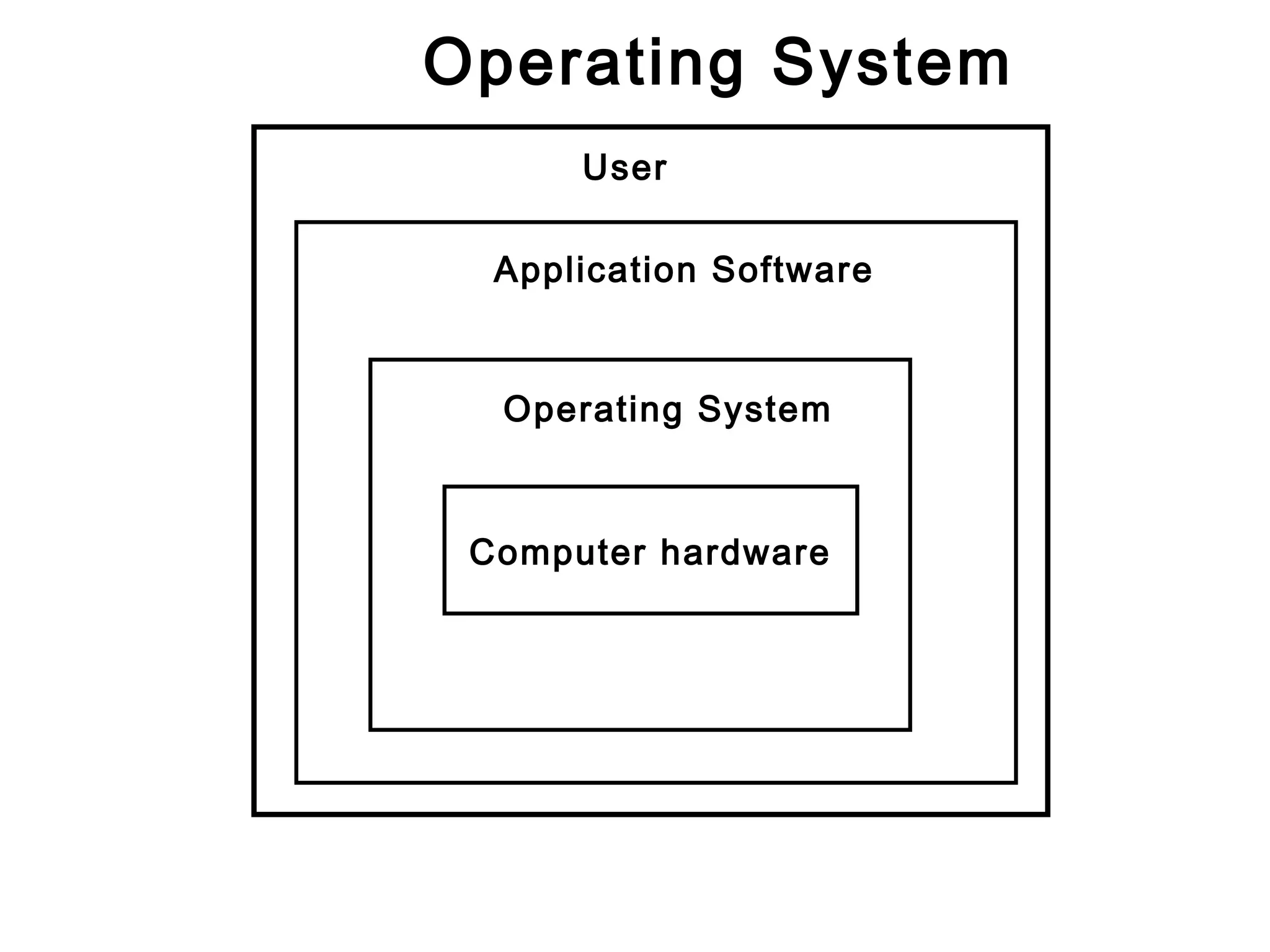
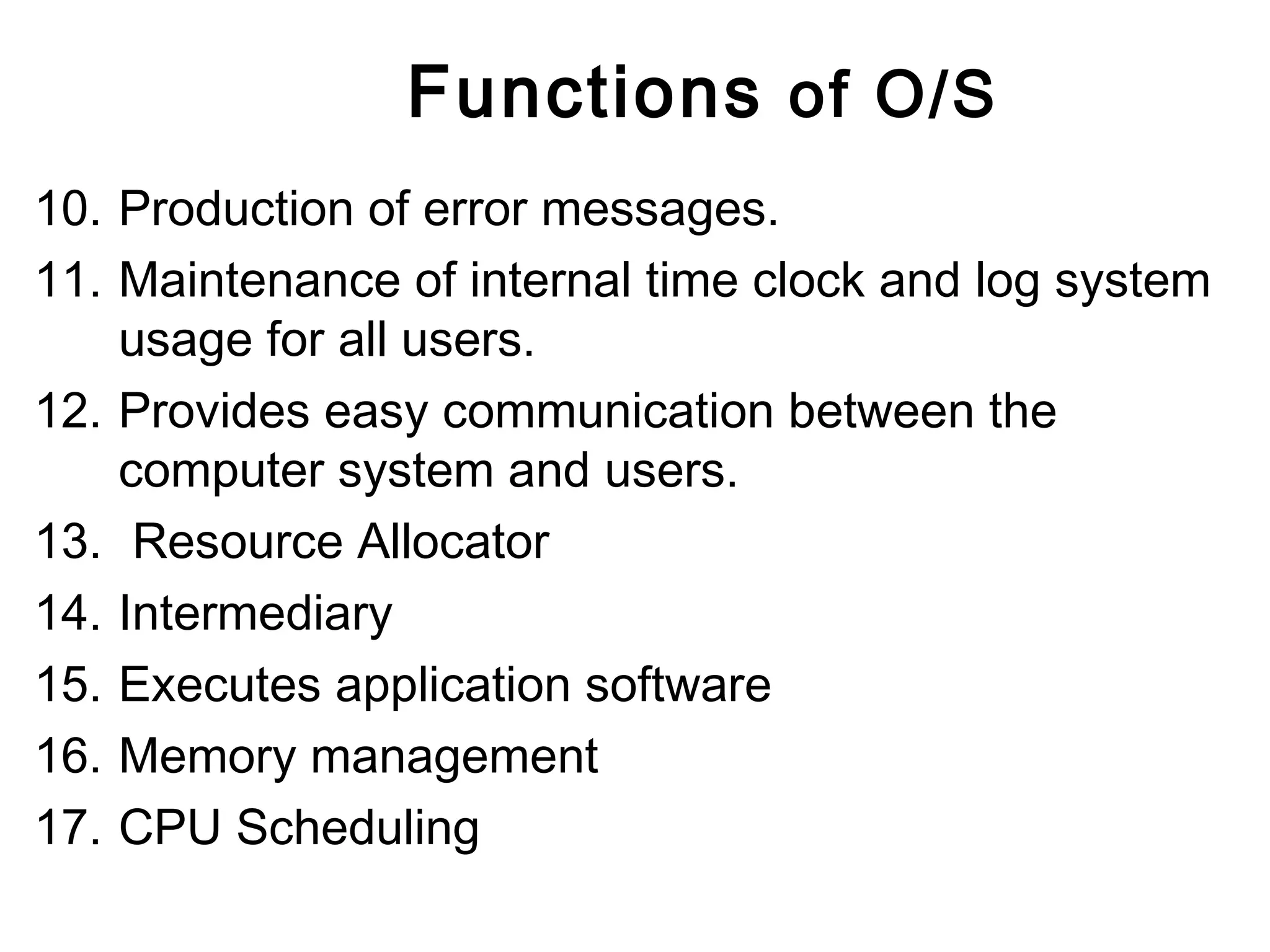
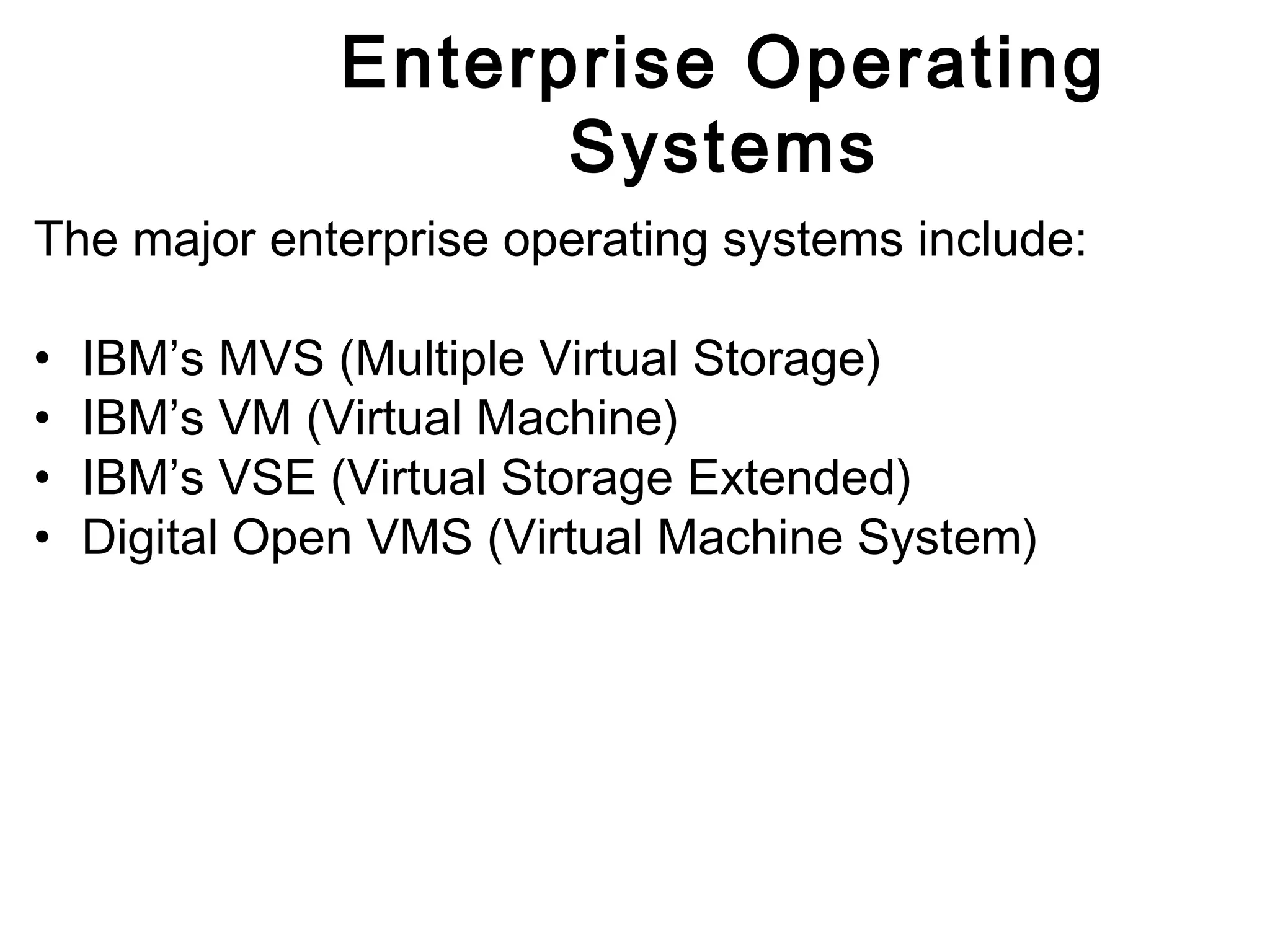
The document discusses different types of operating systems including desktop, departmental, and enterprise operating systems. It describes the key functions of an operating system as acting as an intermediary between the user and computer hardware to provide an efficient environment to run programs. Examples are given of different categories of operating systems based on the number of users supported and level of sophistication, including desktop systems for single users, departmental systems for dozens to hundreds of users, and enterprise systems for thousands of users.