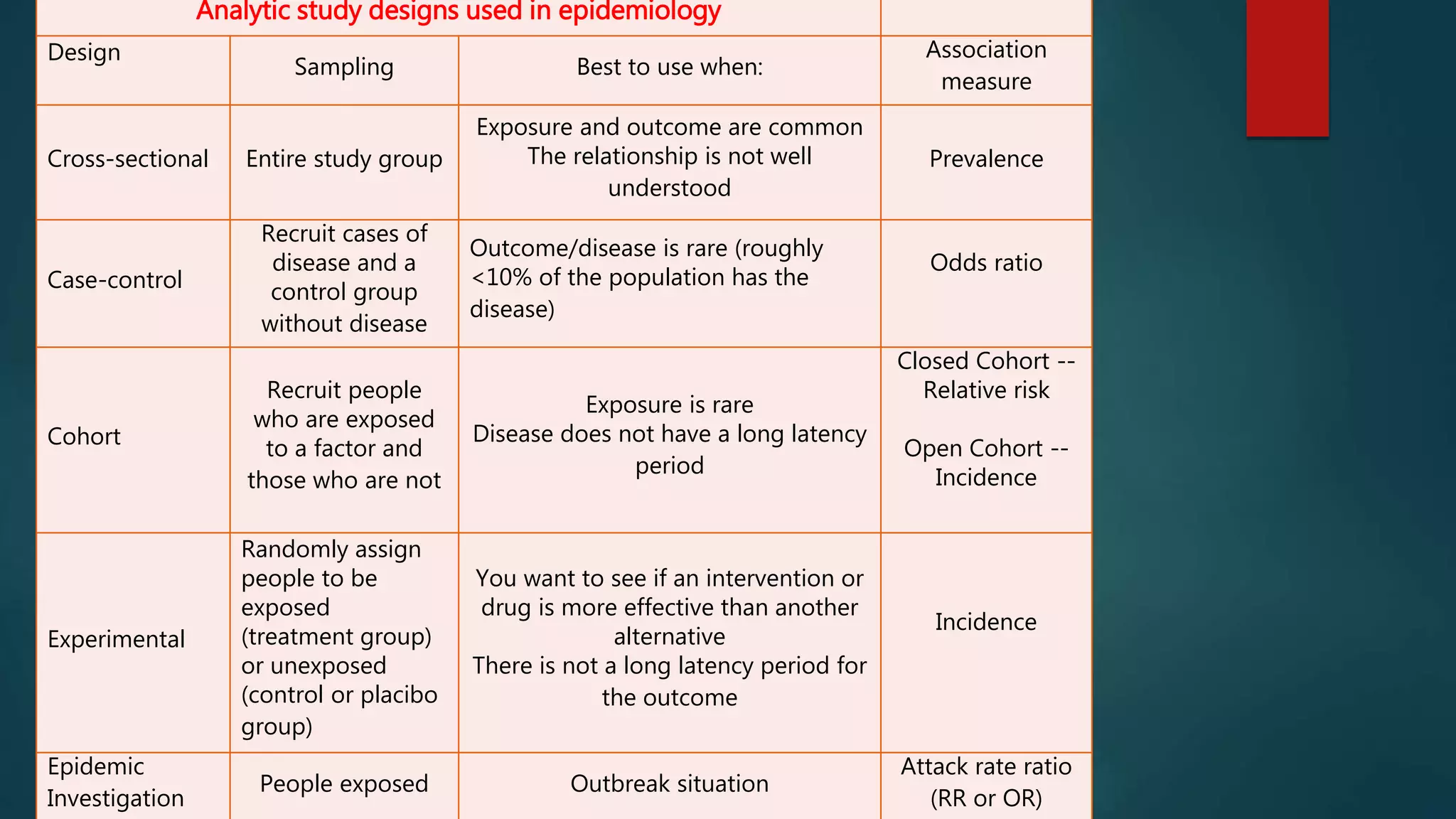
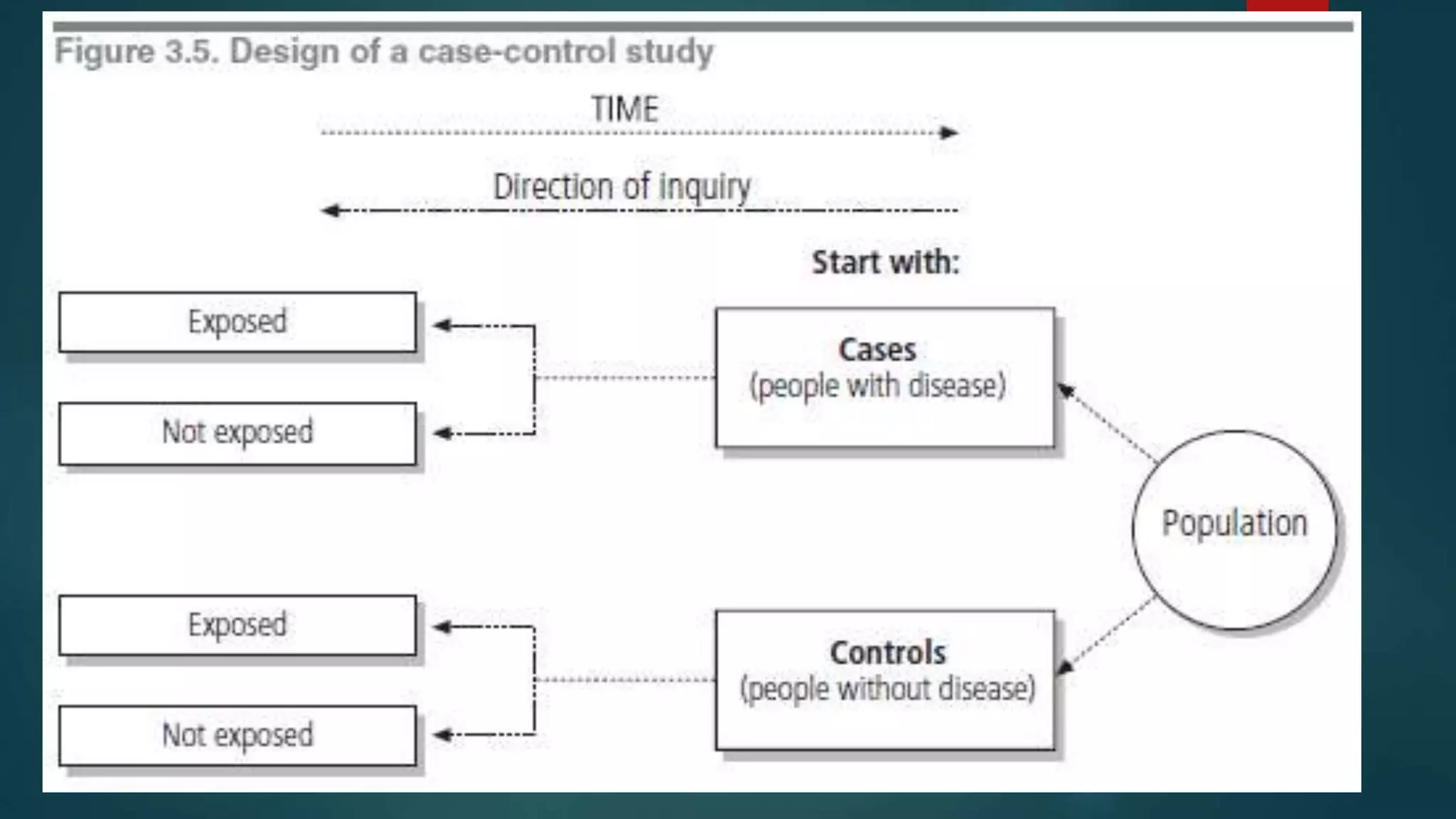
Analytical case-control studies compare exposures in groups with and without a disease. Cases are selected who have the disease, and controls without the disease are matched on characteristics like age and sex. Investigators measure past exposures and compare frequencies between cases and controls. The odds ratio association measure compares the odds of exposure in cases versus controls. Selection bias can occur if cases or controls are not representative, and recall bias can occur if cases remember past exposures differently than controls.