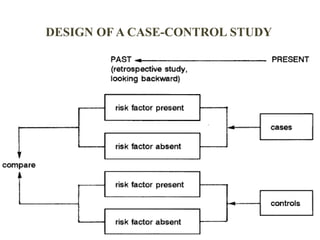
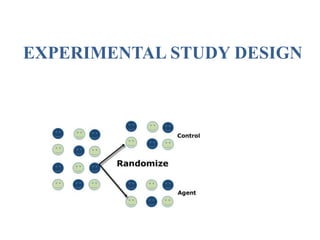
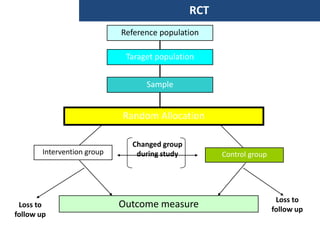
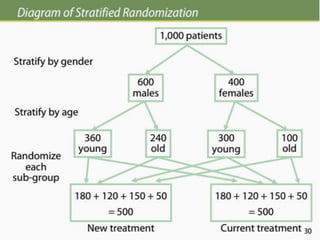
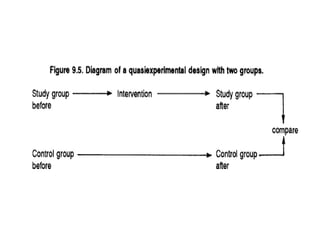
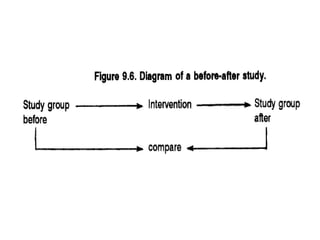
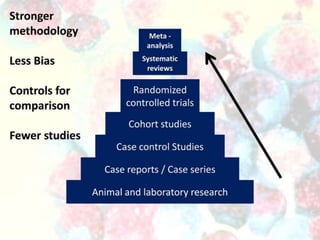
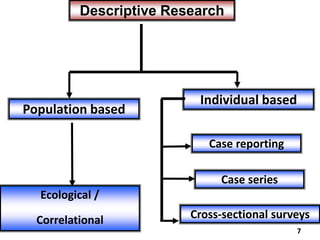
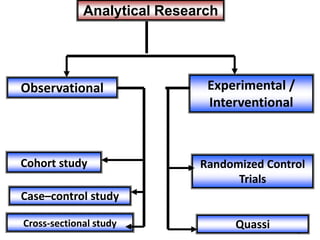
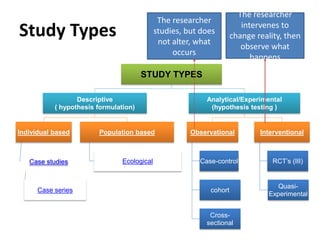
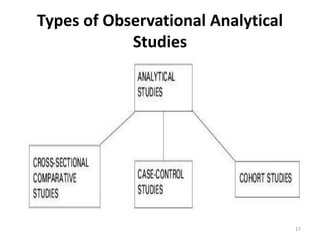
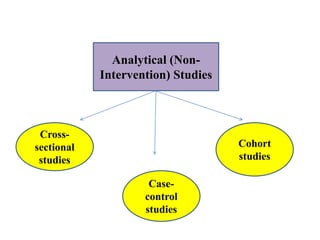
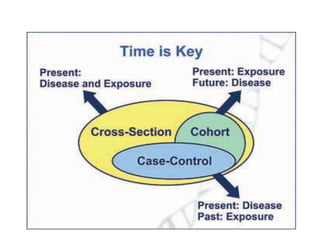
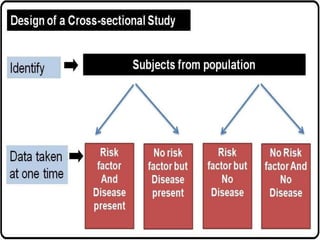
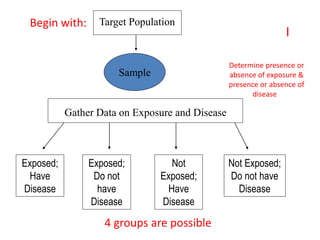
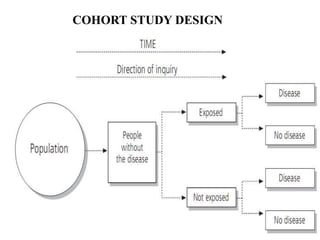
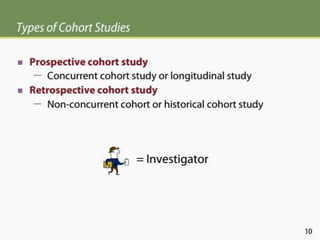
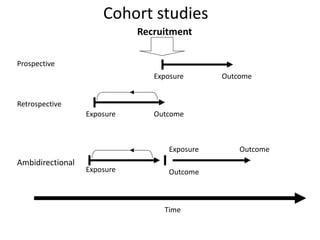
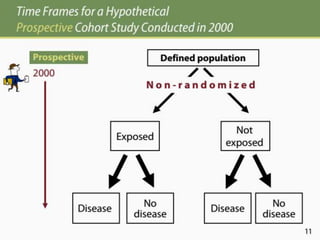
The document discusses various epidemiological study designs and their classifications, including descriptive and analytical research. It outlines specific study types such as cohort, case-control, and randomized controlled trials, detailing their objectives, procedures, and advantages or disadvantages. Understanding these designs is crucial for conducting effective public health research and establishing causal relationships in epidemiology.




























![ATTRIBUTABLE RISK
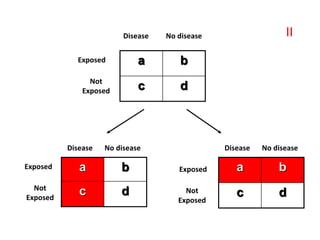
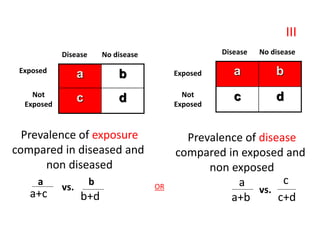
• This is determined by the “Attributable Risk”, which is
defined as “the amount or proportion of diseases incidence
(or disease risk) that can be attributed to a specific
exposure”.
• Attributable Risk is calculated as follow:
• Risk Difference = (Incidence in exposed group ) – (Incidence
in non-exposed group [Background risk]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epidemiologicalstudydesigns-240421115515-f7ba1489/85/Epidemiological-Study-Designs-by-zafar-sir-pptx-48-320.jpg)