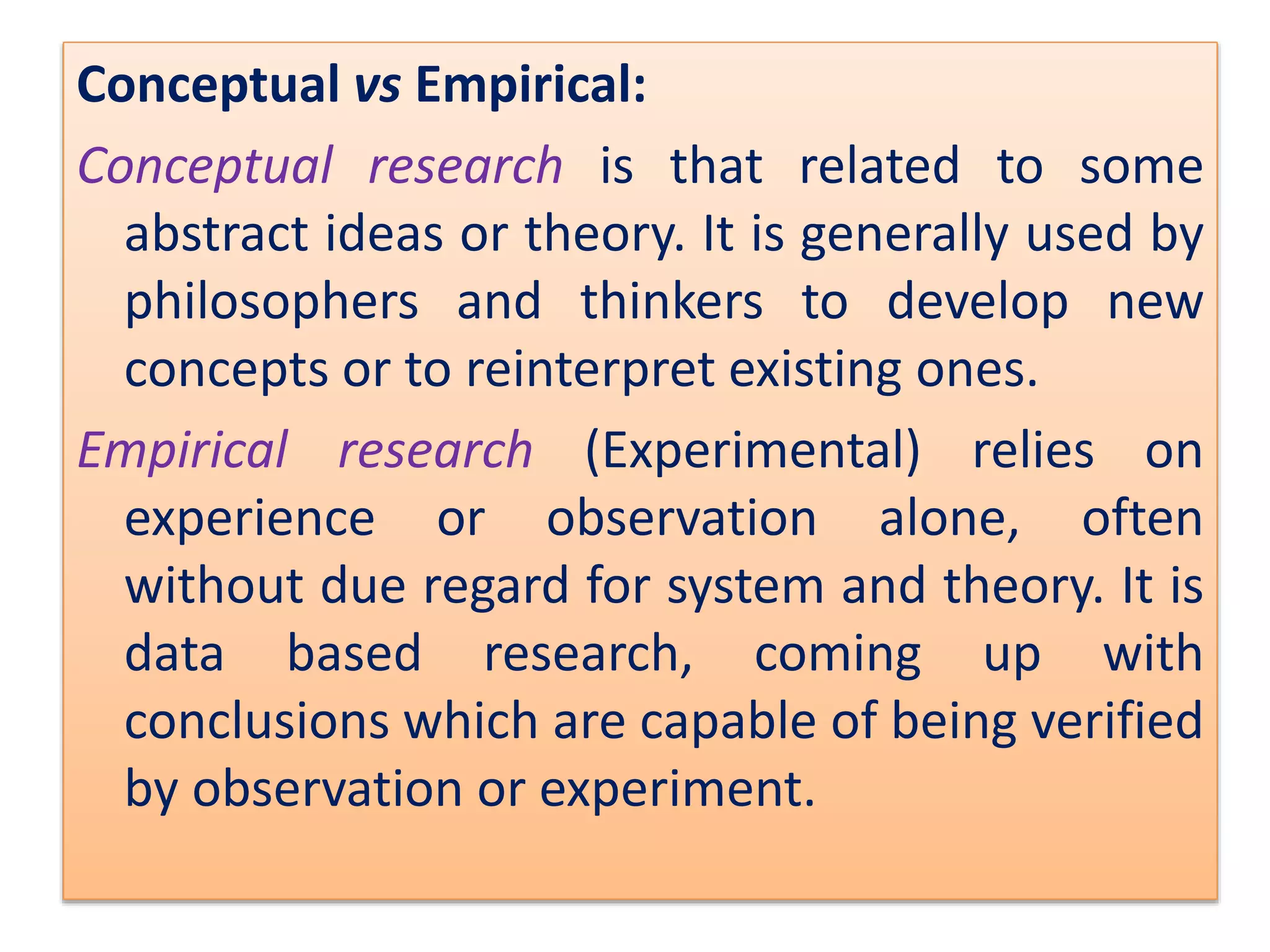
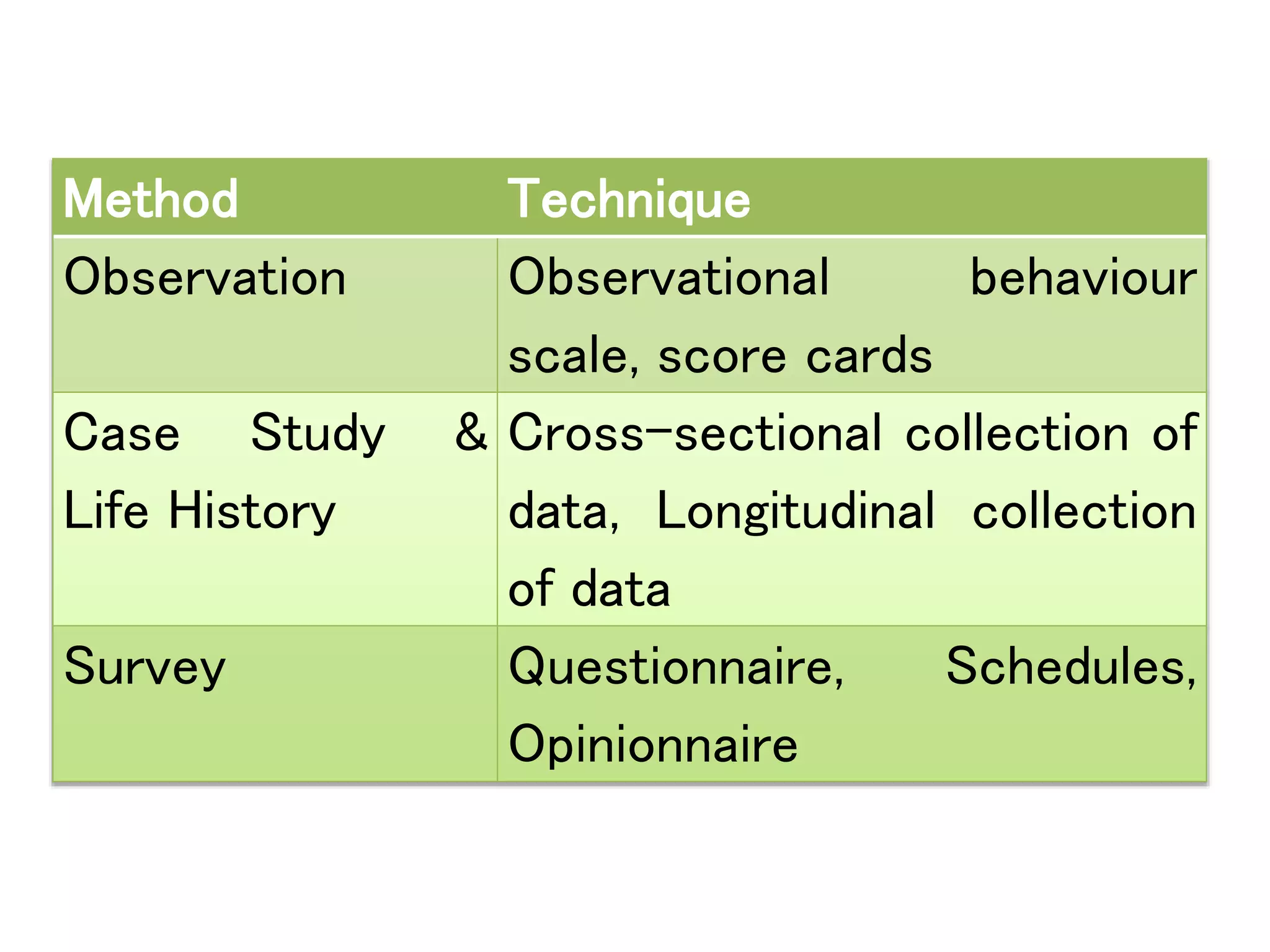
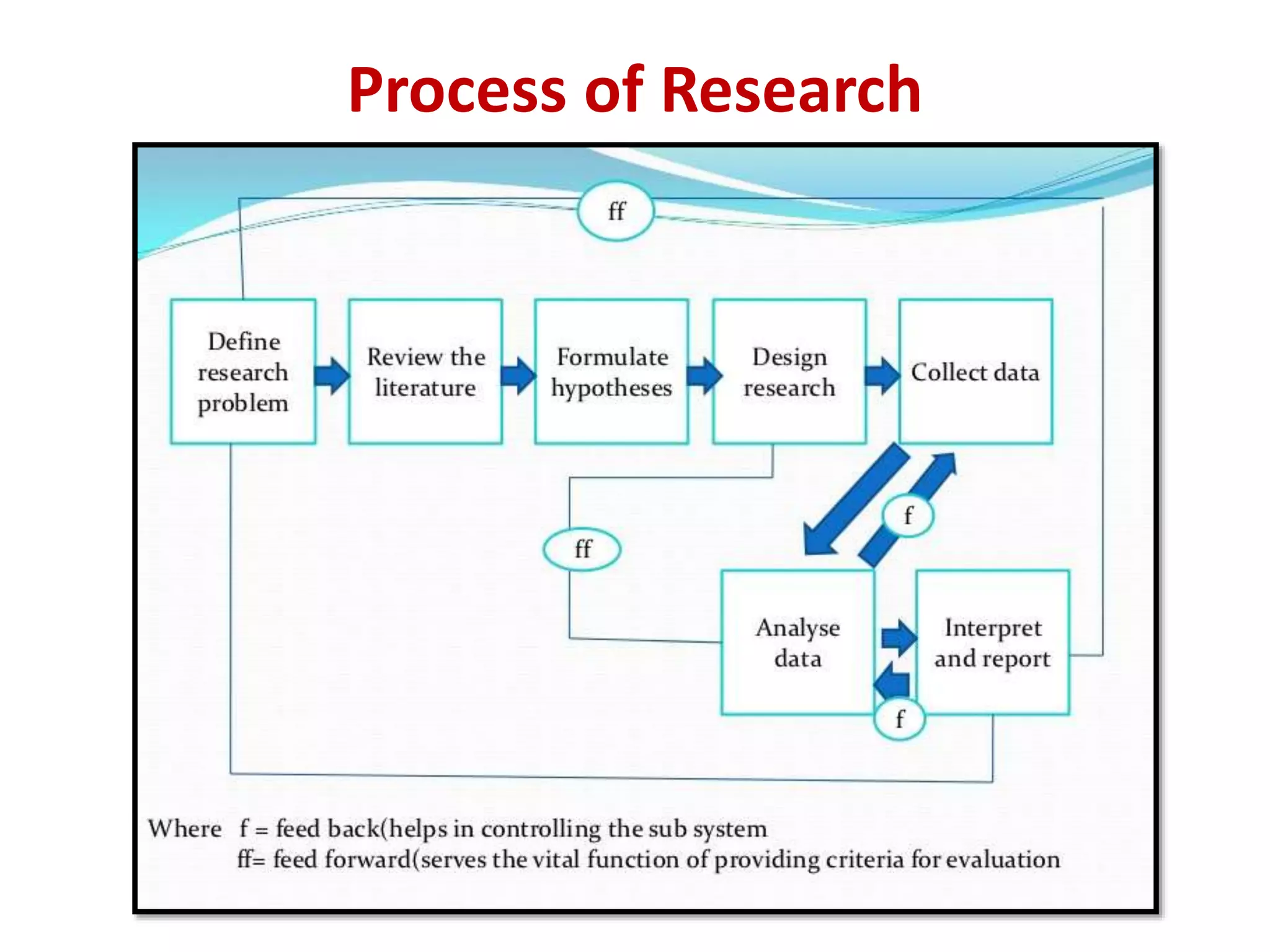
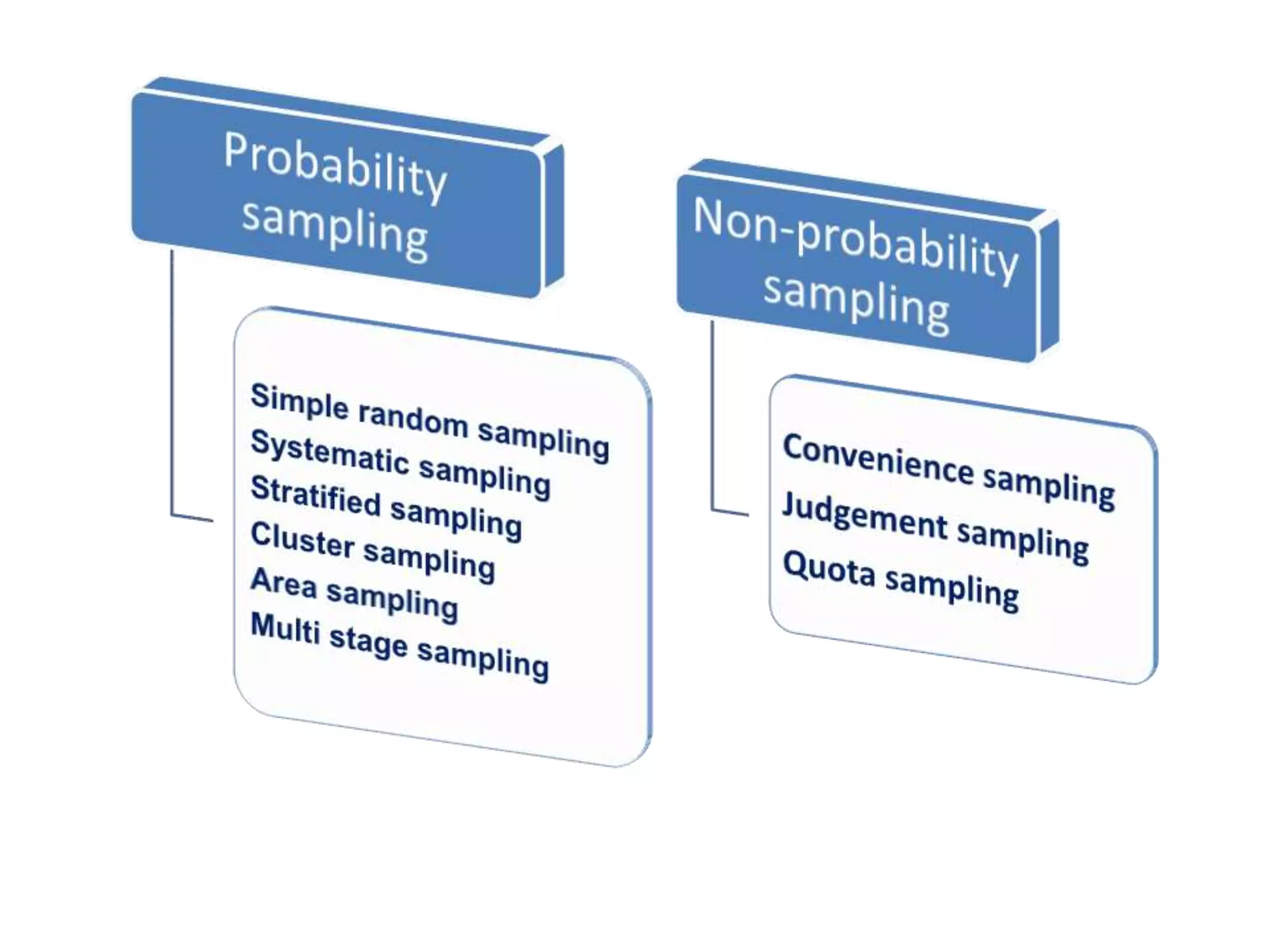
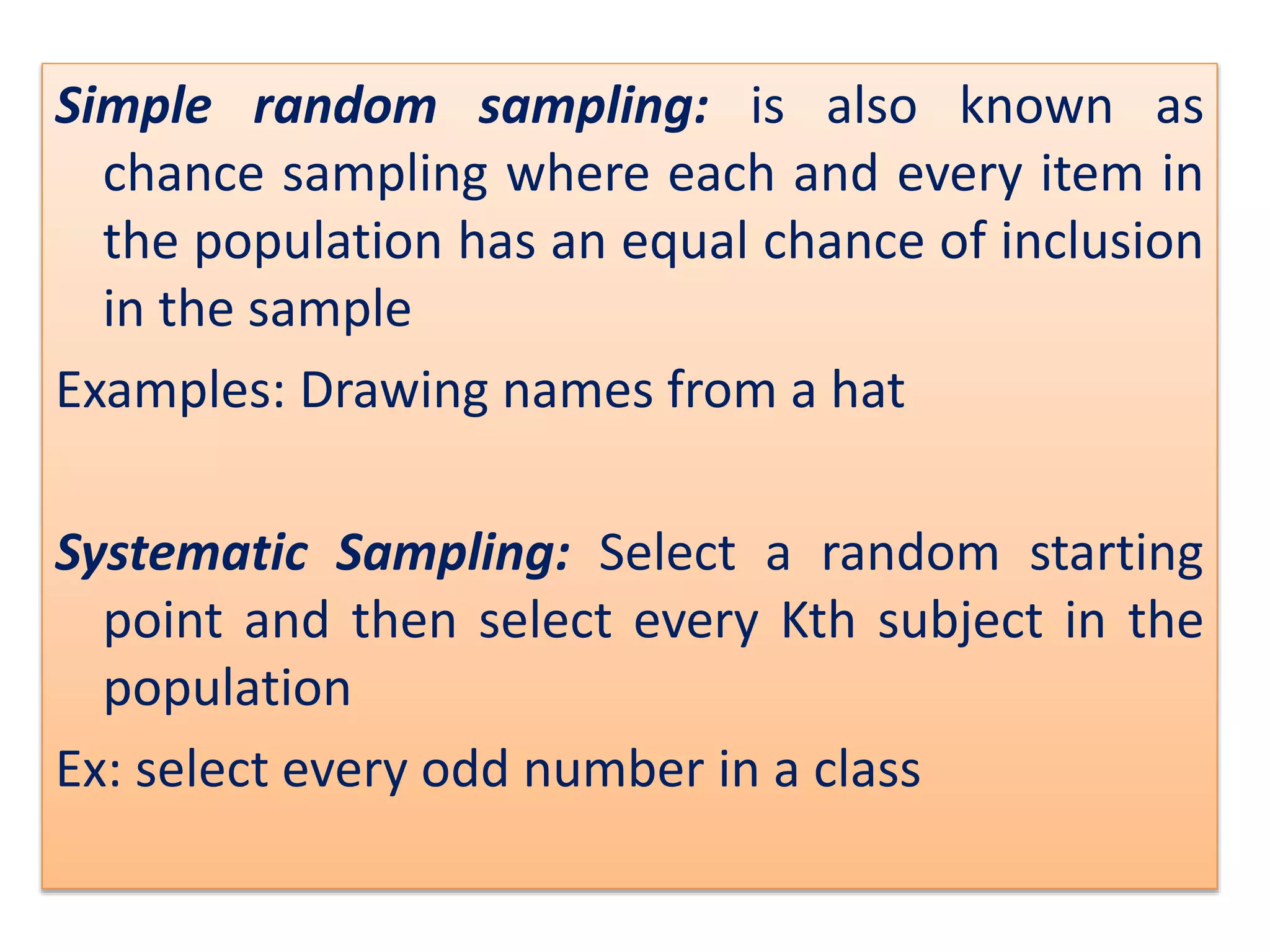
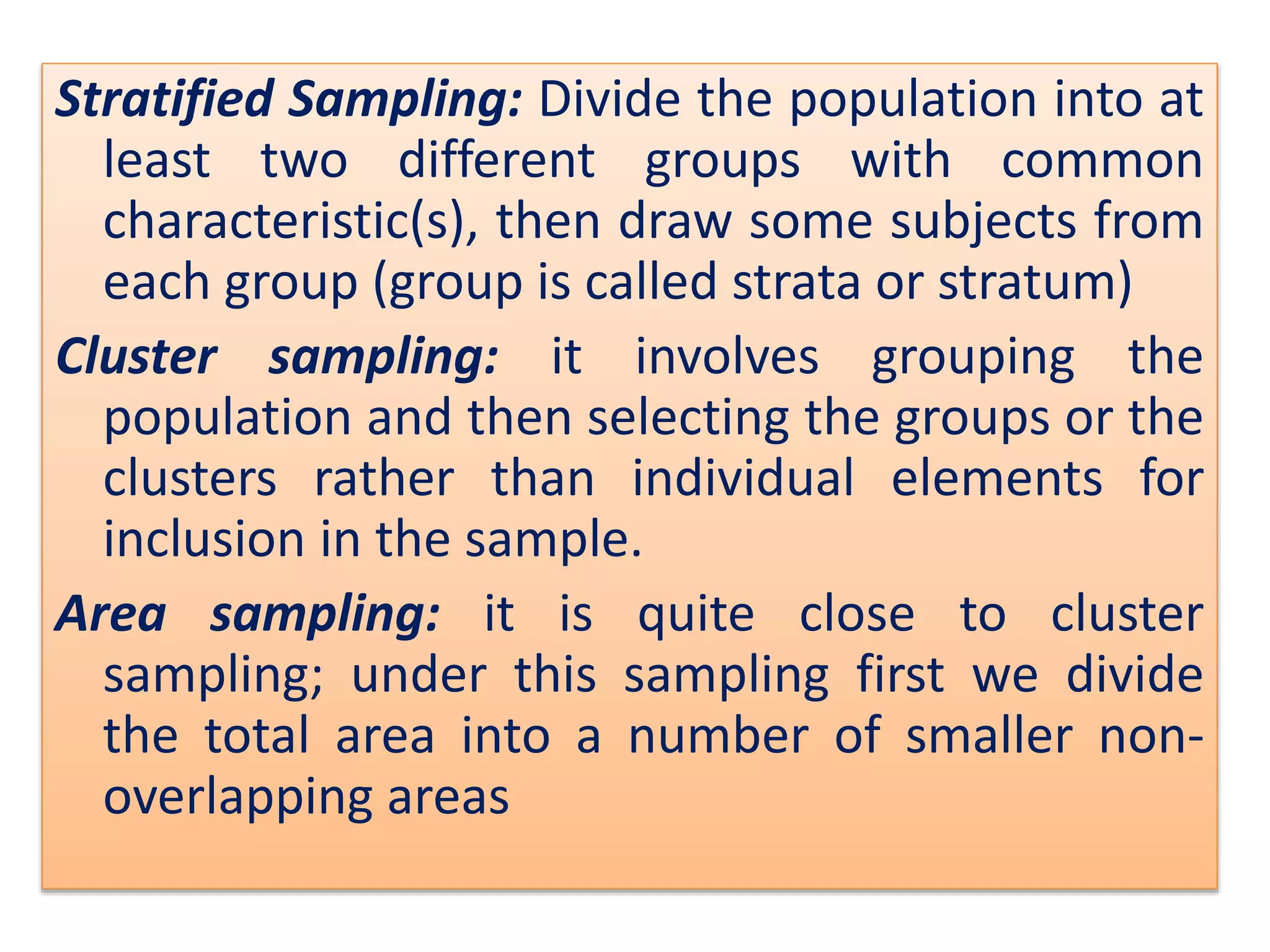
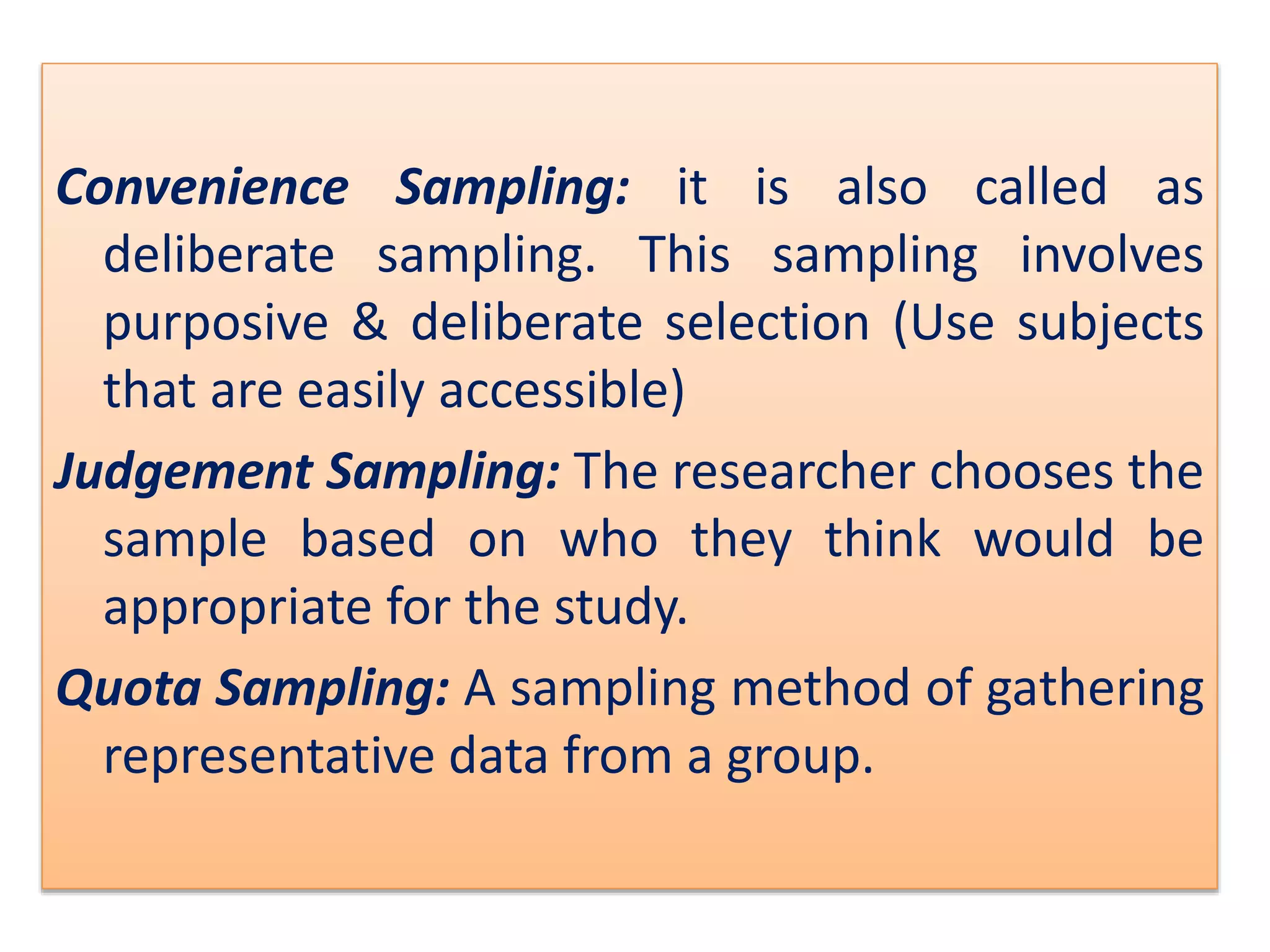
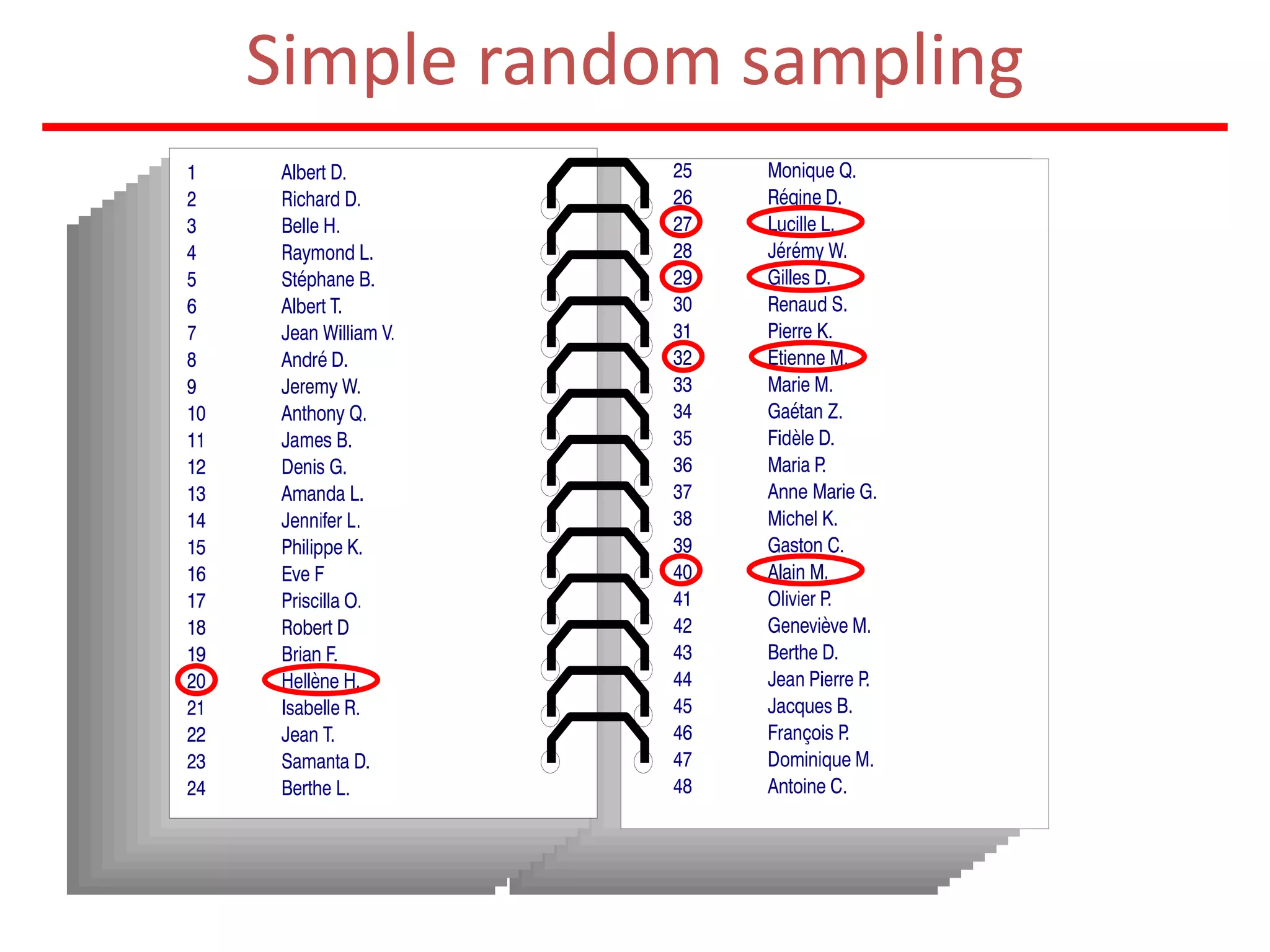
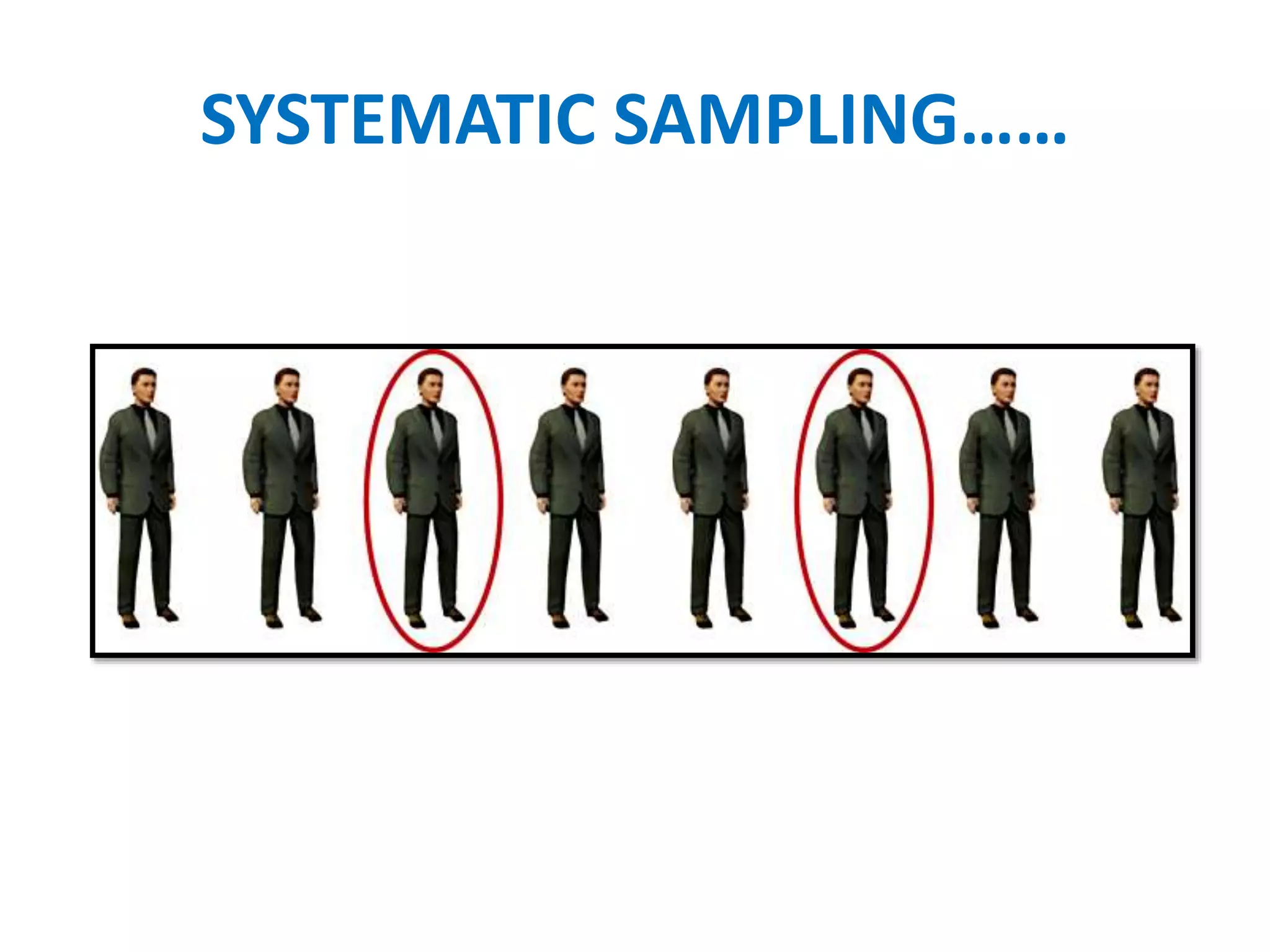
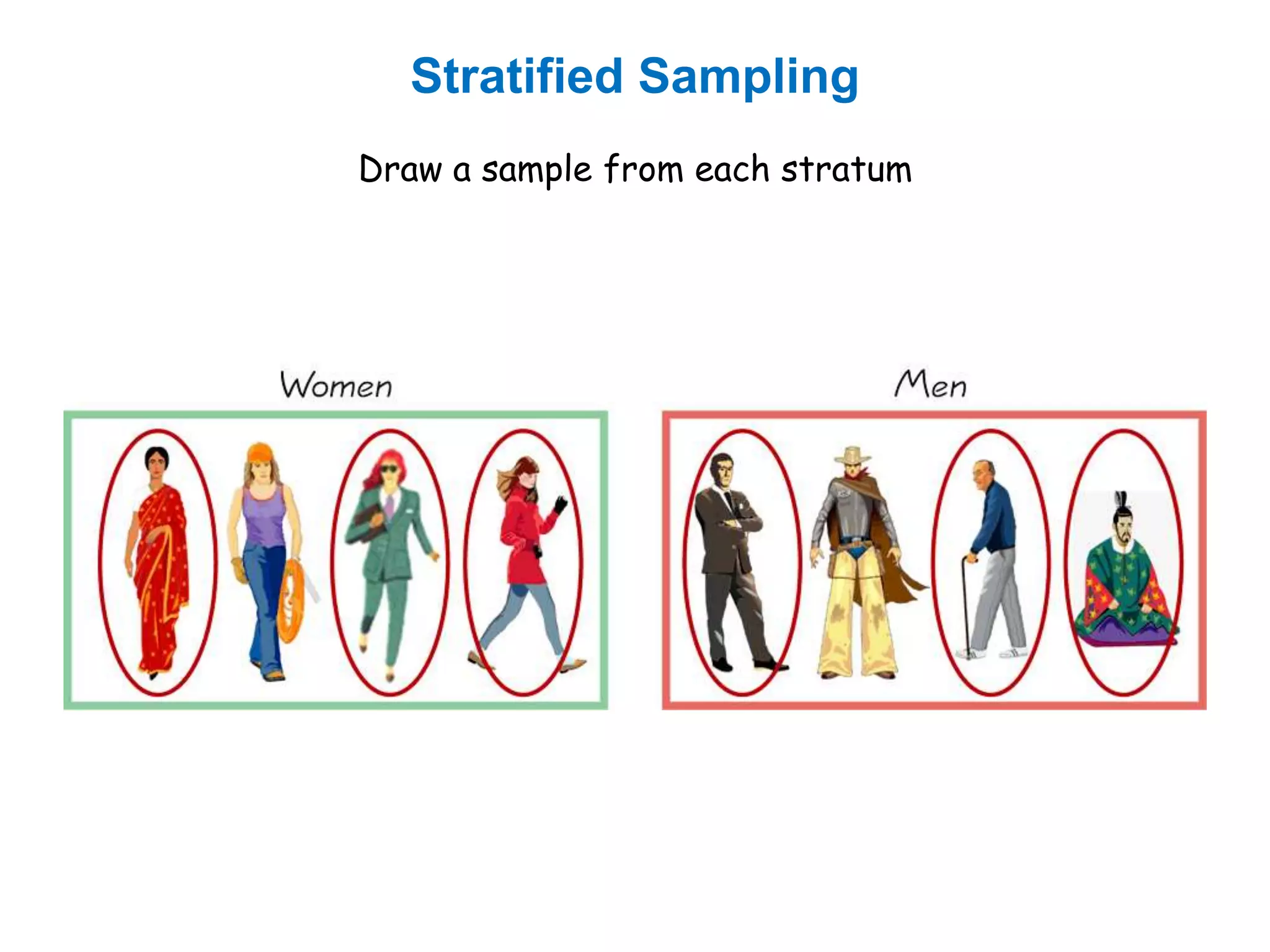
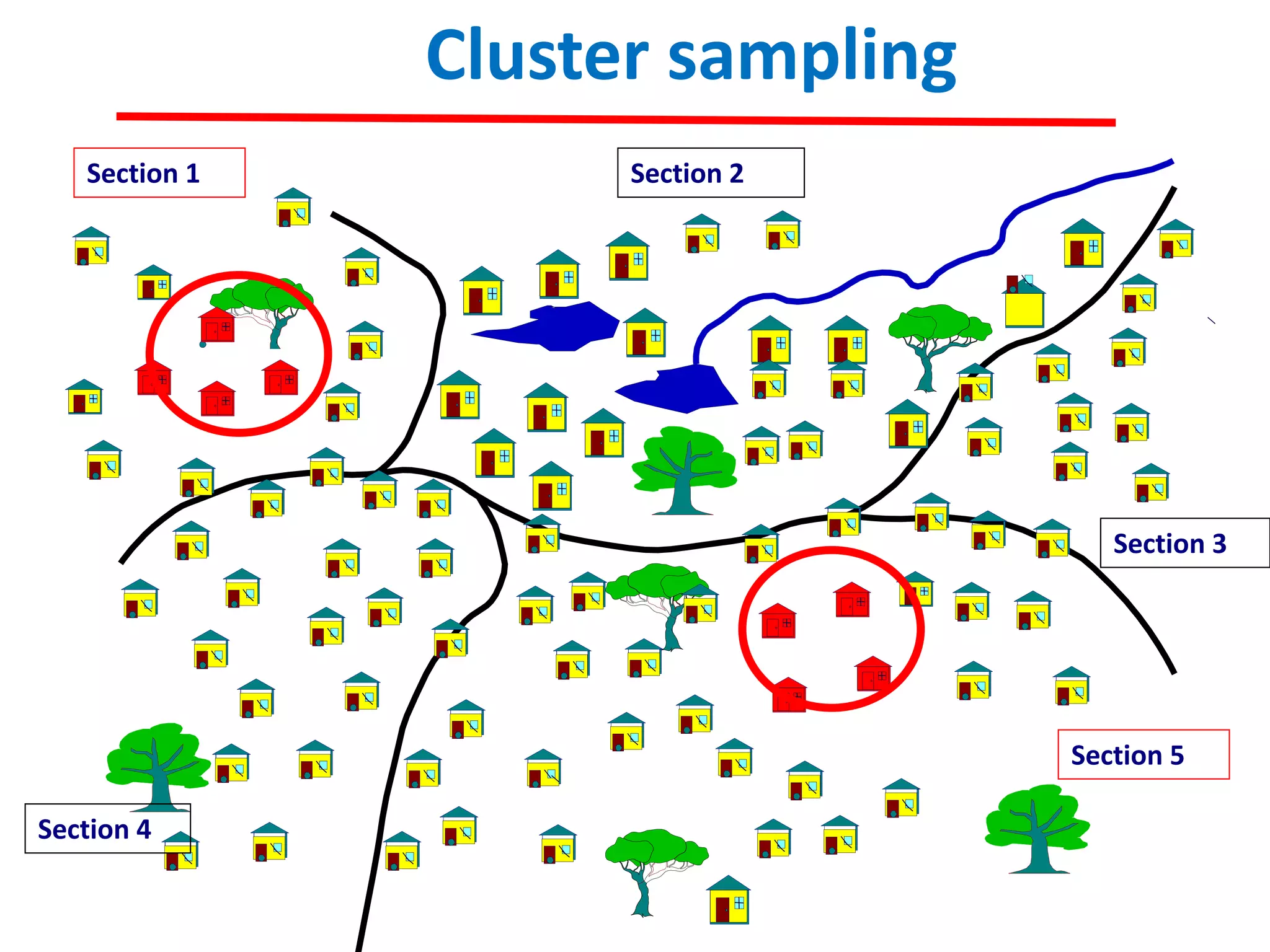
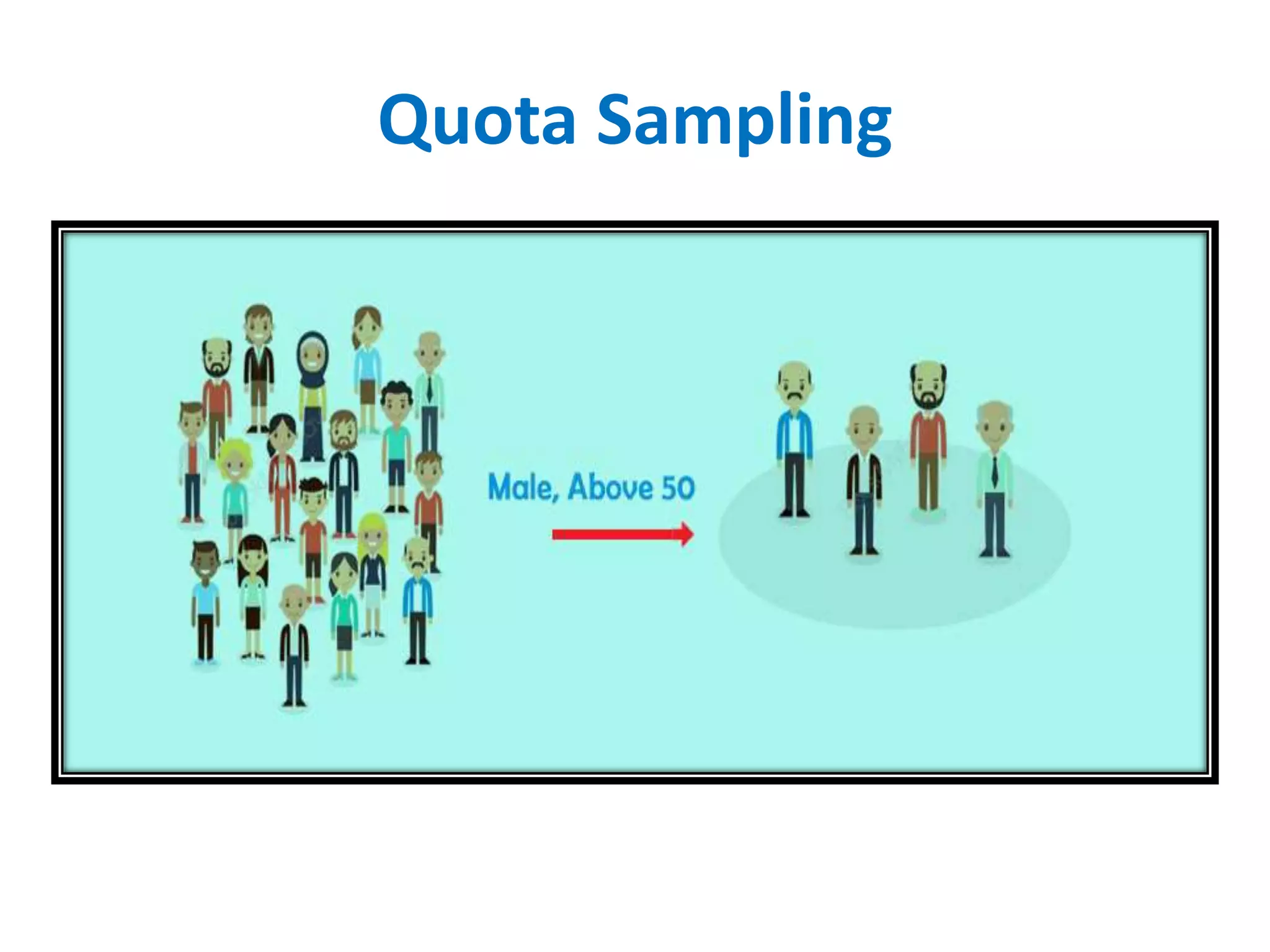
The document discusses research methodology, defining research as a systematic inquiry aimed at obtaining information on specific topics. It outlines various types of research such as descriptive, analytical, applied, and fundamental, and also differentiates between quantitative and qualitative methods. Additionally, the document explains the research process and different sampling techniques including simple random, systematic, stratified, and convenience sampling.