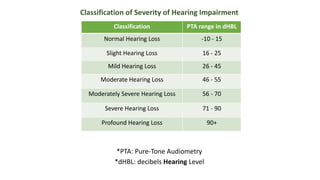
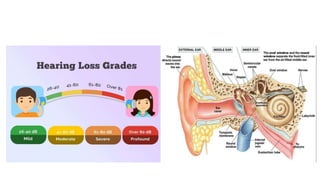
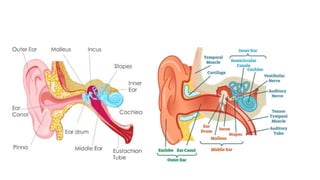
The document discusses hearing impairment, its classifications, assessment methods, symptoms, types, causes, and the role of teachers in supporting hearing-impaired students. It outlines the severity levels of hearing loss and various factors leading to impairment, including genetic and non-genetic causes. Additionally, the document emphasizes effective teaching strategies that can aid in the education of hearing-impaired children, such as the use of visual aids and direct interaction.