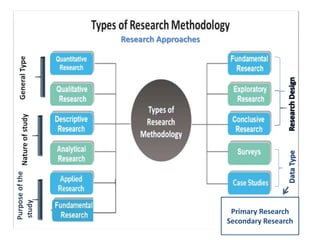
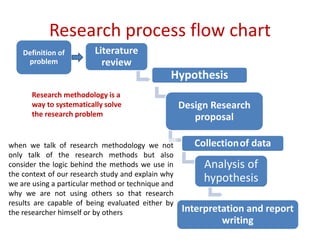
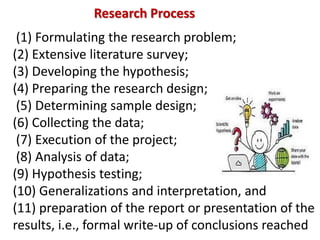
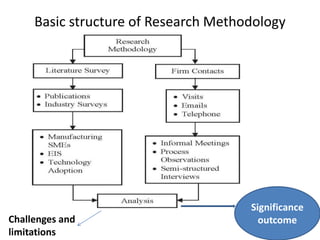
The document discusses research methodology, outlining its definitions, various types, and approaches such as qualitative vs. quantitative and applied vs. fundamental research. It emphasizes the importance of systematic investigation and the components necessary for conducting research, including data collection, analysis, and report writing. The significance of research in fostering scientific thinking and addressing real-world problems is also highlighted.