1) Henri Becquerel discovered that uranium salts would expose photographic plates even when wrapped in black paper, showing they emitted invisible "rays" he called radioactivity.
2) Marie Curie discovered the radioactive elements polonium and radium, and found radium was over a million times more radioactive than uranium.
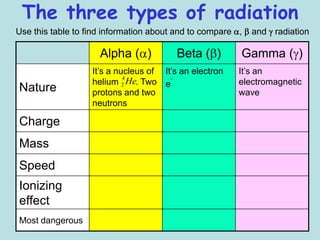
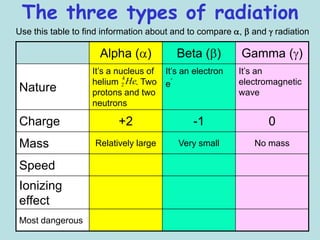
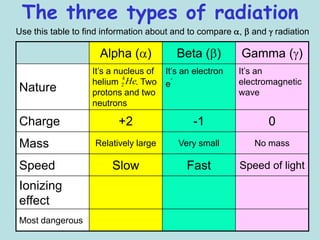
3) Ernest Rutherford discovered there were at least two types of radiation, which he called alpha and beta based on how far they could penetrate matter and their opposite electric charges.