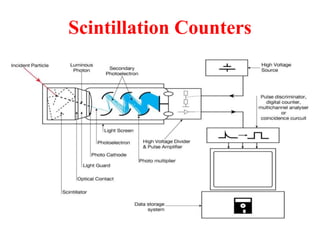
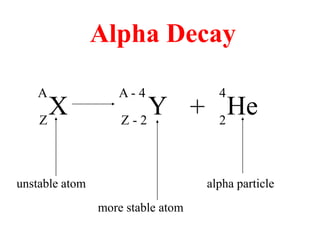
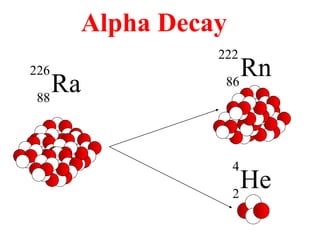
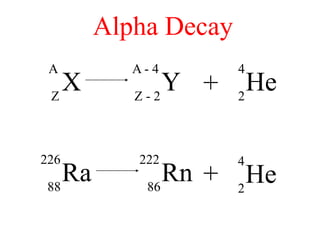
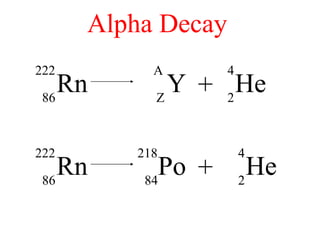
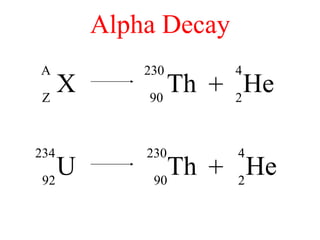
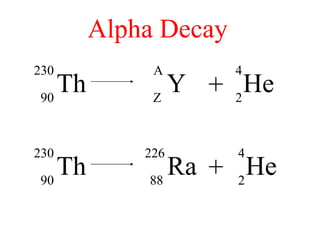
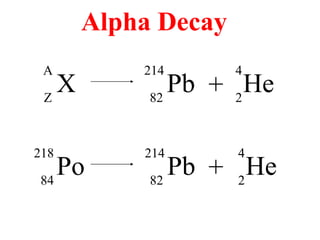
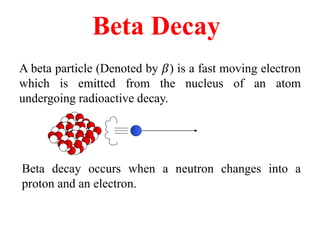
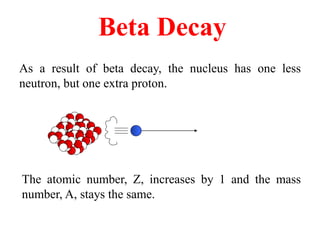
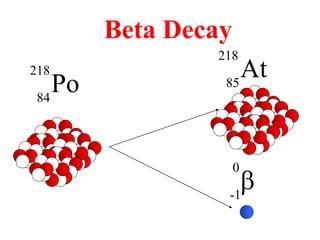
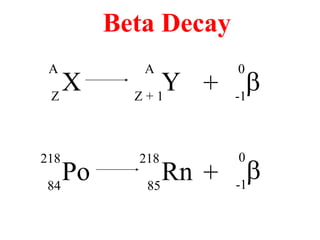
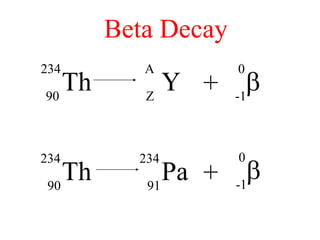
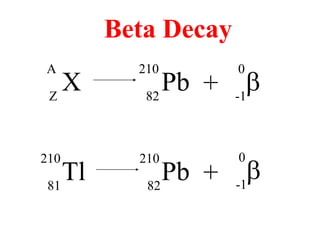
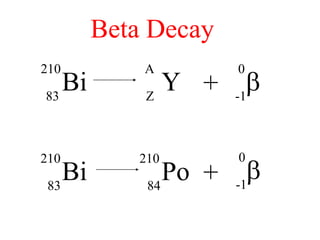
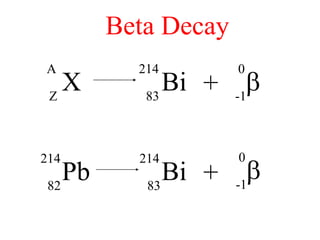
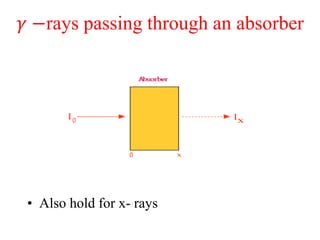
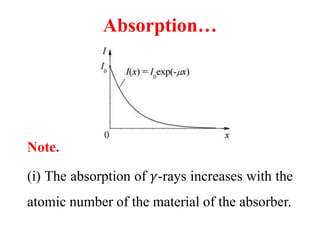
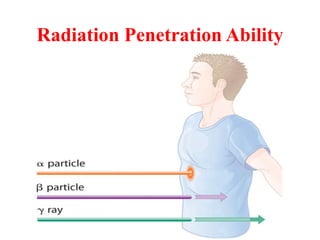
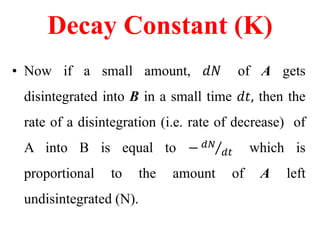
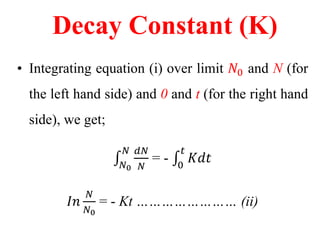
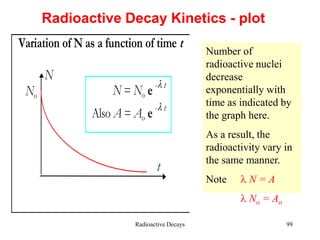
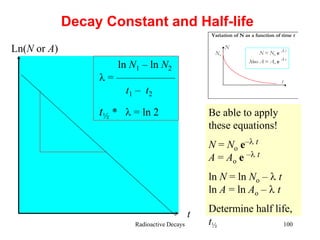
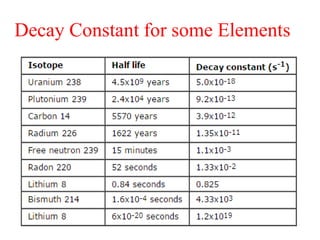
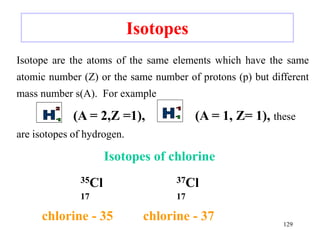
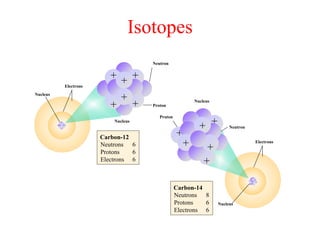
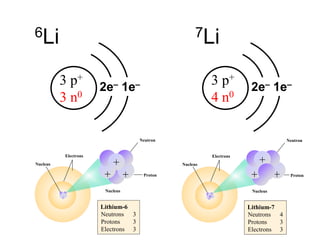
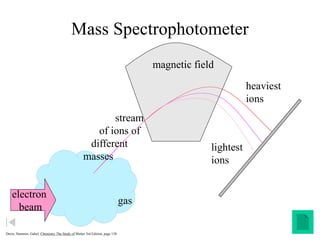
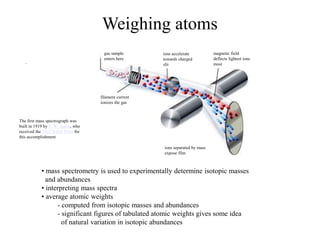
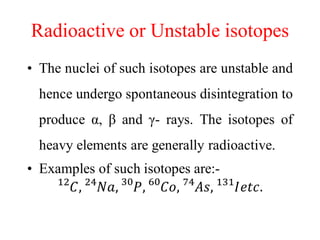
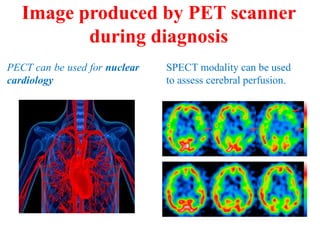
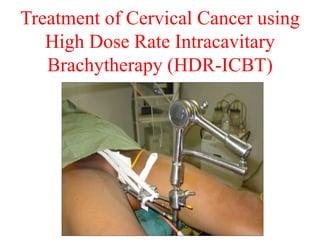
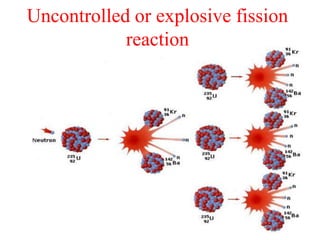
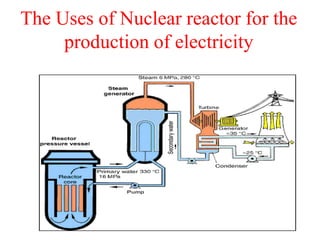
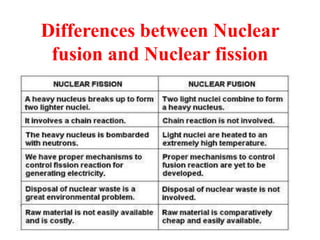
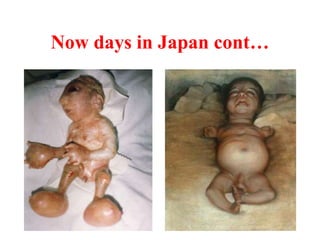
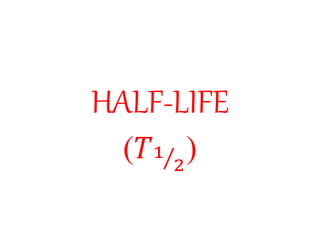Radioactivity is the process of spontaneous disintegration of unstable nuclei through emission of radiation. There are three main types of radiation emitted: alpha, beta, and gamma rays. Alpha particles have the highest ionizing power but lowest penetration ability. Beta particles are high energy electrons emitted from neutron decay. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation emitted during nuclear transitions. Radioactivity can be natural, occurring in heavy elements like uranium, or artificial through bombardment of stable nuclei. It is measured using instruments like Geiger counters and detected through ionization of matter.