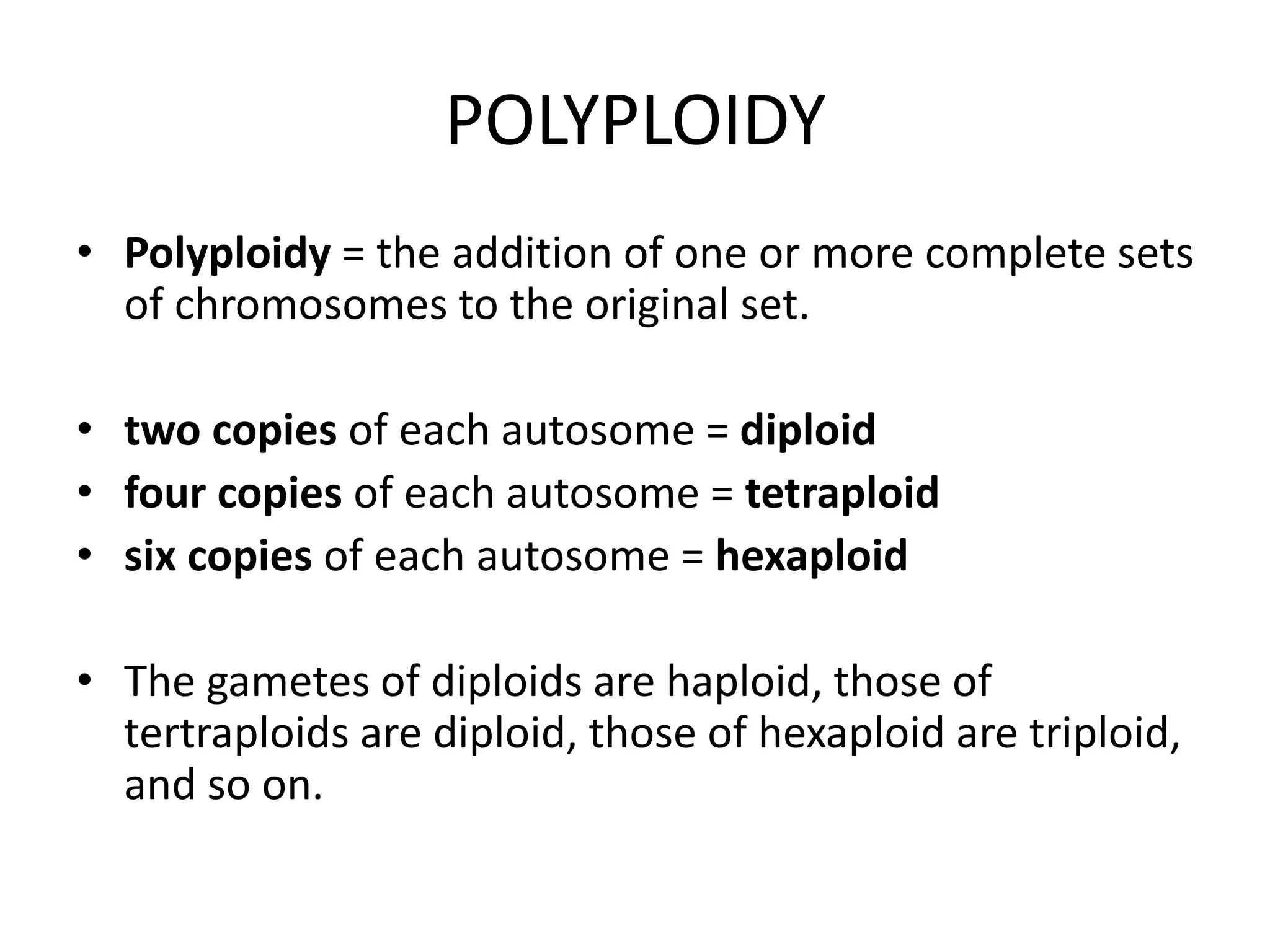
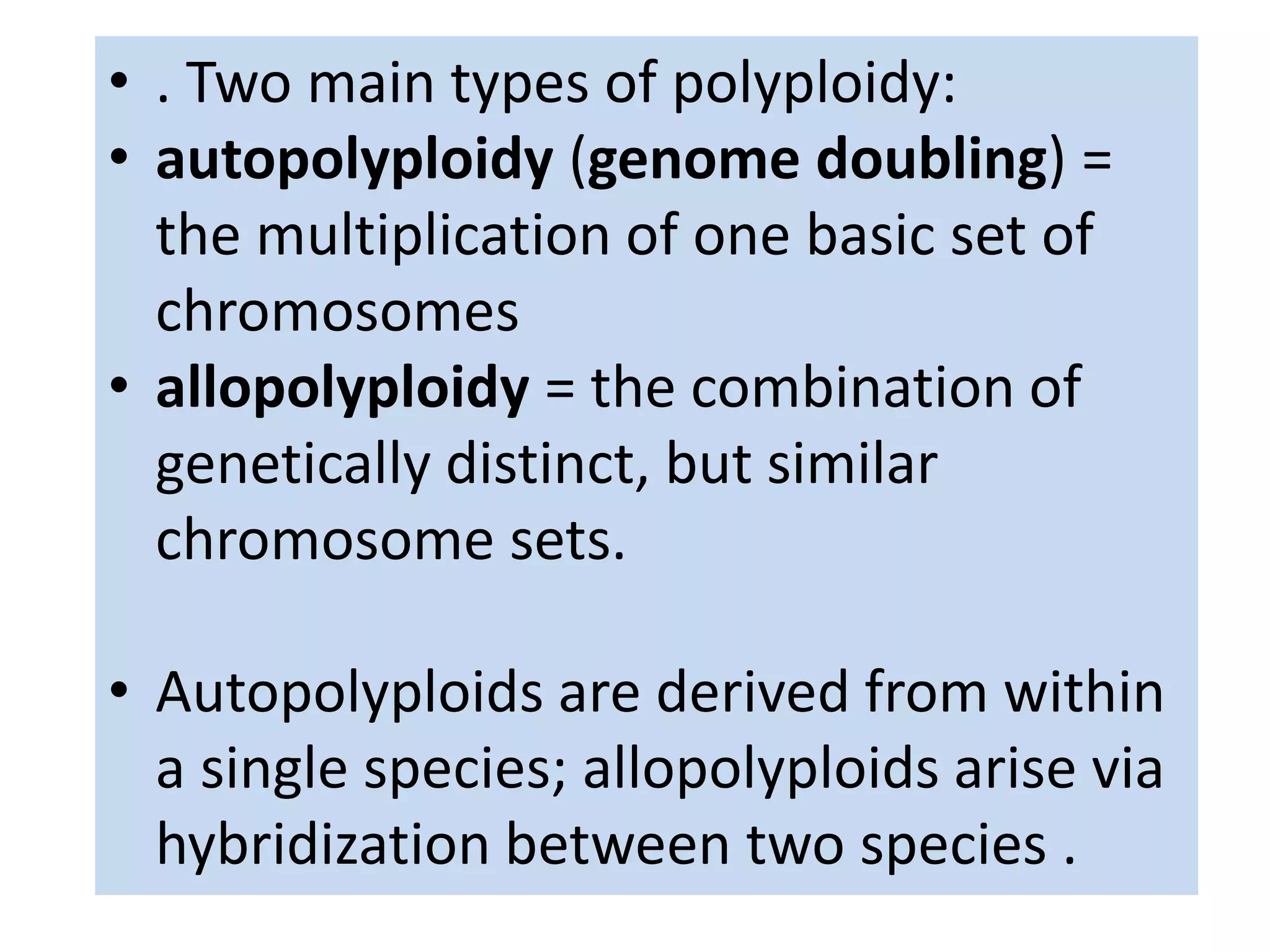
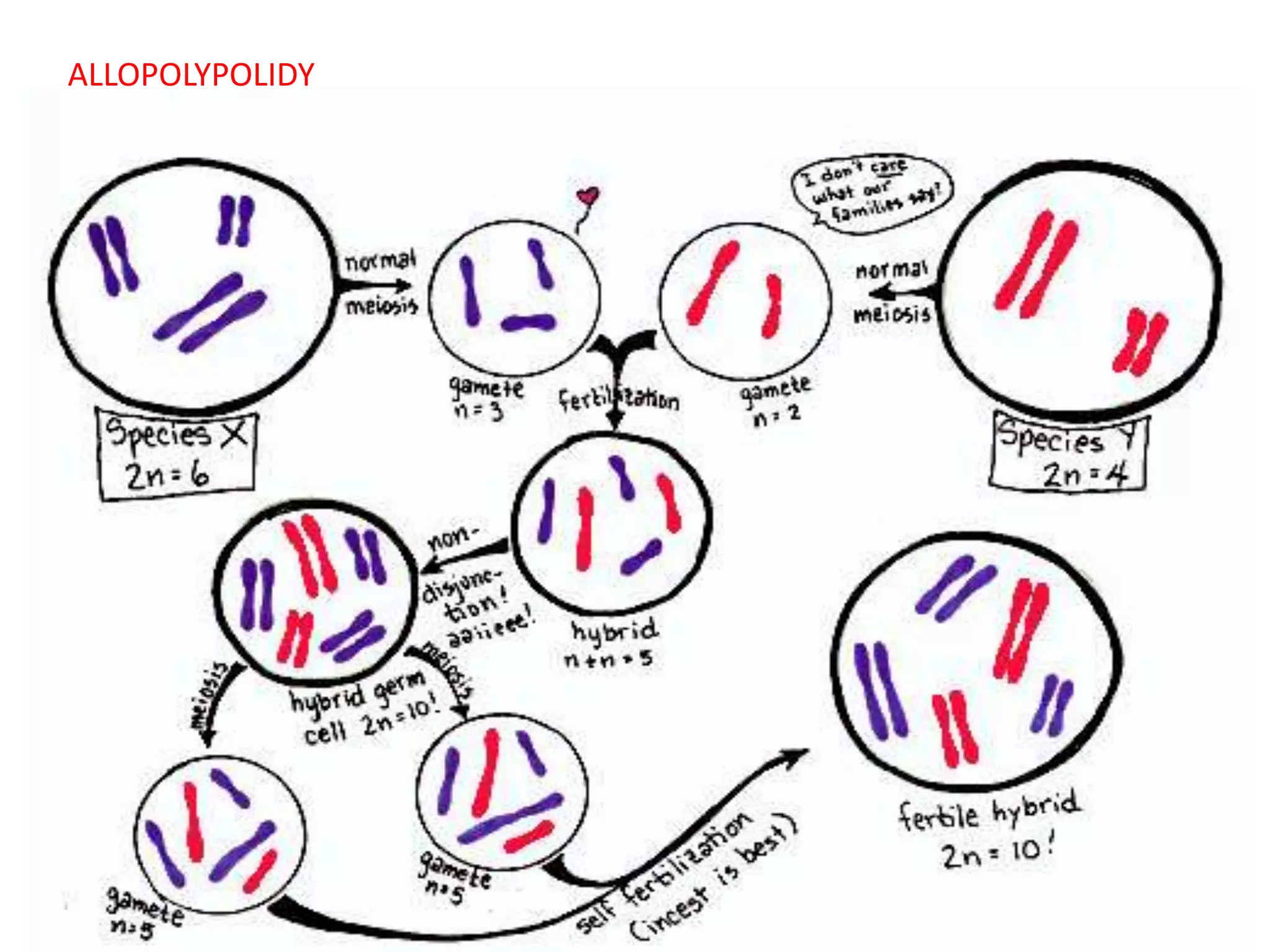
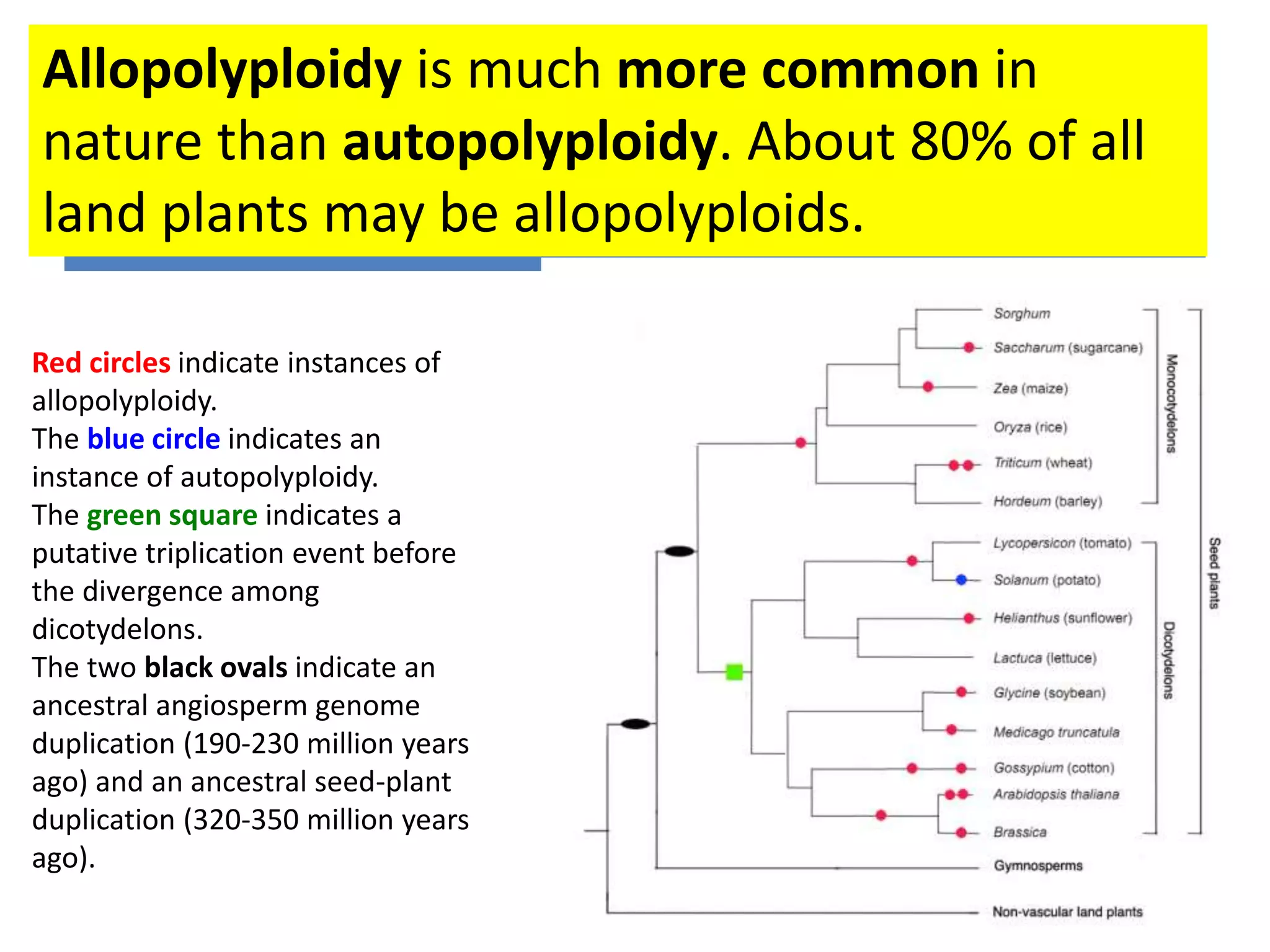
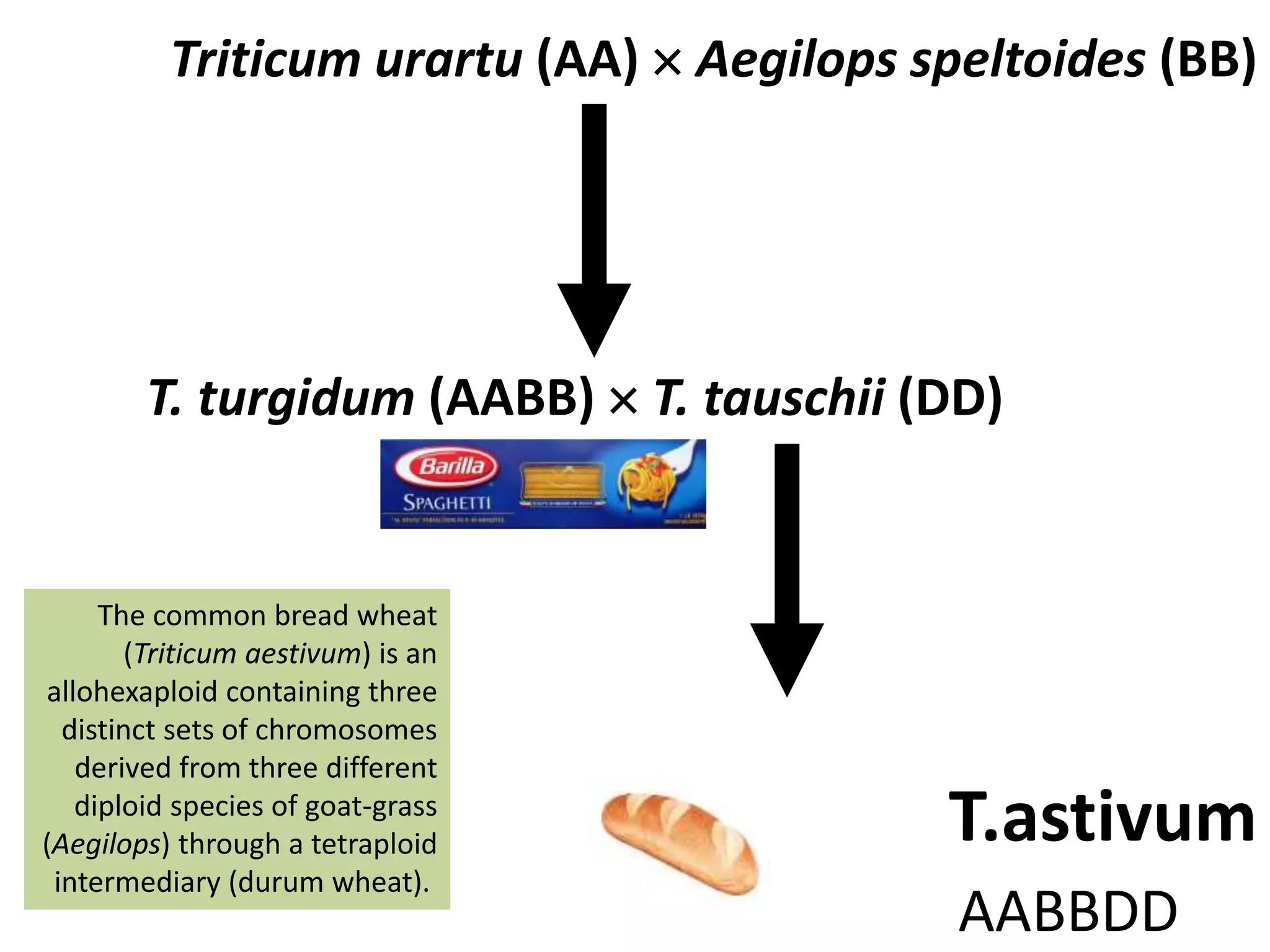
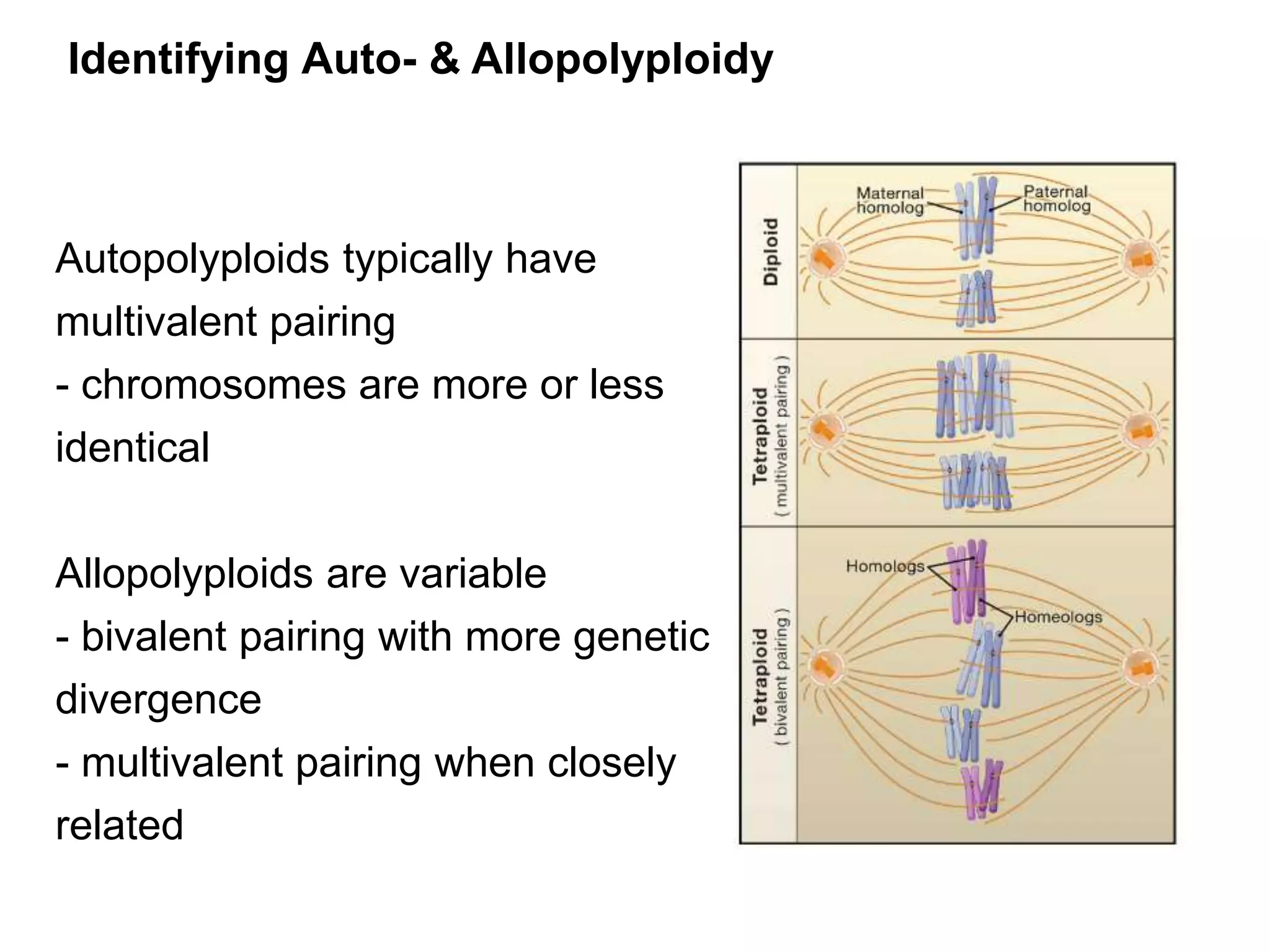
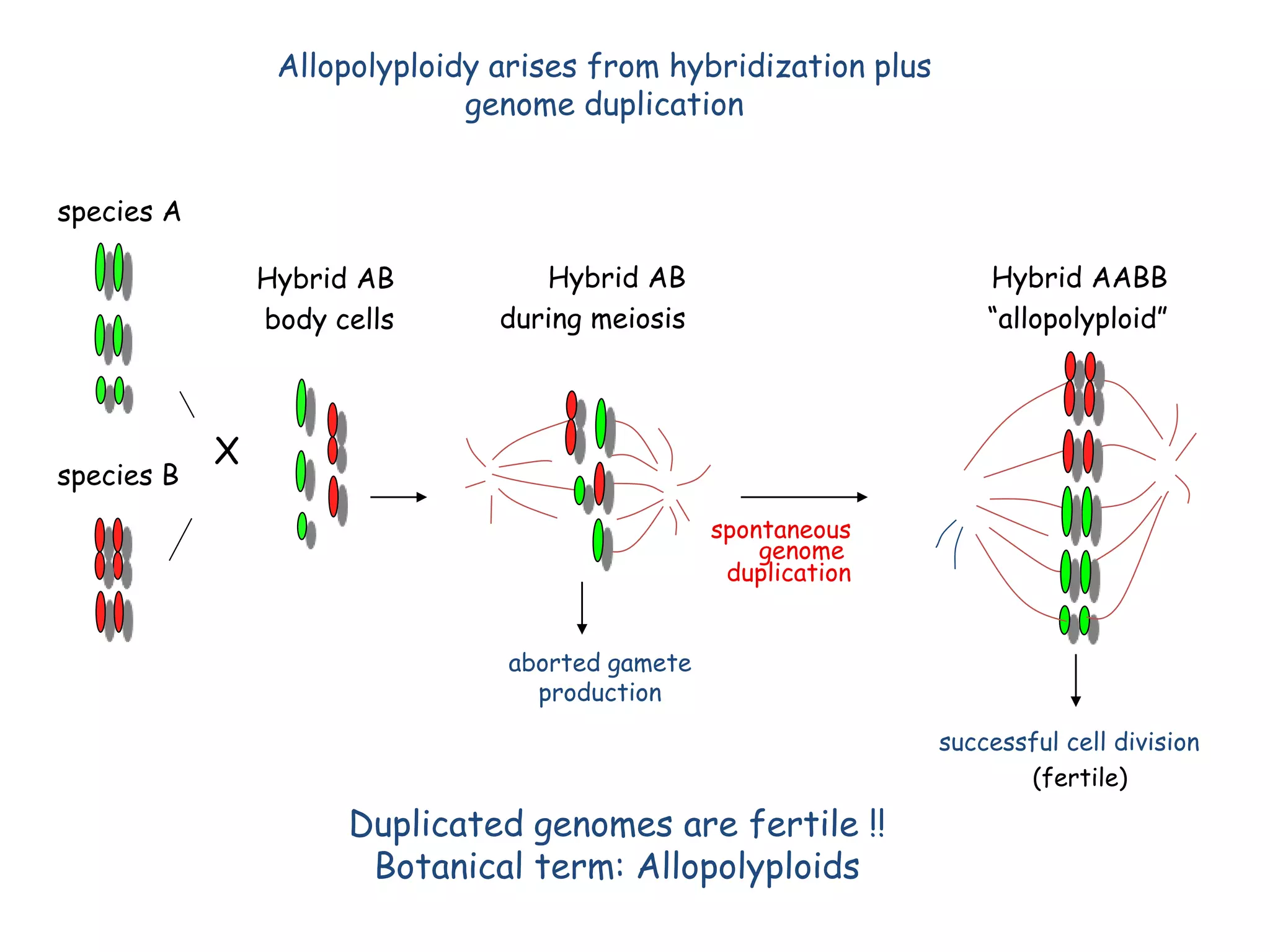
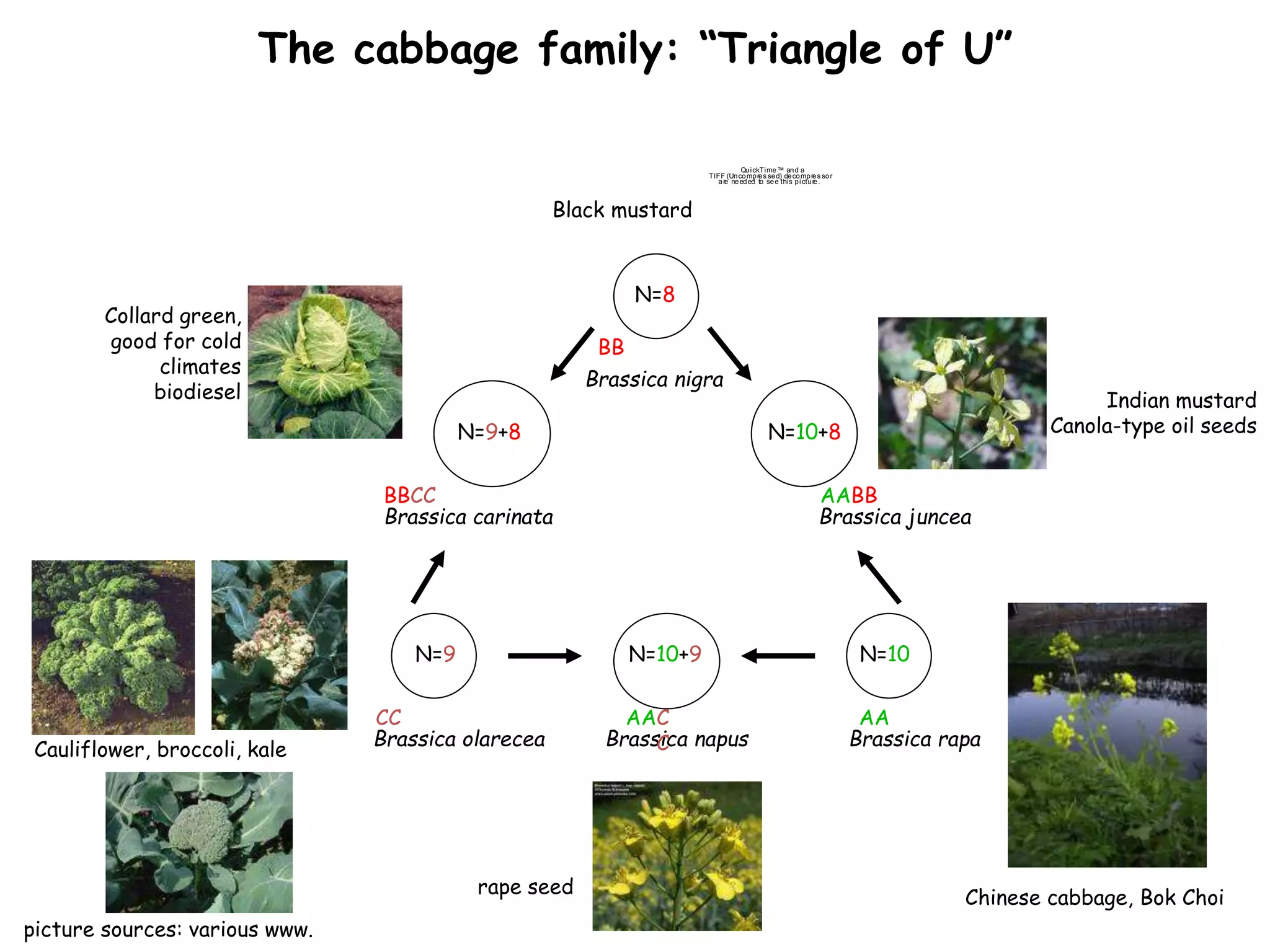
This document discusses polyploidy, specifically allopolyploidy. It defines polyploidy as having extra sets of chromosomes beyond the diploid amount. The two main types are autopolyploidy, which involves genome doubling within a species, and allopolyploidy, which involves hybridization between two distinct species. Allopolyploidy is much more common in plants than animals, making up about 80% of land plants. The document provides examples of allopolyploid species formation and their uses in plant breeding.