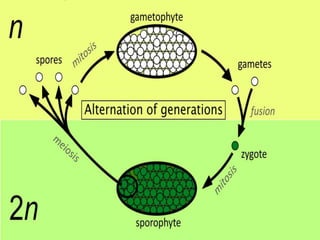
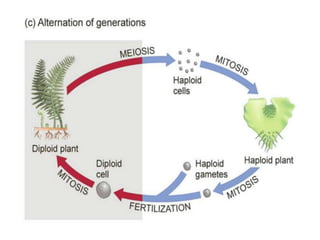
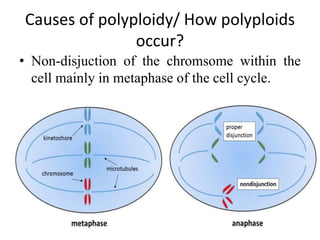
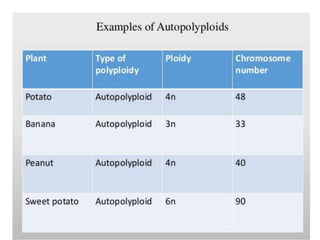
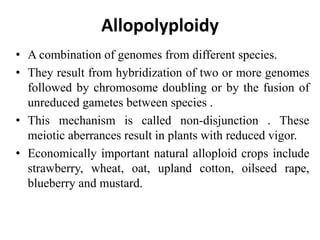
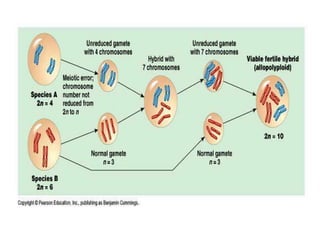
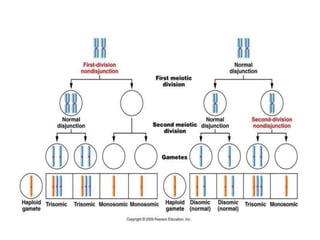
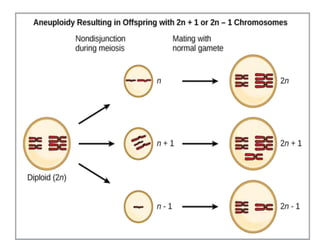
Polyploidy refers to organisms that have more than two complete sets of chromosomes. It commonly occurs through mechanisms like non-disjunction during cell division and hybridization between species. Polyploids are classified as euploids, which are multiples of the normal chromosome number, and aneuploids, which have extra or missing chromosomes. Polyploidy provides benefits like increased vigor, seedlessness, and stress tolerance, and has applications in breeding crops, inducing mutations, and producing secondary metabolites. However, newly formed polyploids can experience issues like gene silencing, sterility, and unpredictable inheritance patterns.