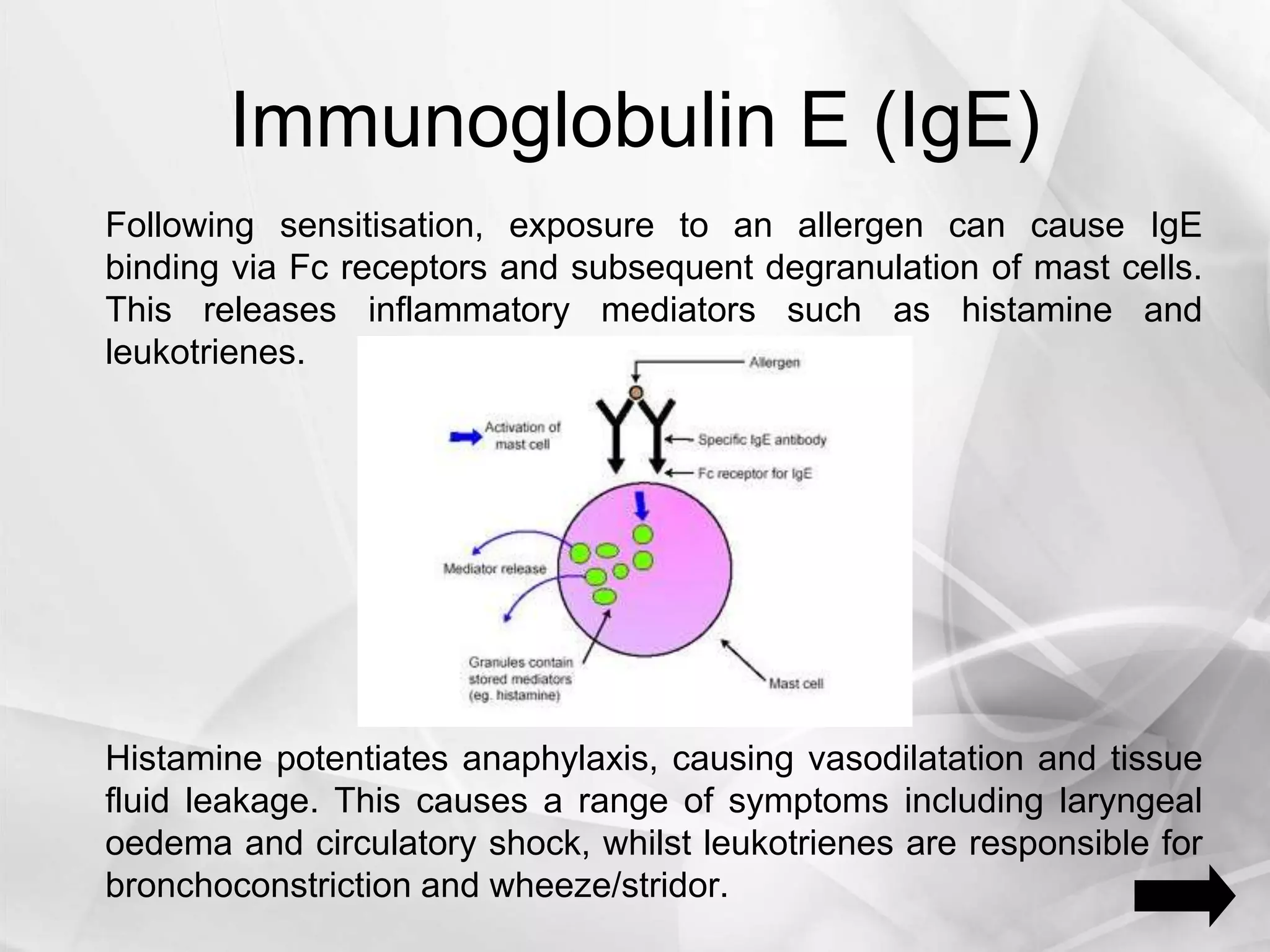
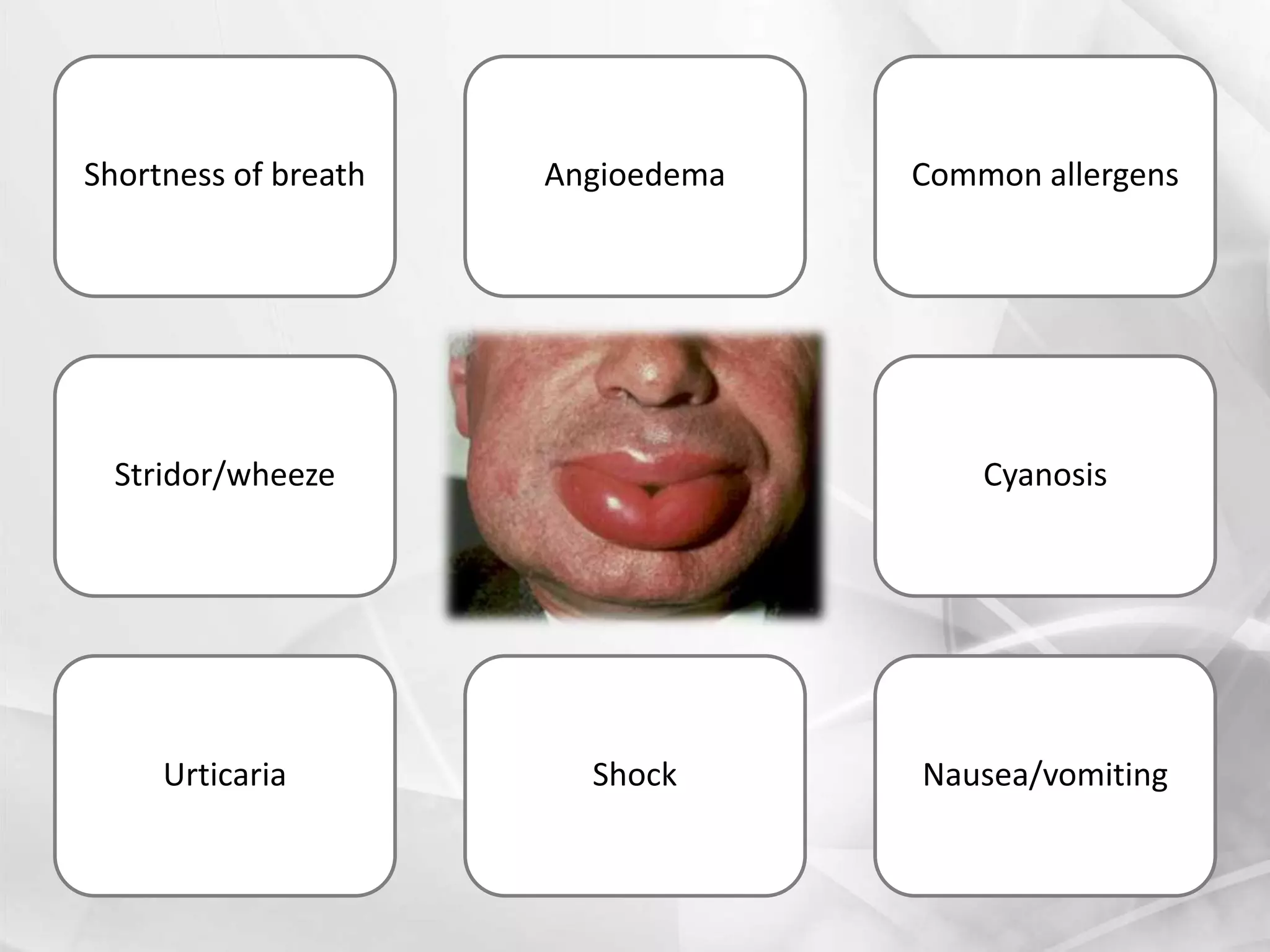
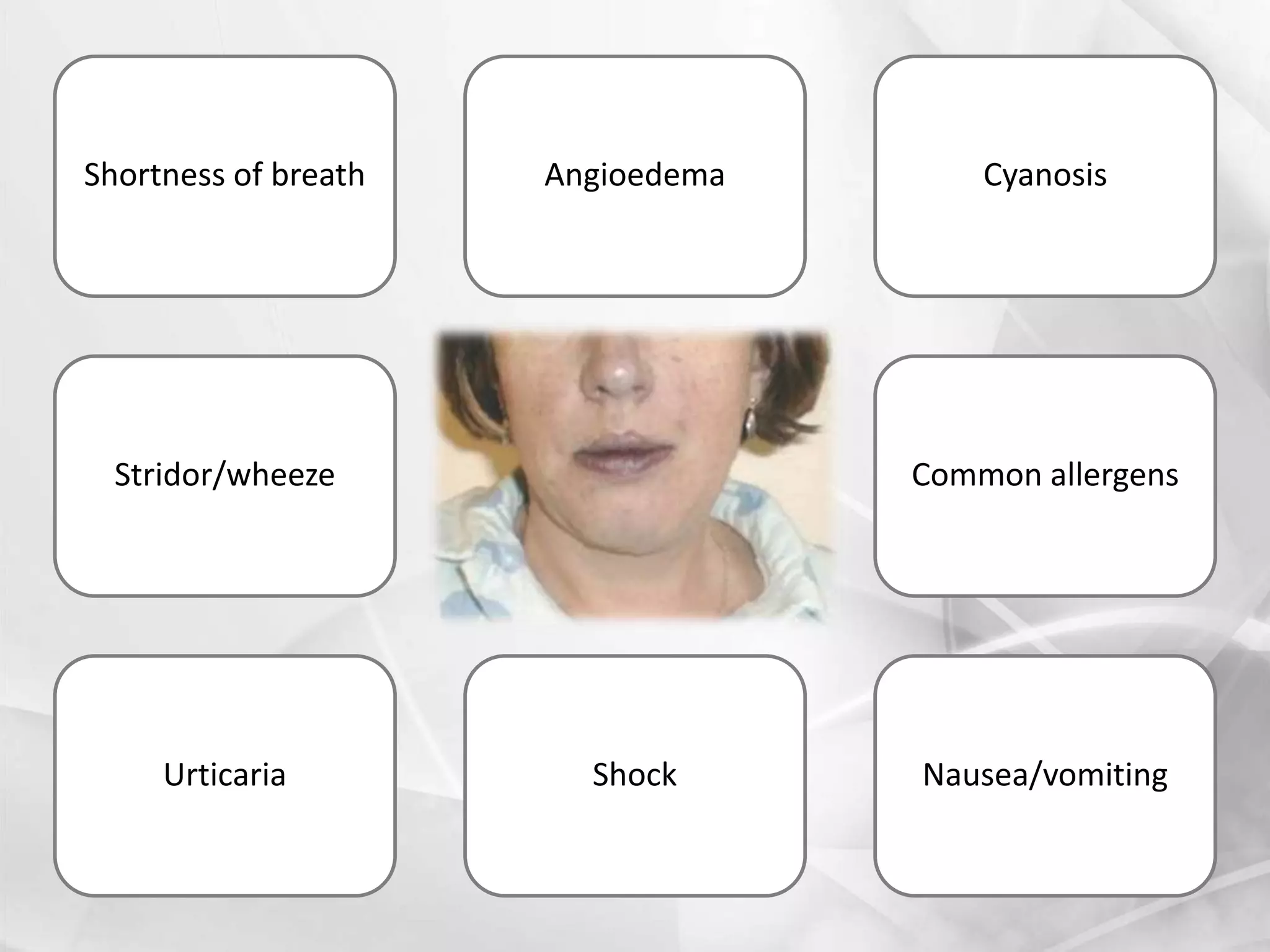
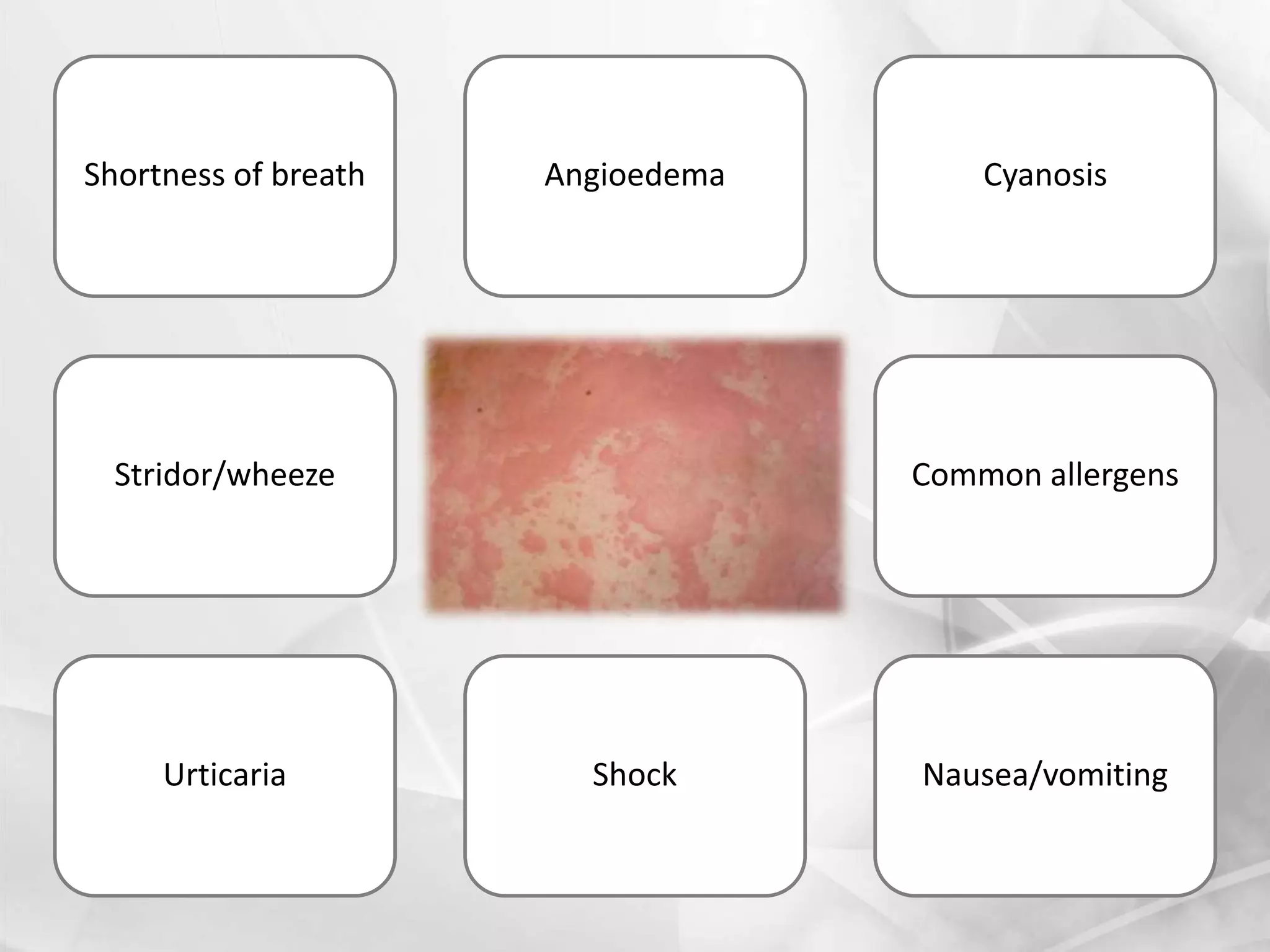
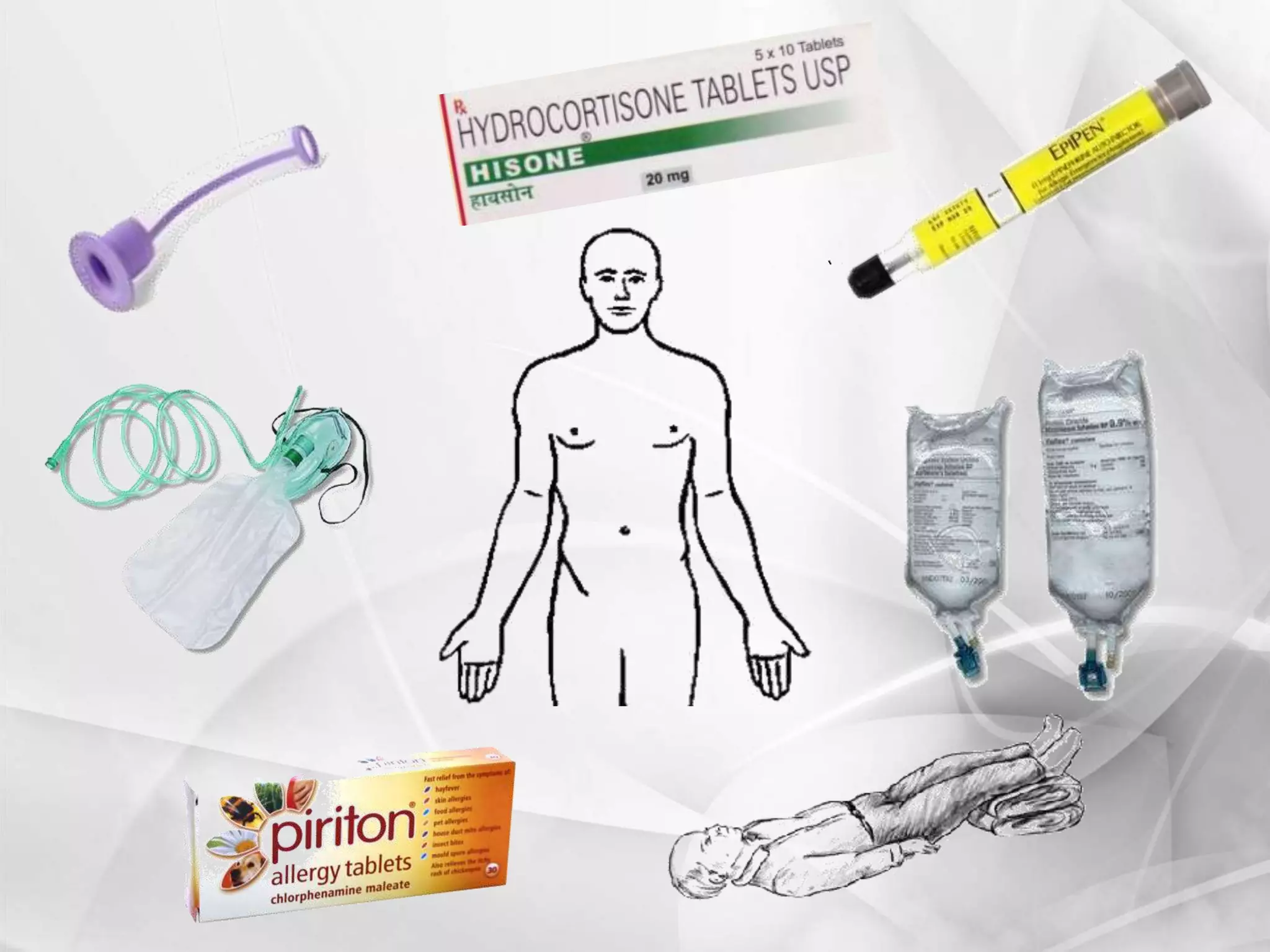
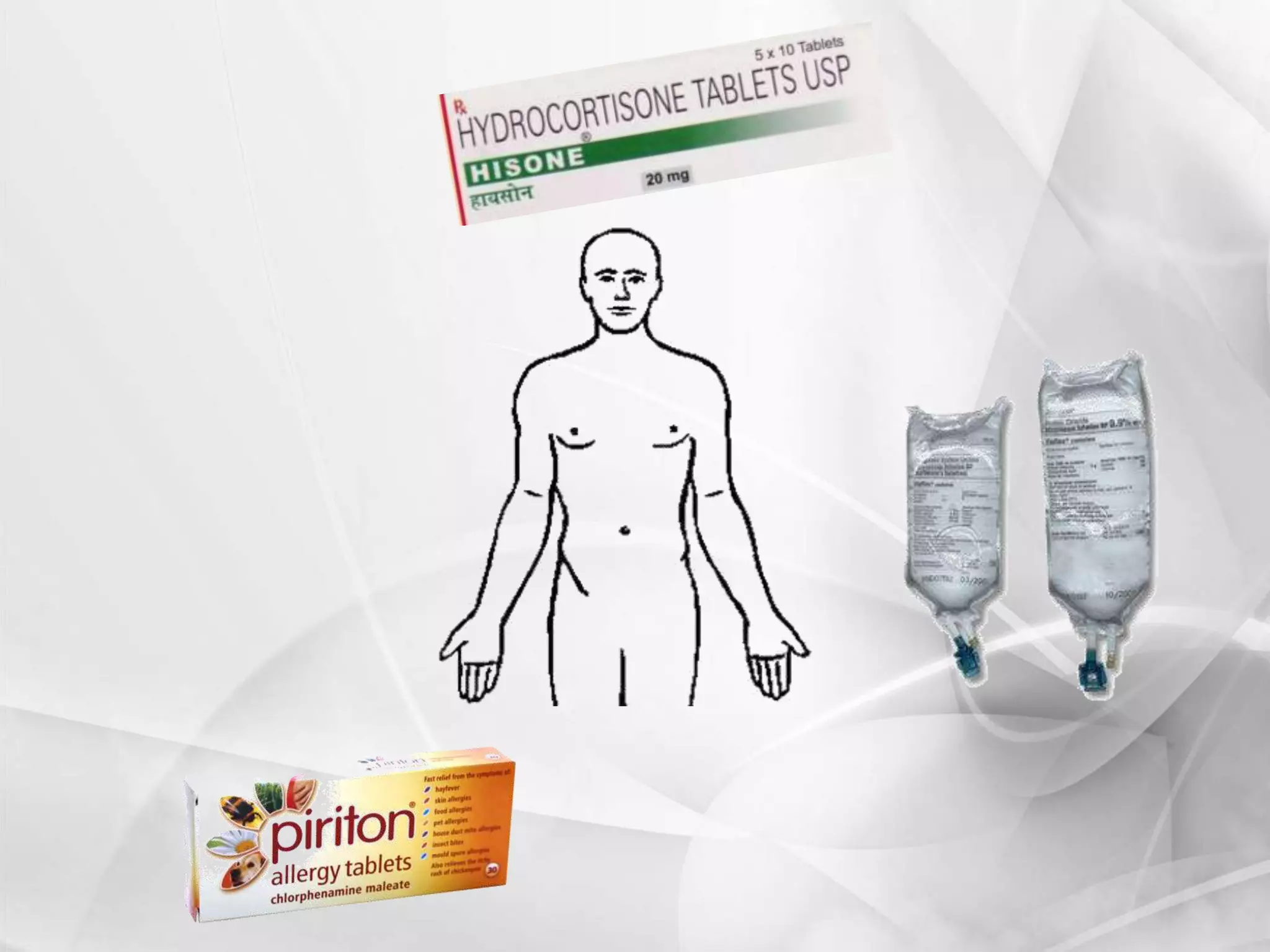
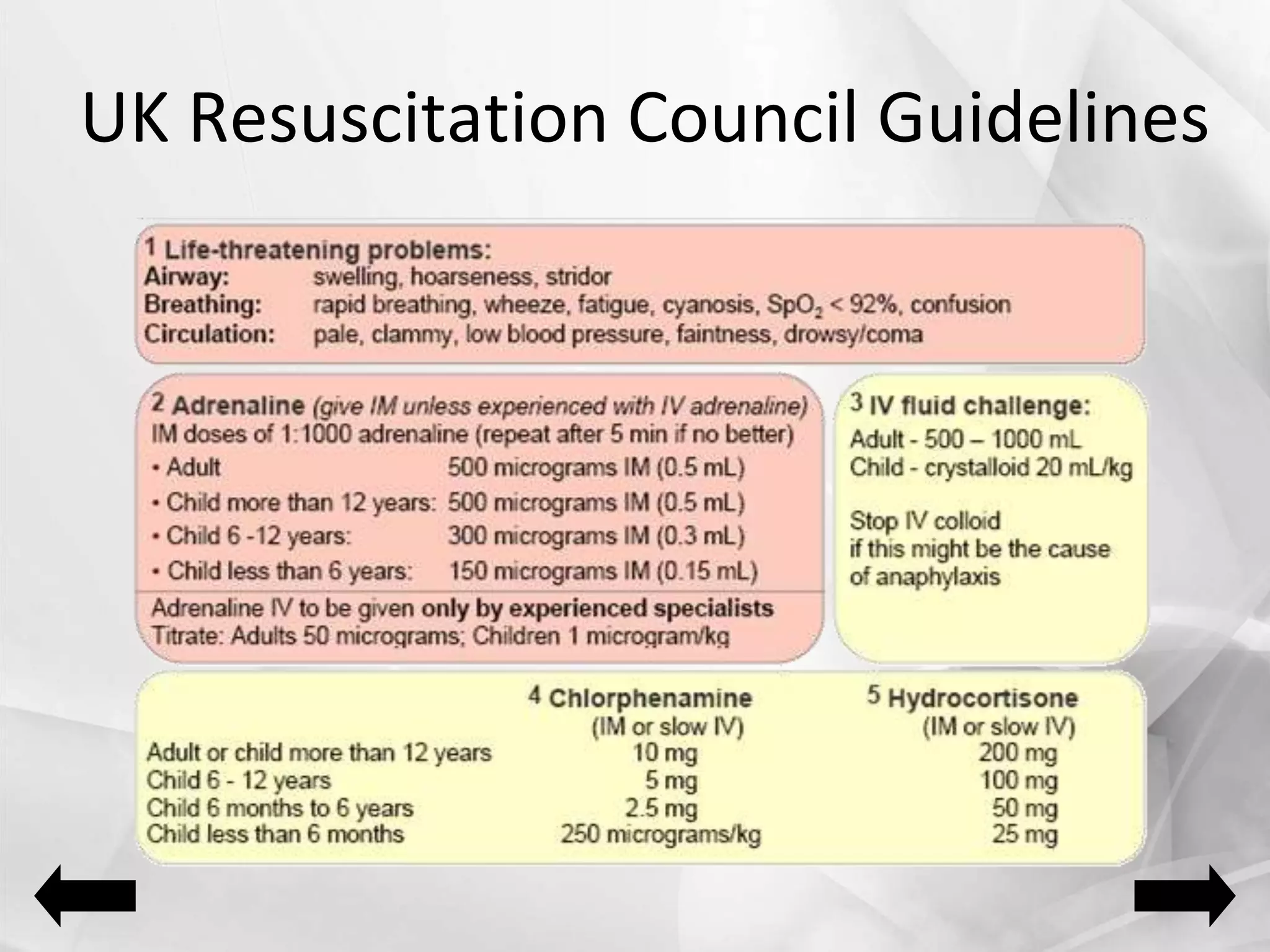
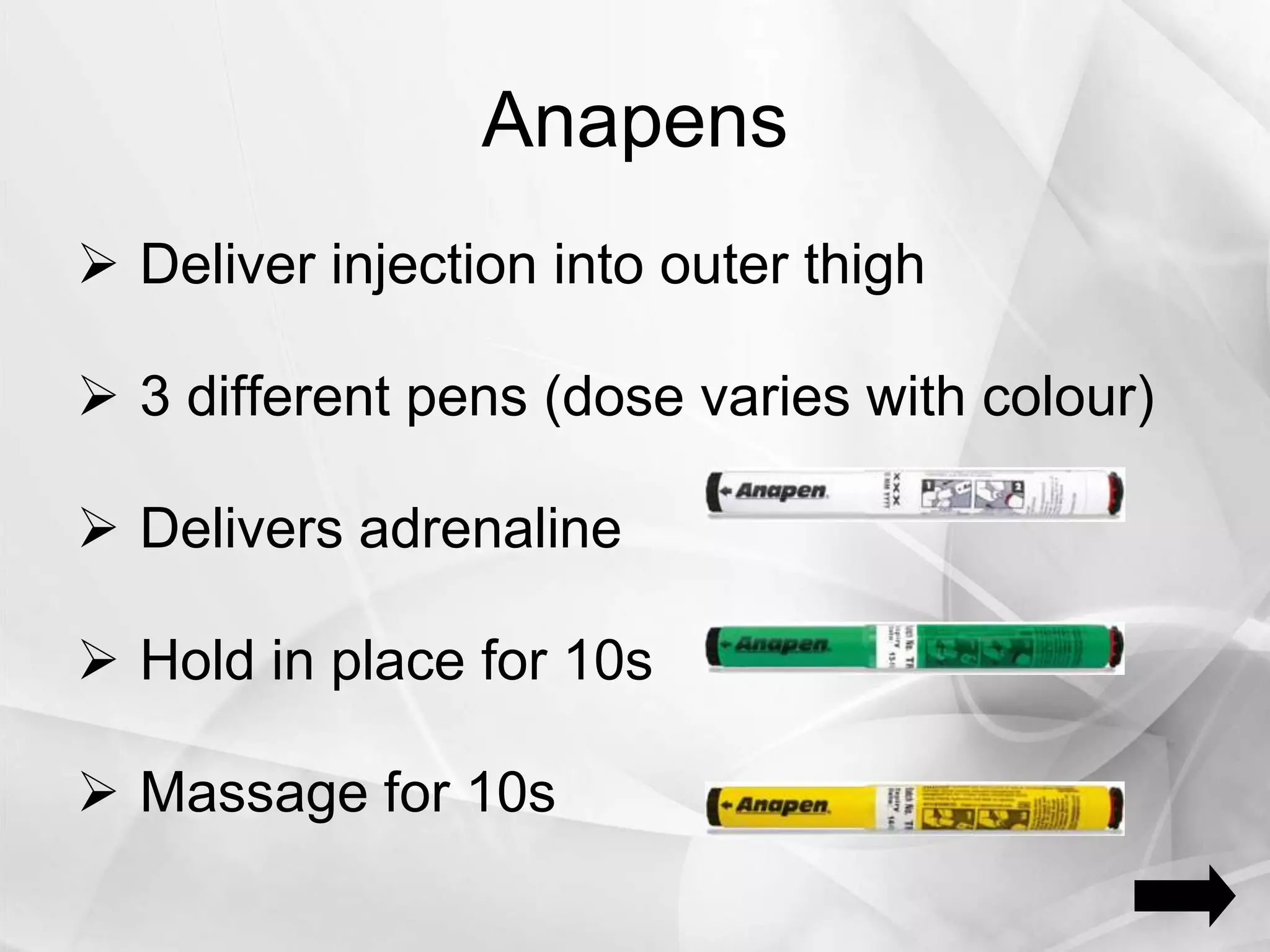
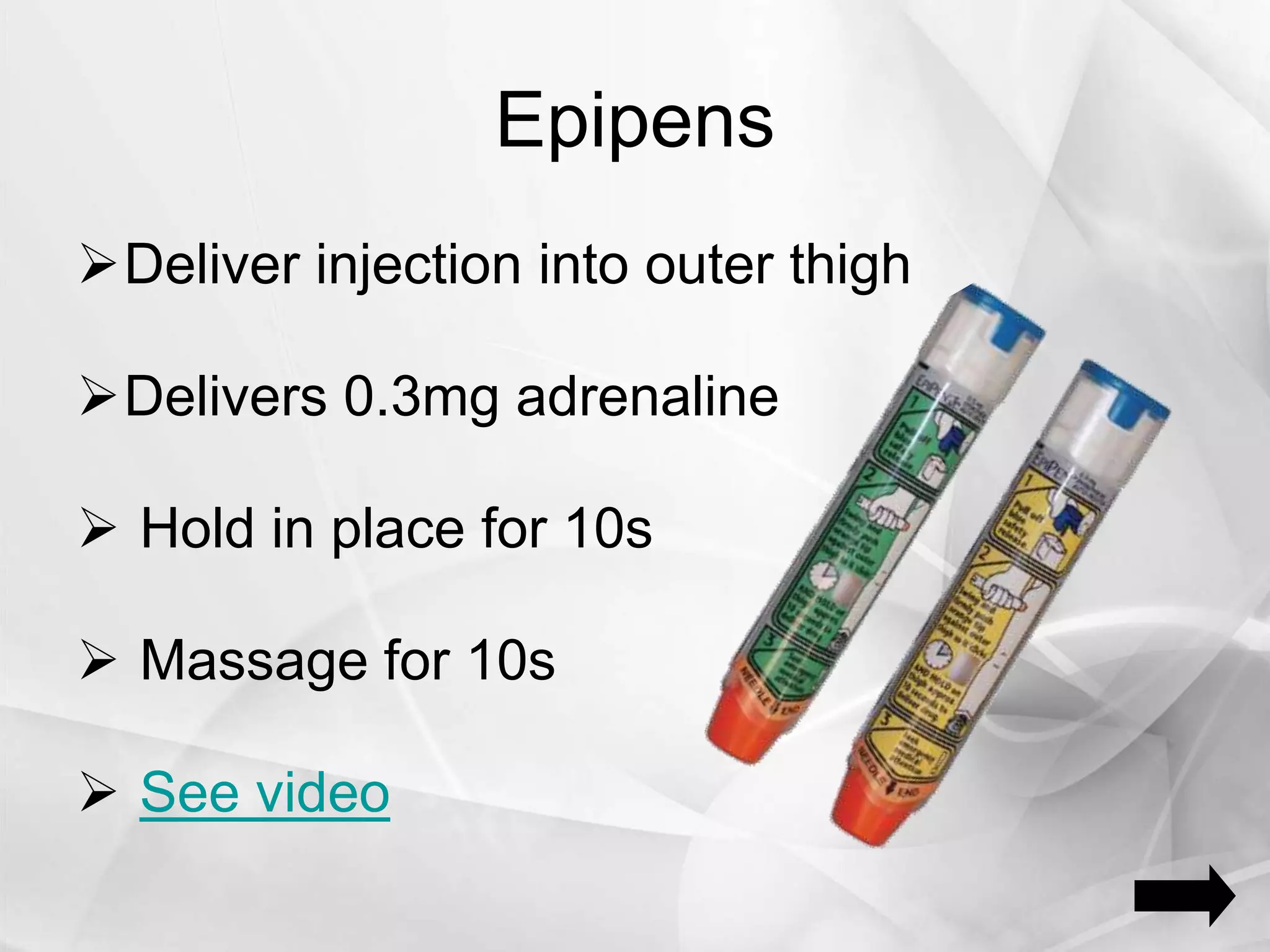
Anaphylaxis is a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction that occurs suddenly following sensitization to an allergen, often after the third exposure. It is mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies binding to allergens and causing degranulation of mast cells and basophils, releasing inflammatory mediators like histamine. Common symptoms include urticaria, angioedema, stridor, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and shock. Epinephrine administered via autoinjector like an EpiPen is the first-line treatment and should be administered immediately if anaphyl