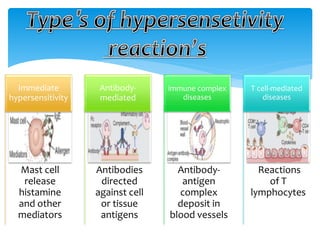
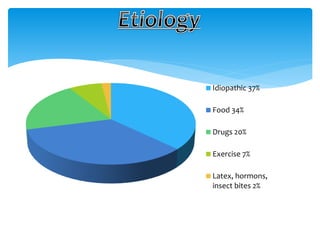
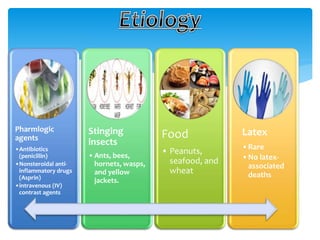
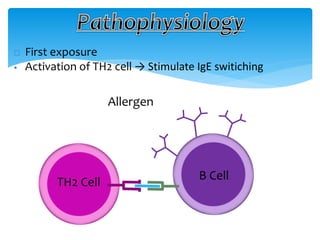
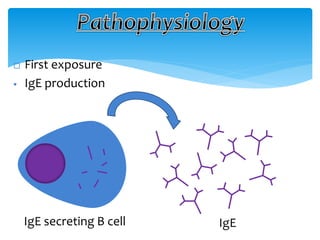
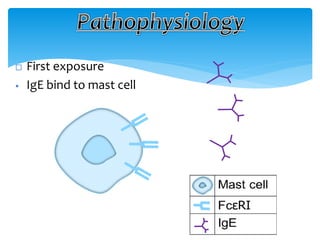
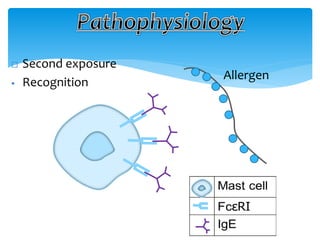
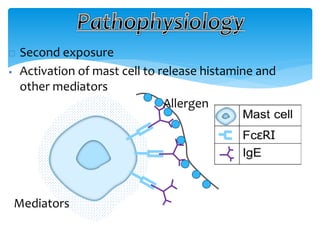
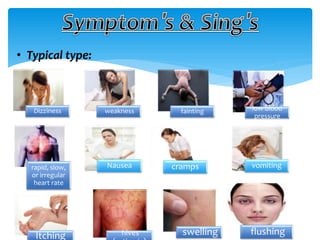
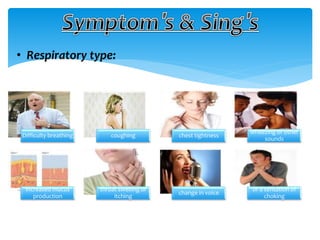
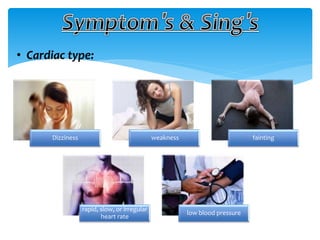
This document discusses anaphylaxis shock, including its classification, etiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Anaphylaxis shock is a severe allergic reaction caused by exposure to a foreign substance like drugs or bee venom. It is characterized by low blood pressure, skin rashes, and breathing difficulties. Emergency epinephrine injections are needed to treat it. Diagnosis is based on sudden symptoms occurring after exposure to a potential trigger. Treatment involves epinephrine injections, IV fluids, corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and placing the patient in a horizontal position. Long term prevention includes avoiding allergens and keeping emergency medication accessible.