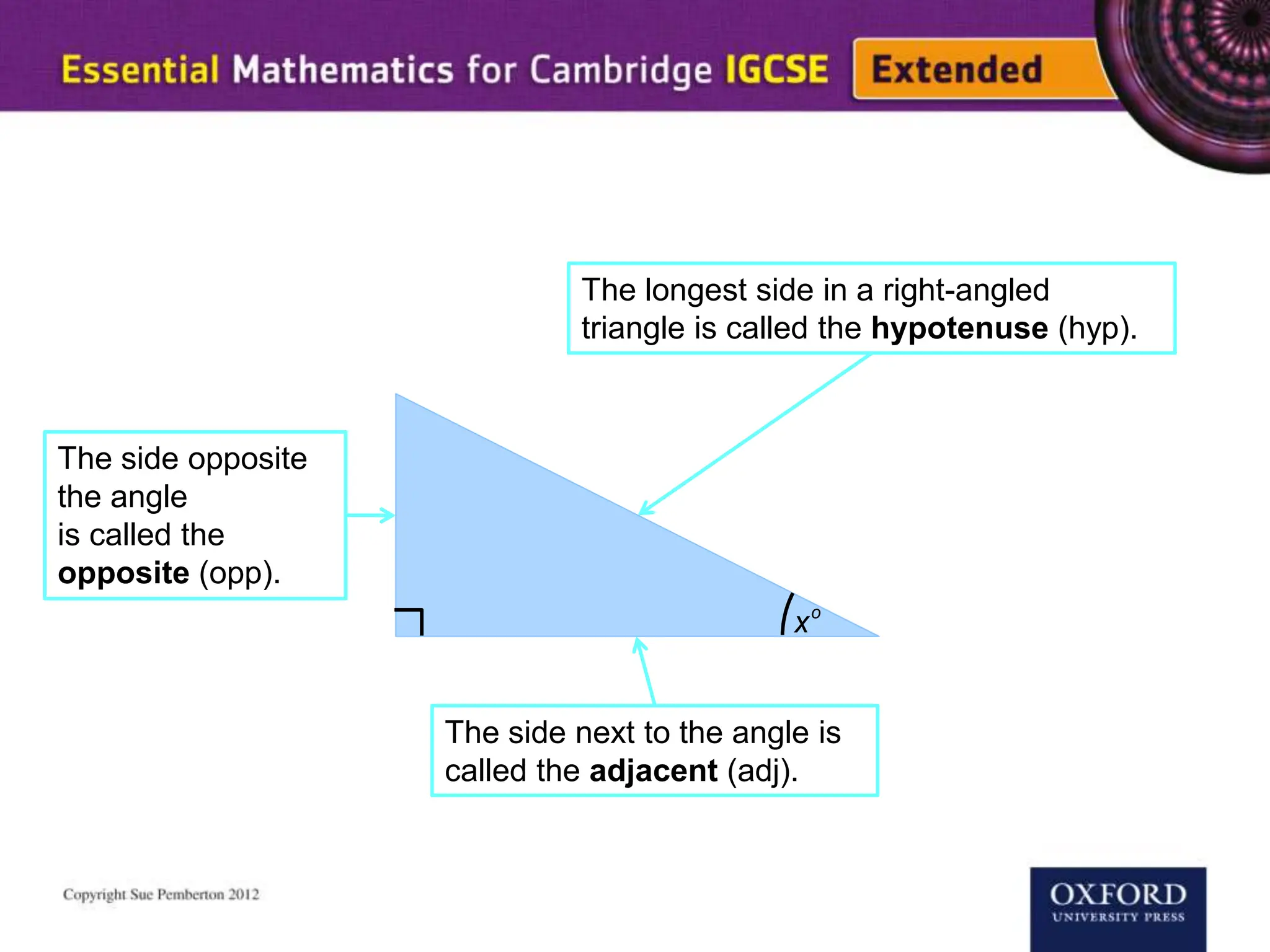
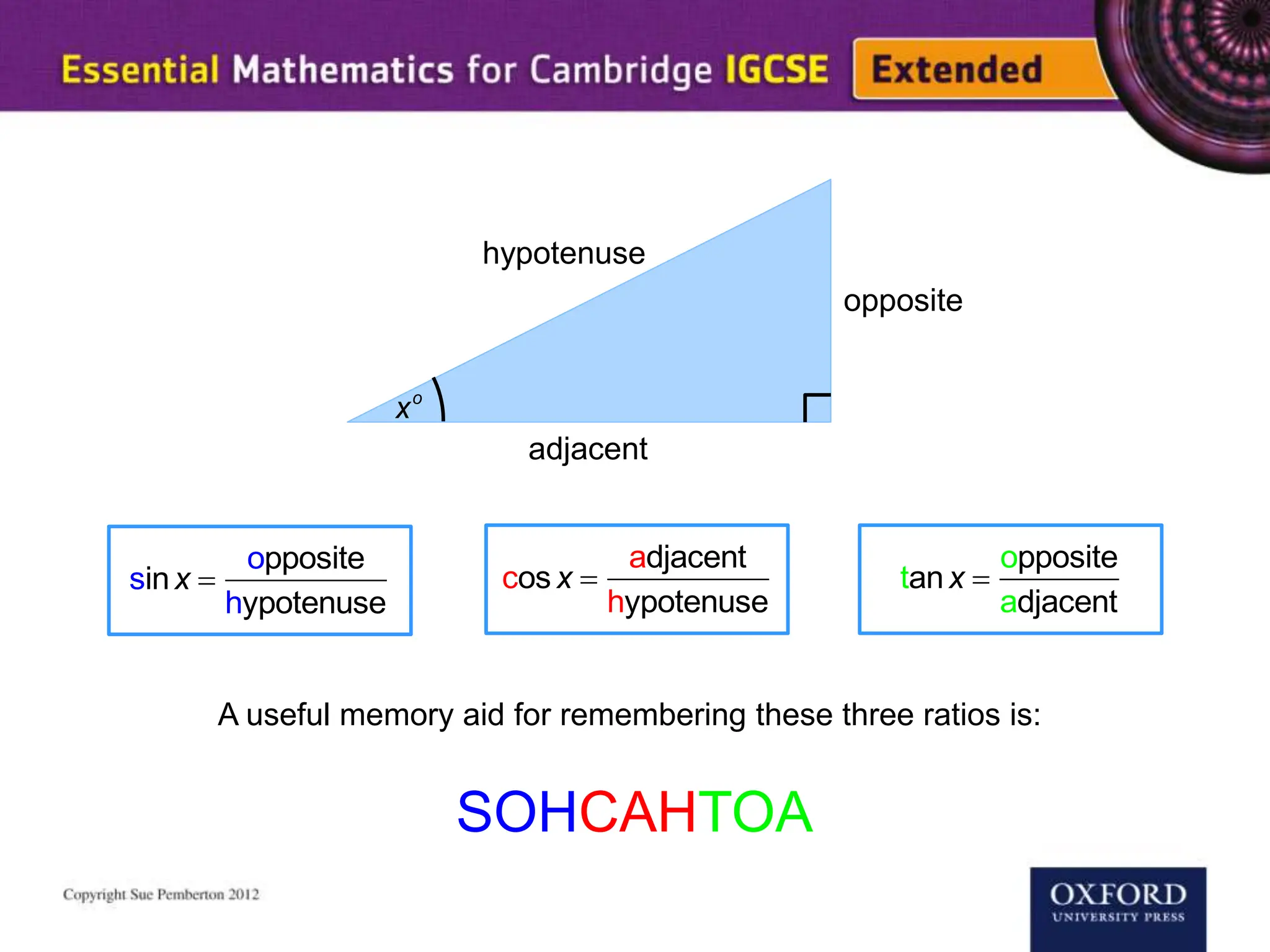
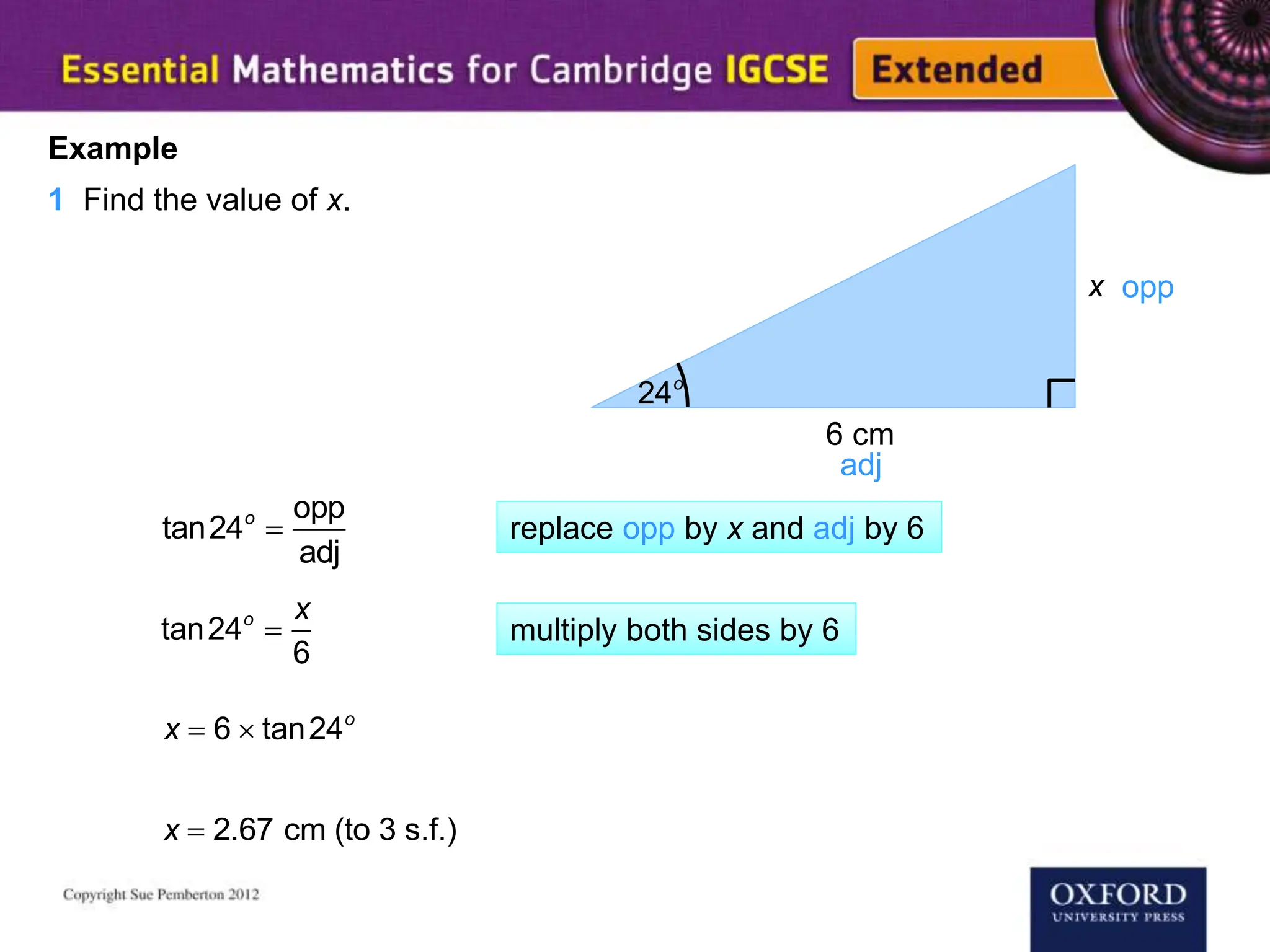
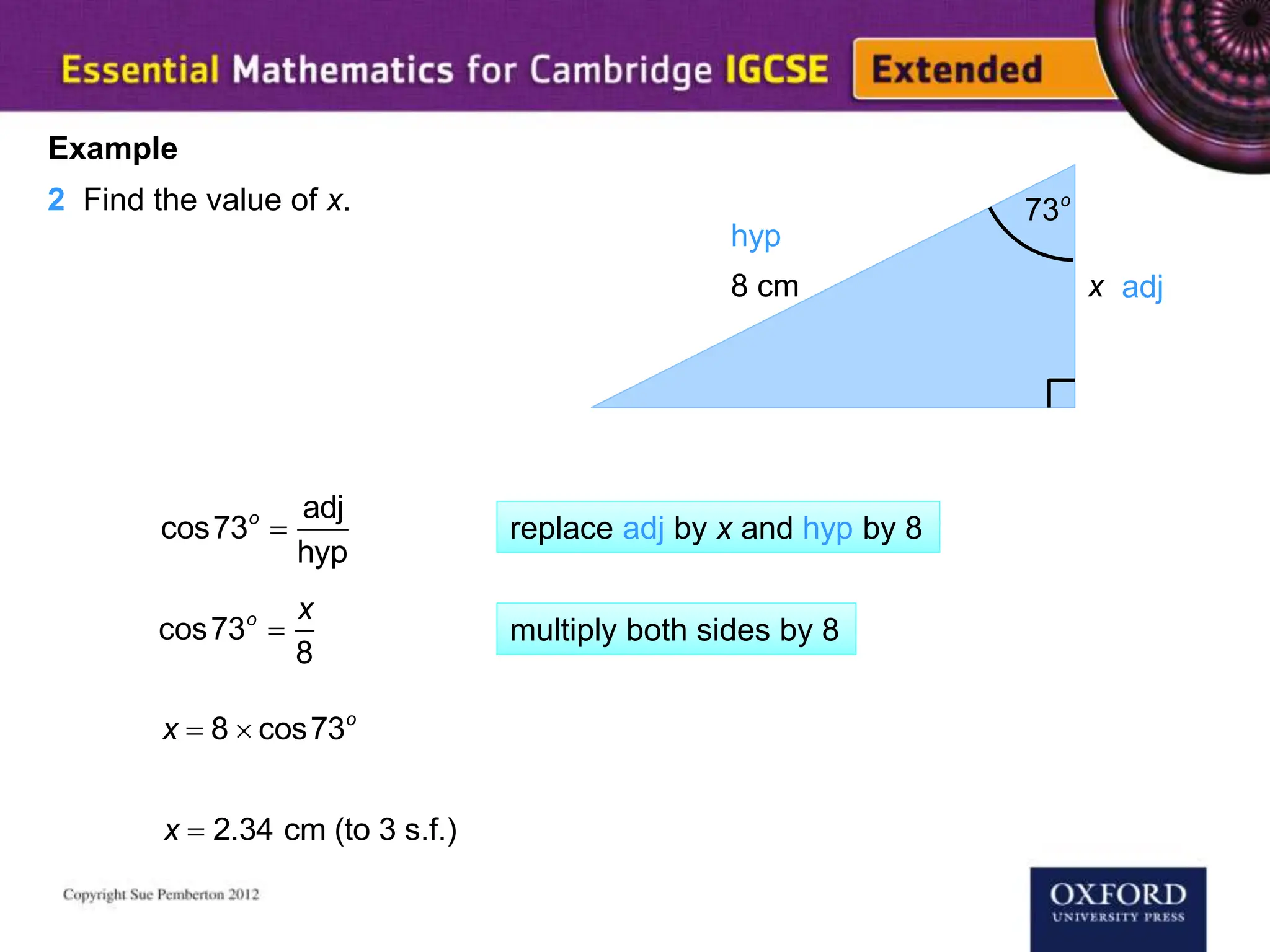
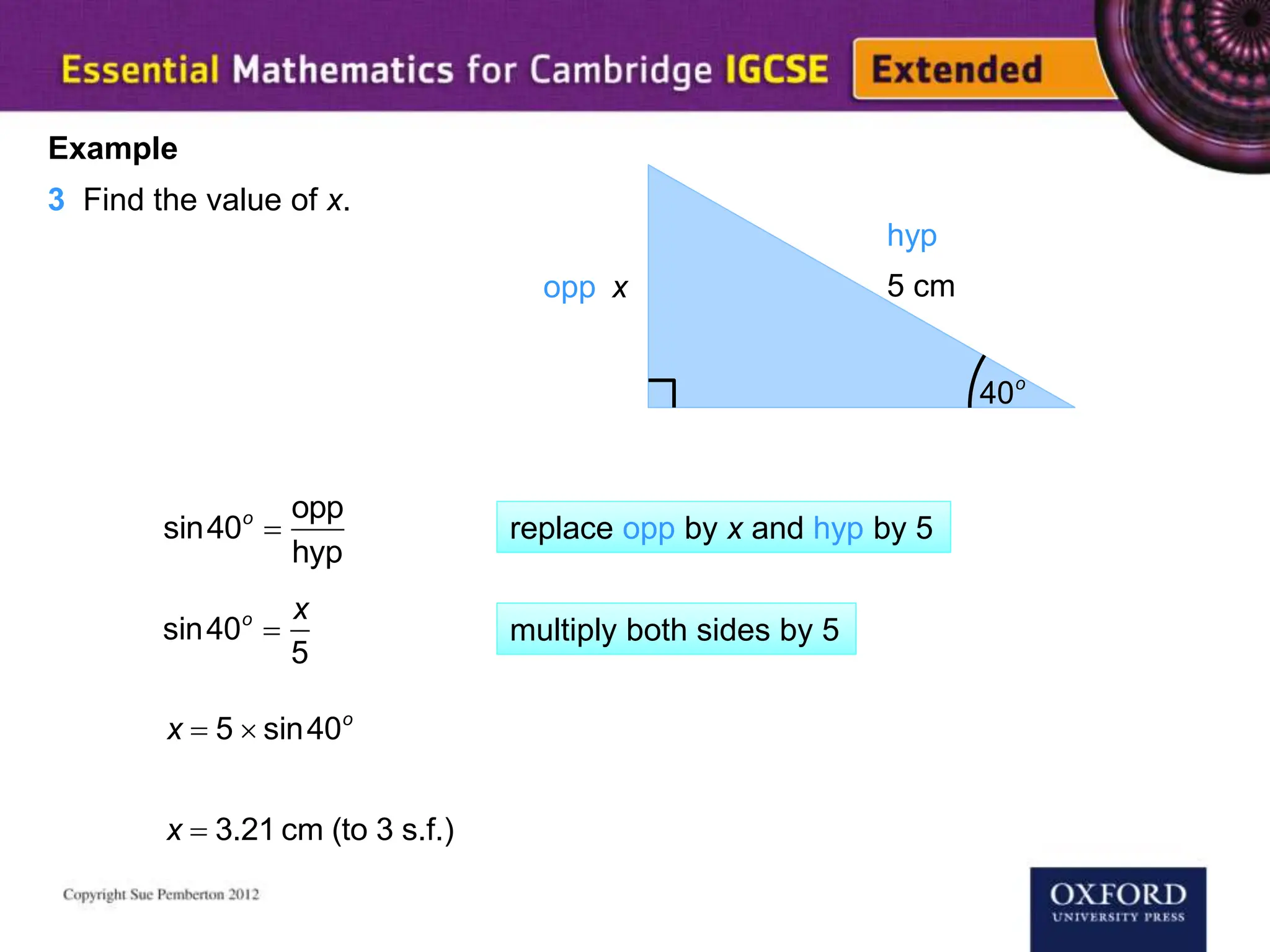
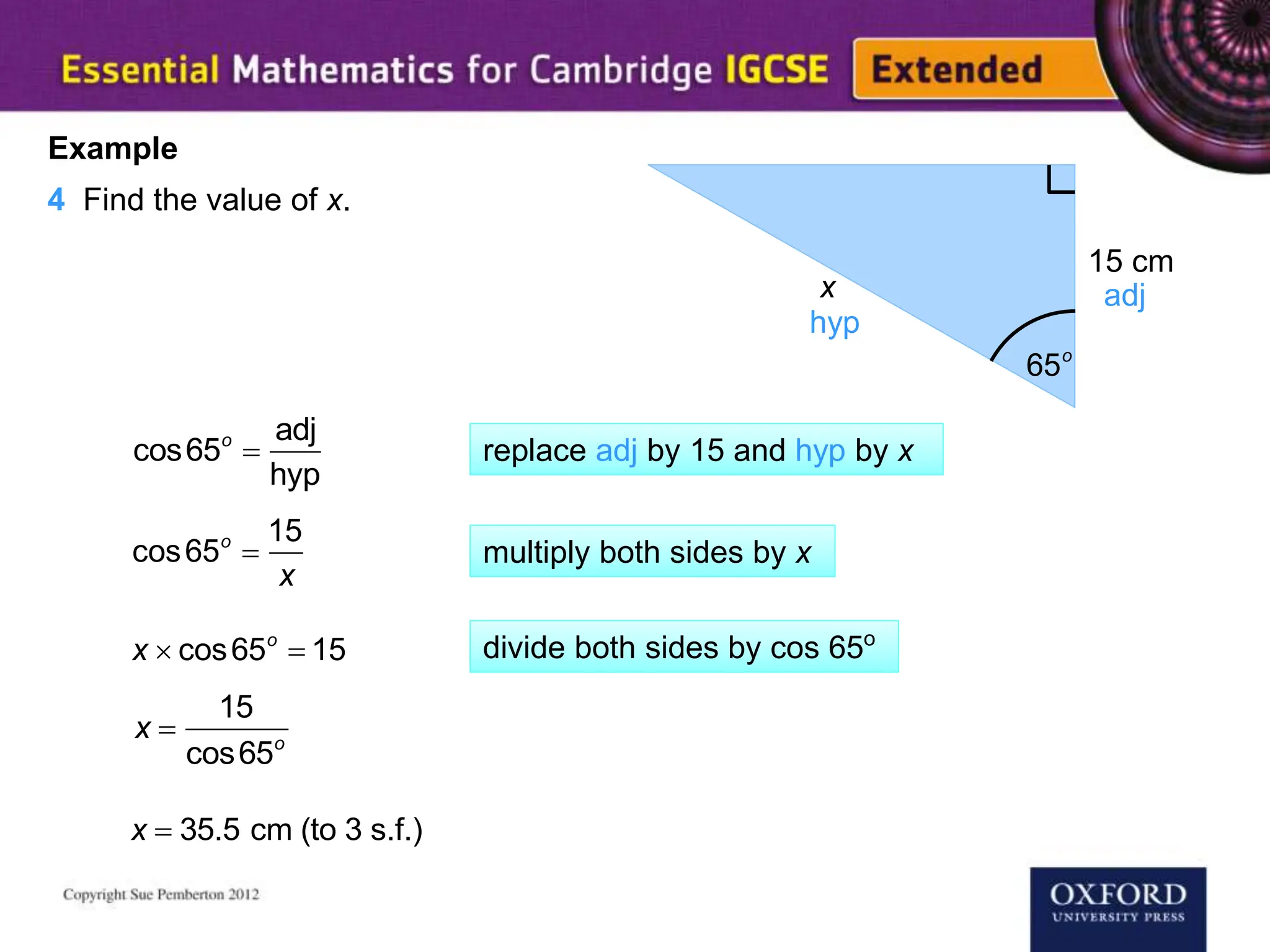
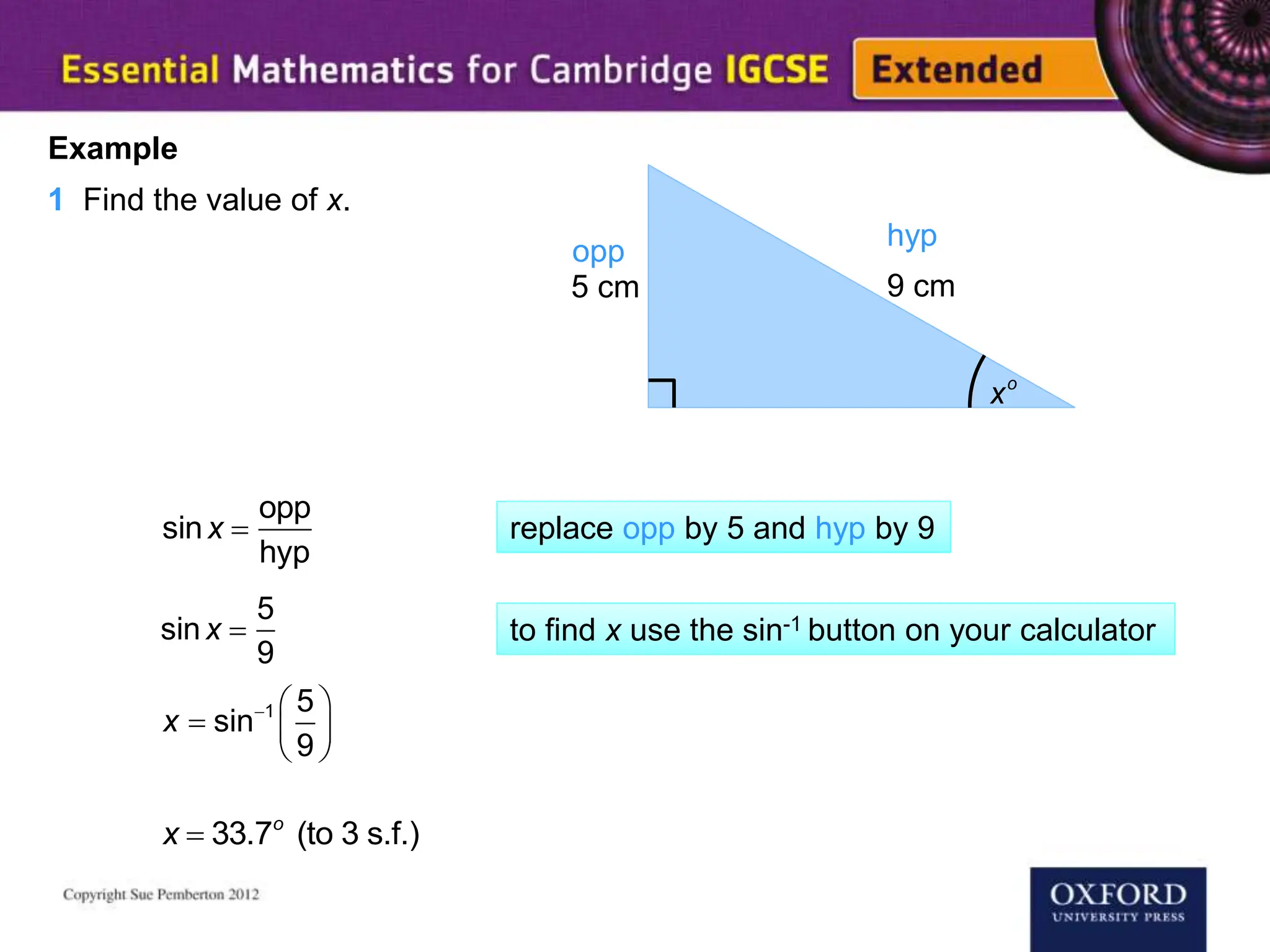
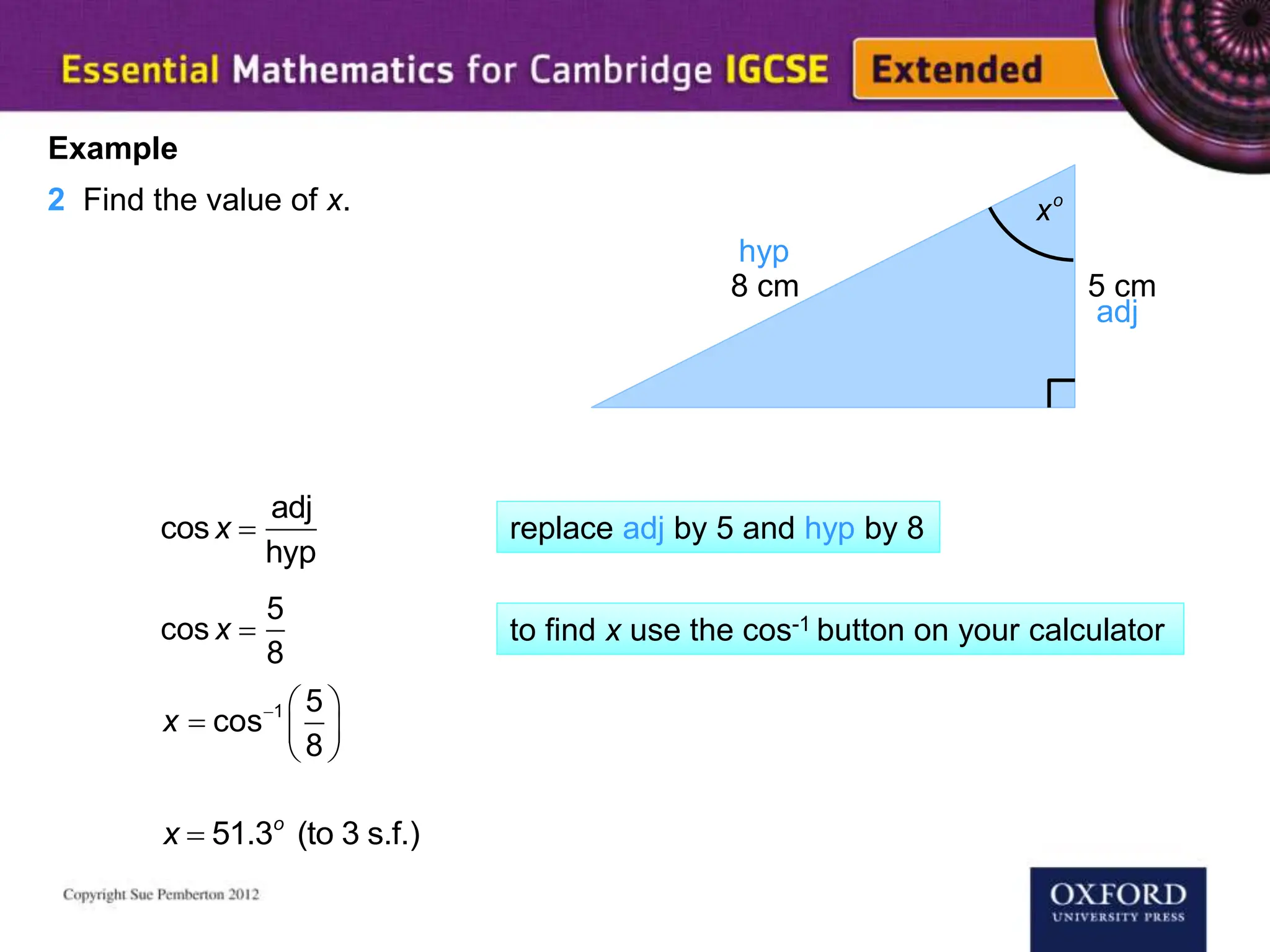
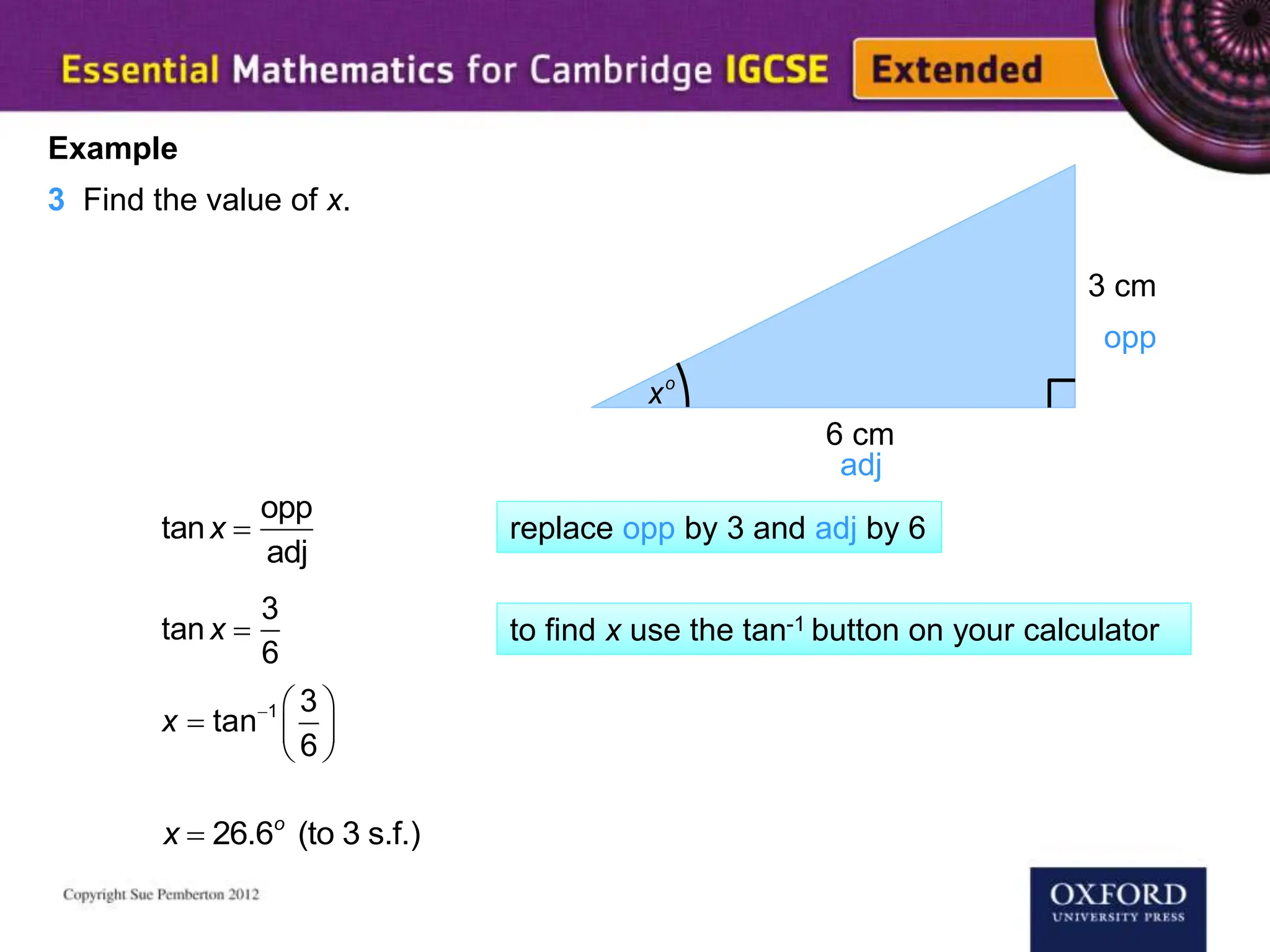
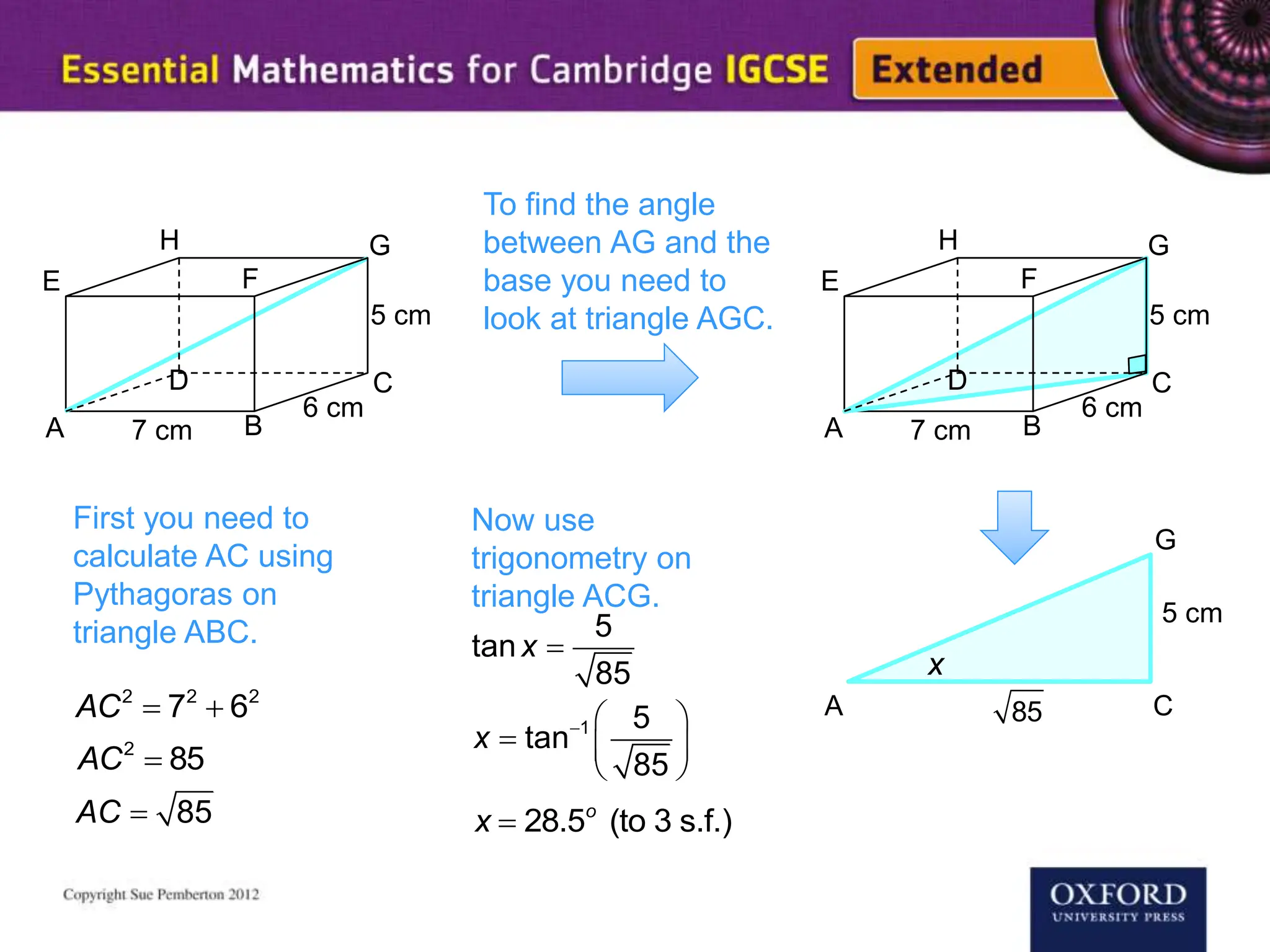
This document explains key concepts of trigonometry, focusing on the definitions of sides in a right-angled triangle: hypotenuse, adjacent, and opposite. It provides examples of calculating the length of sides and angles using trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent. Additionally, it touches on three-dimensional trigonometry with an example involving the calculation of angles and side lengths using Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric functions.