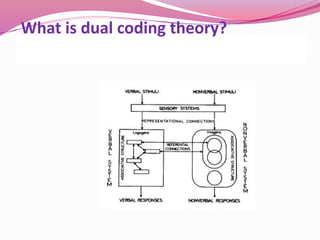
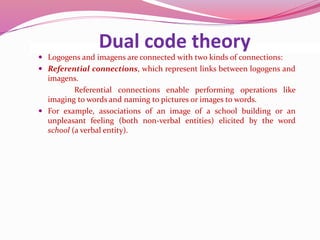
Dual coding theory proposes that there are two separate channels for processing information - a verbal system that handles language and a nonverbal system specialized for visual and spatial processing. Information can be coded verbally as words or nonverbally as mental images. These coding systems operate independently but are interconnected, allowing information to be represented and retrieved through both verbal and nonverbal codes. Dual coding theory suggests that combining words and images leads to better memory than relying on just one code alone.